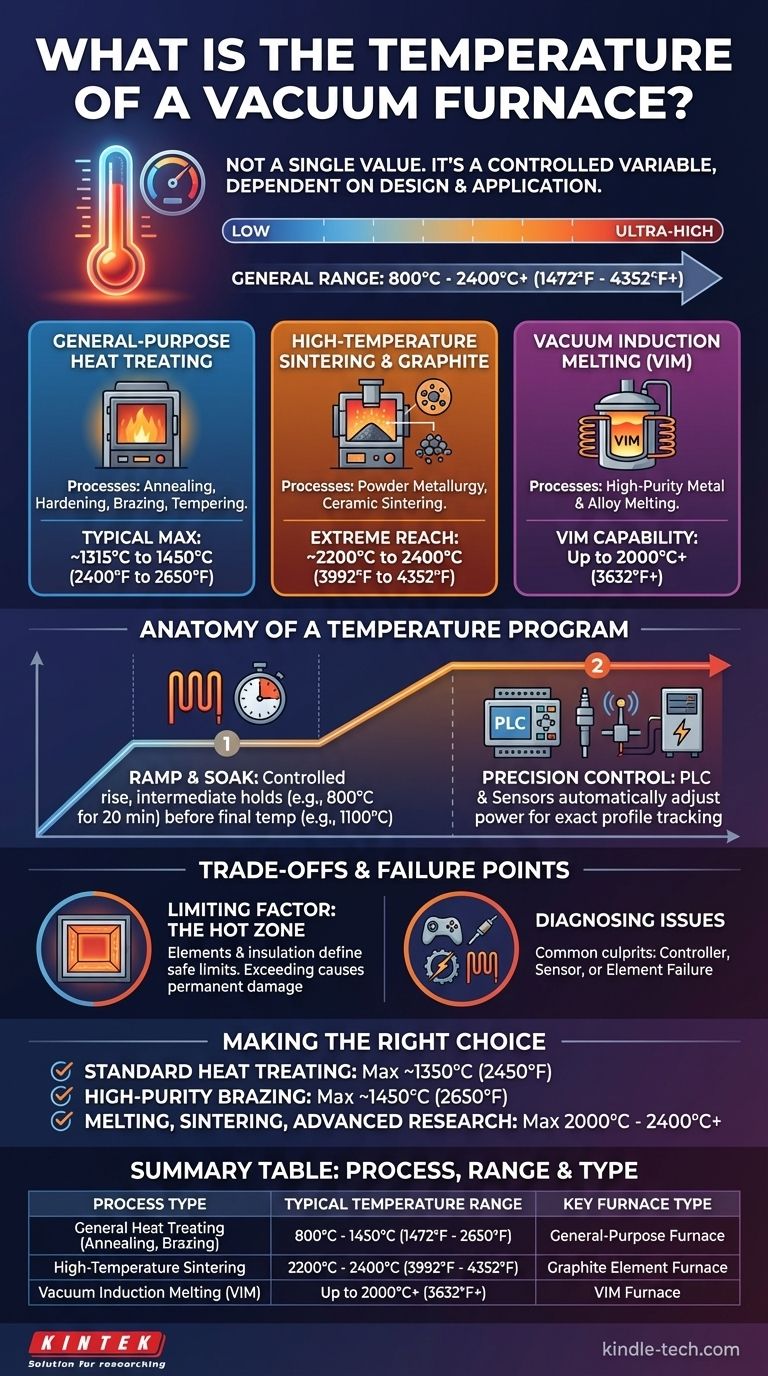
The temperature of a vacuum furnace is not a single value but a highly controlled variable that depends entirely on the furnace's design and its intended application. While a typical heat treatment program might run between 800°C and 1100°C (1472°F - 2012°F), the maximum temperature capabilities vary drastically by furnace type. General-purpose models often reach up to 1450°C (2650°F), whereas specialized furnaces for melting or sintering can exceed 2400°C (4352°F).
The required temperature is dictated by the material process—such as brazing, sintering, or melting—which in turn determines the type of furnace needed. Understanding this relationship is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your specific application.

How Furnace Type Dictates Temperature Range
The maximum achievable temperature of a vacuum furnace is fundamentally linked to its construction and heating method. Different designs are engineered to meet the demands of specific industrial or research processes.
General-Purpose Heat Treating Furnaces
These are the most common types of vacuum furnaces, used for processes like annealing, hardening, brazing, and tempering.
Their typical operating range is broad, but they generally have a maximum temperature capability of around 1315°C to 1450°C (2400°F to 2650°F). The higher end of this range is often reserved for specific alloys or for performing high-temperature "clean-up" cycles to burn off contaminants.
High-Temperature Sintering & Graphite Furnaces
Designed for creating solid parts from metal or ceramic powders, vacuum sintering requires extremely high temperatures.
Furnaces built for this purpose, often using graphite heating elements, can regularly reach 2200°C to 2400°C (3992°F to 4352°F). This ultra-high temperature capability is necessary to bond the particles of specialized materials effectively.
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) Furnaces
These furnaces use electromagnetic induction to heat and melt metals and alloys in a vacuum environment, ensuring high purity.
Due to the efficiency of inductive heating, VIM furnaces can achieve temperatures up to 2000°C (3632°F) or more, depending on the coupling between the induction coil and the material being melted.
Anatomy of a Temperature Program
A furnace's temperature is not a static setpoint but a dynamic, precisely controlled profile. A typical cycle involves several distinct stages to ensure the material is processed correctly.
The Ramp and Soak
A process rarely involves heating directly to the final temperature. Instead, the temperature is "ramped" up at a controlled rate to a specific point, often for an intermediate "soak."
For example, a program might heat to 800°C and hold for 20 minutes to ensure uniform temperature throughout the part before ramping again to a final process temperature of 1100°C for a longer soak. This prevents thermal shock and ensures consistent material properties.
Precision Control Systems
Achieving and holding these temperatures with precision is critical. Modern furnaces use a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) that reads data from sensors like thermocouples.
This system automatically adjusts power to the heating elements, ensuring the actual furnace temperature follows the programmed profile exactly. It also manages safety interlocks for the water, electricity, and vacuum systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Points
Reaching and maintaining extreme temperatures in a vacuum is a significant engineering challenge with inherent limitations and potential points of failure.
The Limiting Factor: The Hot Zone
The "hot zone"—the insulated interior chamber containing the heating elements—is the heart of the furnace. The materials used for the elements (e.g., graphite, molybdenum) and insulation directly determine the furnace's maximum safe operating temperature.
Pushing a furnace beyond its designed temperature limit can cause permanent damage to these critical components.
Diagnosing Temperature Issues
If a furnace fails to reach its target temperature, the issue often lies in one of three areas. The problem could be the controller (thermostat) not sending the right signal, the sensor (thermocouple) providing an incorrect reading, or the heating element itself being broken or having a faulty electrical connection.
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking each component to identify and resolve the source of the failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating a vacuum furnace, your process requirements must drive your decision. The maximum temperature is not just a specification—it's a direct reflection of the furnace's capability.
- If your primary focus is standard heat treating (annealing, hardening): A furnace with a maximum temperature around 1350°C (2450°F) is typically sufficient for most common alloys and processes.
- If your primary focus is high-purity brazing or specialized alloys: Look for a model capable of reaching up to 1450°C (2650°F) to provide greater process flexibility and the ability to run cleaning cycles.
- If your primary focus is melting, sintering, or advanced materials research: You will need a specialized furnace, such as a vacuum induction or graphite model, capable of reaching 2000°C to 2400°C.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's temperature capabilities to your specific material and process is the key to achieving successful, repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| General Heat Treating (Annealing, Brazing) | 800°C - 1450°C (1472°F - 2650°F) | General-Purpose Furnace |
| High-Temperature Sintering | 2200°C - 2400°C (3992°F - 4352°F) | Graphite Element Furnace |
| Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) | Up to 2000°C+ (3632°F+) | VIM Furnace |
Ready to find the perfect vacuum furnace for your specific temperature needs?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing precision vacuum furnaces for everything from standard heat treating to advanced materials research. Our experts will help you select the right equipment to ensure precise temperature control, process repeatability, and optimal results for your laboratory.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are ceramics sintered? Transform Powder into High-Performance Solid Components
- What is the cooling process of hardening? Master the Quenching Step for Maximum Hardness
- How does arc melting work? A Guide to High-Purity Metal and Alloy Production
- What are the disadvantages of heat treatment? Managing the Risks of Distortion and Cost
- What is the annealing process in heat treatment? Make Metals Softer and More Workable
- How long does it take to anneal metal? From minutes to days for perfect results.
- What is the process of a mesh belt furnace? Achieve Consistent, High-Volume Heat Treatment
- What is three step sintering process? A Guide to Blending, Compacting, and Heating



















