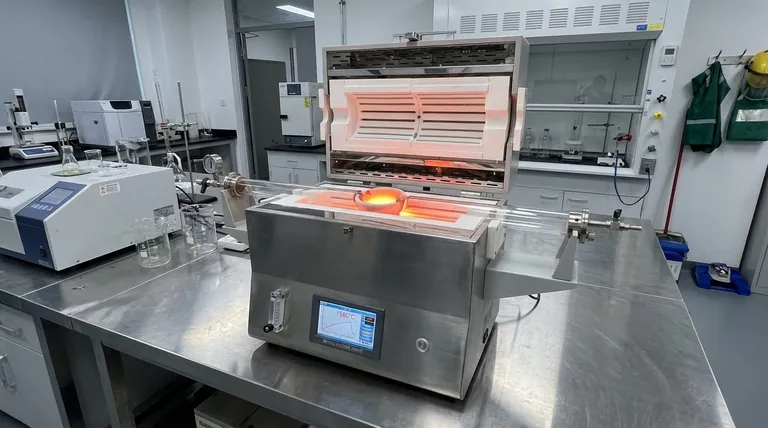
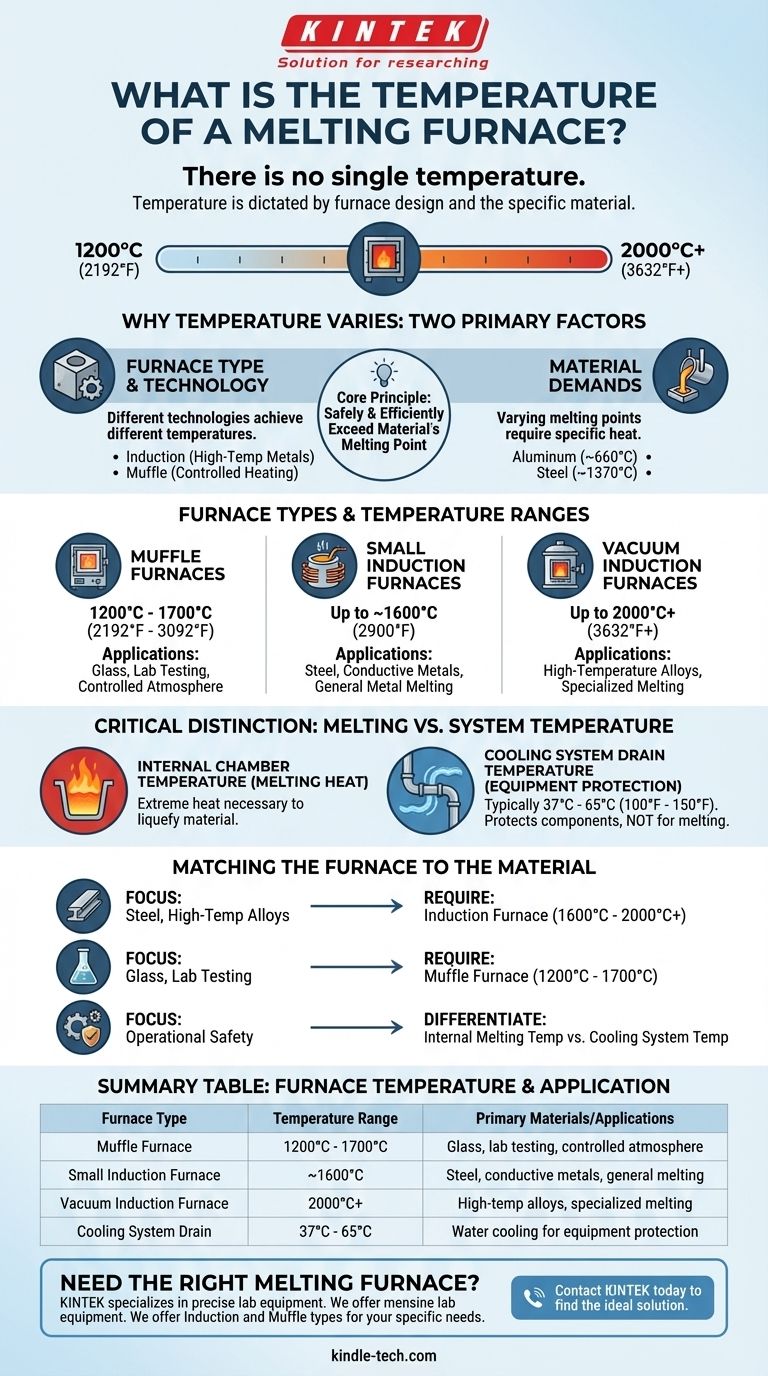
There is no single temperature for a melting furnace. The required temperature is dictated entirely by the furnace's design and the specific material being melted, with operational temperatures commonly ranging from 1200°C (2192°F) to over 2000°C (3632°F).
A melting furnace's temperature is not a fixed value but a required capability. The core principle is that the furnace must be able to safely and efficiently exceed the melting point of the target material, whether that is glass, aluminum, or high-strength steel.

Why Temperature Varies So Widely
The term "melting furnace" covers a broad category of industrial equipment. The two primary factors that determine its operational temperature are the type of furnace technology used and the material it is designed to process.
The Demands of the Material
Different materials have vastly different melting points. A furnace designed for aluminum (melting point ~660°C) has fundamentally different requirements than one designed for steel (melting point ~1370°C).
The furnace’s temperature range dictates its suitability for a specific task. Matching the furnace's capability to the material's requirements is the most critical factor for optimal results.
Induction Furnaces: For High-Temperature Metals
Induction furnaces use electromagnetic currents to heat and melt conductive metals directly. This method is highly efficient and capable of achieving extremely high temperatures.
A small induction melting furnace can typically reach a maximum temperature of 1600°C (2900°F).
More advanced systems, such as a vacuum induction melting furnace, can reach even higher temperatures, often up to 2000°C (3632°F).
Muffle Furnaces: For Controlled Heating
Muffle furnaces operate differently, using an external heat source like a burner to heat an isolated inner chamber, or "muffle." This protects the material inside from direct contact with flames and combustion byproducts.
The maximum temperature for muffle furnaces typically falls within a range of 1200°C (2192°F) to 1700°C (3092°F), depending on their specific design and construction.
A Critical Distinction: Melting vs. System Temperature
Confusing the internal melting temperature with other operational temperatures is a common point of error. The temperatures required to liquefy metal are orders of magnitude higher than those of the machine's support systems.
Internal Chamber Temperature
This is the true "melting temperature" of the furnace. It is the extreme heat generated inside the crucible or chamber that is necessary to change the state of the material from solid to liquid.
Cooling System Drain Temperature
High-power furnaces, especially induction types, require robust water-cooling systems to protect components like the induction coils from overheating.
The temperature of this cooling water, often called the furnace drain temperature, is typically very low, ranging from 37°C to 65°C (100°F to 150°F). Safety switches often turn off the power supply if this water temperature exceeds a limit like 79°C (175°F) to prevent equipment damage.
Matching the Furnace to the Material
To determine the necessary furnace temperature, you must first identify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is melting steel or other high-temperature alloys: You require an induction furnace with a maximum temperature capability of 1600°C to 2000°C or higher.
- If your primary focus is melting materials like glass or for laboratory testing: A muffle furnace with a range of 1200°C to 1700°C is often the correct choice, especially when a controlled atmosphere is needed.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and maintenance: Always differentiate between the internal melting temperature and the much lower cooling system temperature to correctly interpret system diagnostics.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about matching the tool's thermal power to the specific demands of your material.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Common Temperature Range | Primary Materials/Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | 1200°C - 1700°C (2192°F - 3092°F) | Glass, laboratory testing, controlled atmosphere melting |
| Small Induction Furnace | Up to ~1600°C (2900°F) | Steel, conductive metals, general metal melting |
| Vacuum Induction Furnace | Up to 2000°C+ (3632°F+) | High-temperature alloys, specialized metal melting |
| Cooling System Drain | 37°C - 65°C (100°F - 150°F) | Water cooling for equipment protection (NOT the melting temperature) |
Need the Right Melting Furnace for Your Specific Material?
Selecting a furnace with the correct temperature capability is critical for efficiency, safety, and achieving optimal results. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment you need.
We offer a range of melting furnaces, including induction and muffle types, designed to meet the exact requirements of your materials—whether you're working with metals, glass, or conducting laboratory tests.
Let our experts help you make the perfect match. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and find the ideal solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How is temperature controlled in a furnace? Mastering Precise Thermal Management
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















