In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a high-tech vacuum coating process where a solid material is vaporized and then deposited atom-by-atom onto a target object. This creates an extremely thin, hard, and durable film that is molecularly bonded to the substrate's surface, fundamentally enhancing its physical properties.
PVD is not simply a layer of paint; it is an advanced surface engineering technique. Its core purpose is to transform the surface of a standard material into a high-performance one, granting it superior hardness, wear resistance, and longevity in a controlled and environmentally friendly manner.
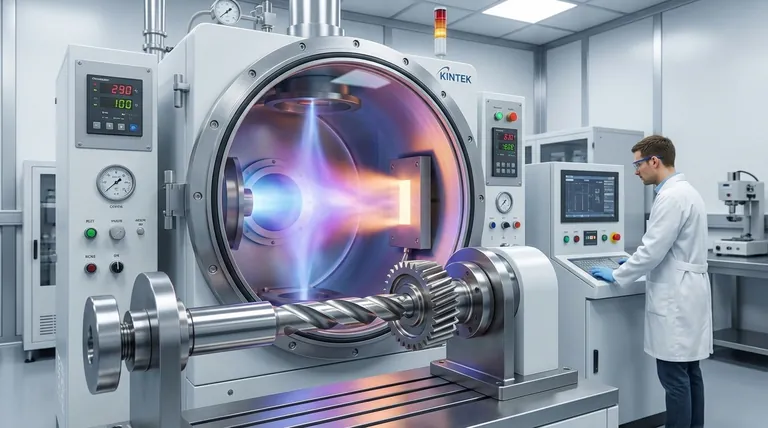

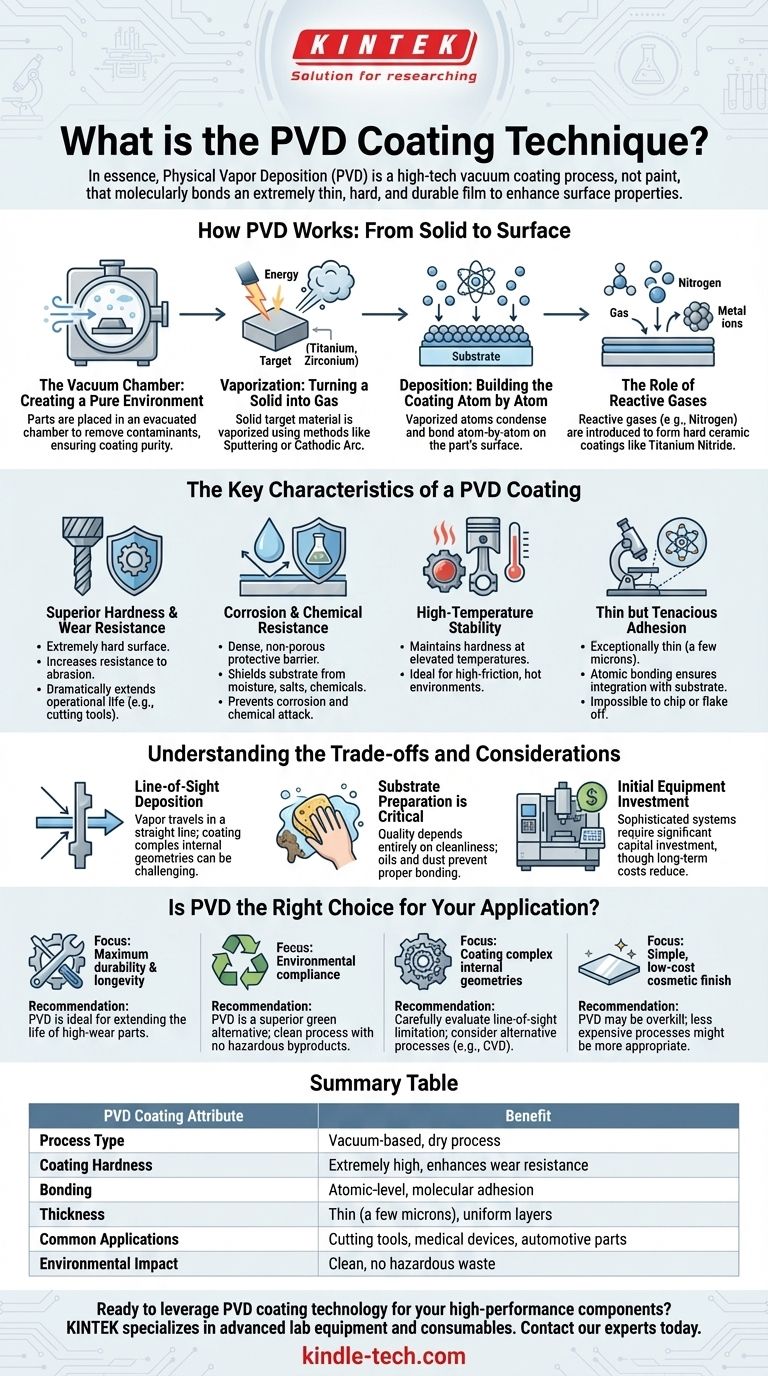
How PVD Works: From Solid to Surface
The PVD process takes place inside a specialized vacuum chamber and can be broken down into a few fundamental steps. Each stage is precisely controlled to achieve the desired coating characteristics.
The Vacuum Chamber: Creating a Pure Environment
First, the parts to be coated are placed inside a chamber from which all air is evacuated. This vacuum is critical because it removes atmospheric contaminants that could otherwise react with the coating material and cause defects or impurities in the final film.
Vaporization: Turning a Solid into Gas
A solid source material, known as a target, is then vaporized. The targets are often pure metals like titanium, zirconium, or chromium. The vaporization is achieved through high-energy methods, most commonly:
- Sputtering: The target is bombarded with high-energy ions from a plasma, which physically knocks atoms off its surface.
- Cathodic Arc: A high-current, low-voltage arc is moved across the target's surface, vaporizing the material and creating a highly ionized vapor.
Deposition: Building the Coating Atom by Atom
This metallic vapor travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses on the cooler substrates (the parts being coated). Because this deposition occurs atom by atom, it creates a very dense, uniform, and strongly bonded layer that conforms precisely to the part's surface.
The Role of Reactive Gases
To create specific ceramic compounds, a reactive gas like nitrogen or a carbon-containing gas is introduced into the chamber. The vaporized metal ions react with this gas to form a hard ceramic coating (e.g., Titanium Nitride) on the substrate, which offers significantly better wear resistance than the pure metal alone.
The Key Characteristics of a PVD Coating
The outcome of the PVD process is a surface with fundamentally new properties. These attributes are what make the technology so valuable across numerous industries.
Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are extremely hard and significantly increase the surface's resistance to abrasion and wear. This is why it is the standard for high-performance cutting tools, as it dramatically extends their operational life.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
The deposited film is dense and non-porous, forming a protective barrier that shields the underlying substrate from moisture, salts, and chemicals. This prevents corrosion and chemical attack.
High-Temperature Stability
Many PVD coatings, especially ceramic compounds, maintain their hardness and stability at elevated temperatures. This makes them ideal for components that experience high friction or operate in hot environments, like engine parts or industrial drills.
Thin but Tenacious Adhesion
While the coating is exceptionally thin (typically a few microns), it is not merely sitting on top of the material. The atomic bonding process ensures it is integrated with the substrate, making it nearly impossible to chip or flake off without damaging the underlying material itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
The PVD process is generally "line-of-sight," meaning the vaporized material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. Coating complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes can be challenging without sophisticated part rotation and fixturing.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The quality of a PVD coating is entirely dependent on the cleanliness and preparation of the substrate. Any oil, dust, or oxide on the surface will prevent proper bonding and lead to coating failure. The pre-treatment and cleaning steps are non-negotiable for success.
Initial Equipment Investment
PVD machines are sophisticated, computer-controlled systems that represent a significant capital investment. While they reduce long-term production costs and turnaround times, the initial barrier to entry is higher than for conventional processes like electroplating.
Is PVD the Right Choice for Your Application?
Choosing a surface treatment requires aligning the technology's strengths with your primary goal. PVD is an excellent choice when performance and precision are paramount.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and longevity: PVD is an ideal solution for extending the life of tools and components subjected to high wear, friction, or abrasion.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: PVD is a clean, dry process with no hazardous byproducts, making it a superior green alternative to traditional hard chrome plating.
- If your primary focus is coating parts with complex internal geometries: You must carefully evaluate if PVD's line-of-sight nature is a limitation and consider specialized fixturing or alternative processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost cosmetic finish: PVD may be overkill; less expensive processes might be more appropriate if high-performance surface properties are not required.
By treating the surface not as an afterthought but as an integral design component, you can leverage PVD to create products with dramatically enhanced value and performance.
Summary Table:
| PVD Coating Attribute | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Vacuum-based, dry process |
| Coating Hardness | Extremely high, enhances wear resistance |
| Bonding | Atomic-level, molecular adhesion |
| Thickness | Thin (a few microns), uniform layers |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, medical devices, automotive parts |
| Environmental Impact | Clean, no hazardous waste |
Ready to leverage PVD coating technology for your high-performance components? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our expertise can help you integrate PVD solutions to enhance durability, reduce wear, and meet stringent environmental standards. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's material science and coating needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- Are all lab grown diamonds CVD? Understanding the Two Main Methods
- What are the challenges of carbon nanotubes? Overcoming Production and Integration Hurdles
- What are nanotubes drawbacks? The 4 Major Hurdles Limiting Their Real-World Use



















