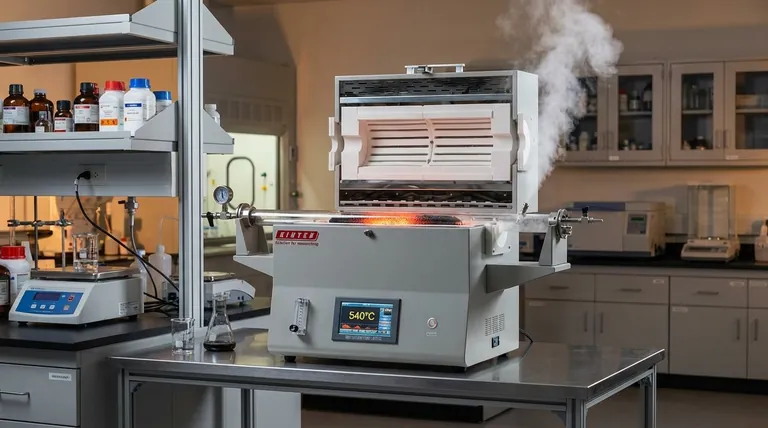
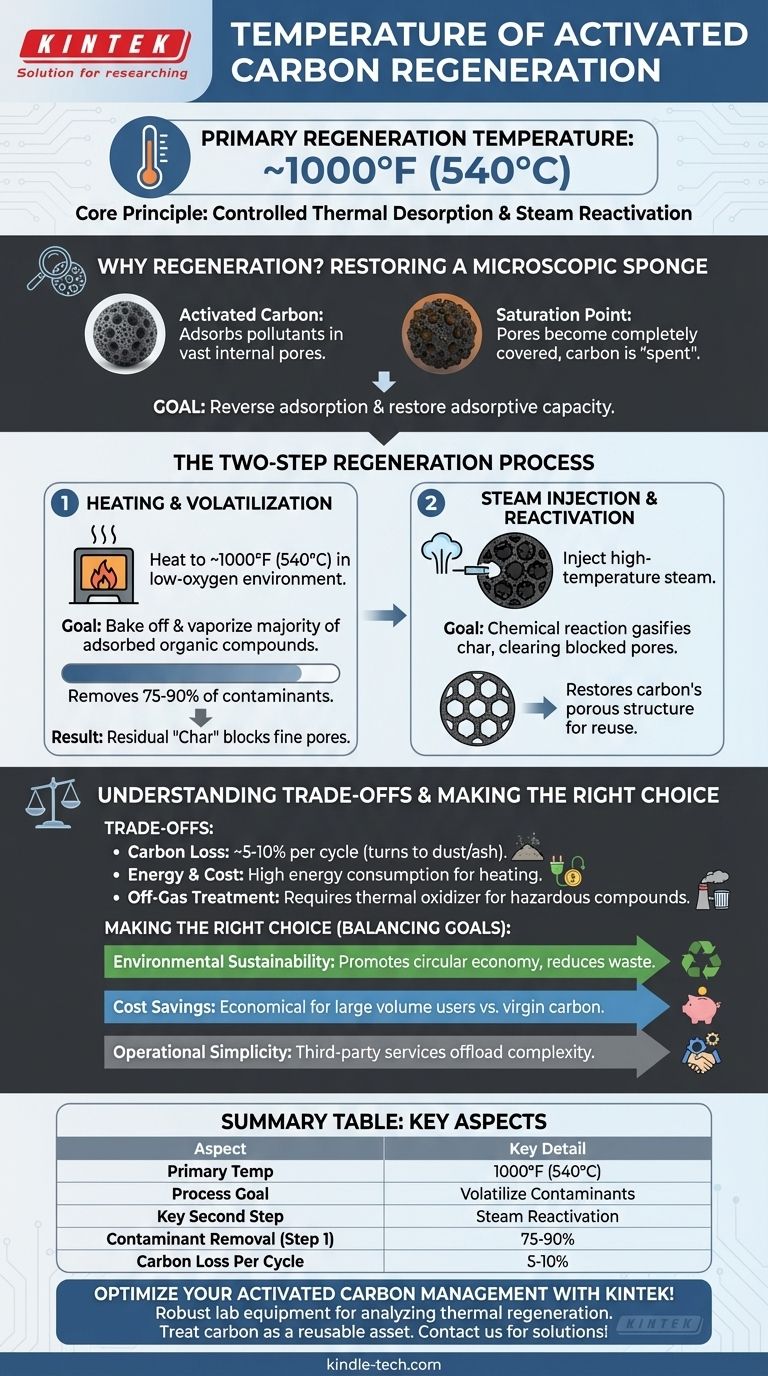
In thermal regeneration, activated carbon is heated to temperatures around 1000°F (approximately 540°C). This high heat is the primary mechanism for vaporizing the contaminants that have been adsorbed onto the carbon's surface. However, temperature is only one part of a two-step process required to fully restore the carbon for reuse.
The core principle of regeneration is not just heating, but controlled thermal desorption followed by steam reactivation. While high temperature drives off most contaminants, the injection of steam is what truly clears the microscopic pores and restores the carbon's adsorptive capacity.

The Goal: Restoring a Microscopic Sponge
Why Carbon Needs Regeneration
Activated carbon works through adsorption, a process where pollutant molecules stick to its vast internal surface area. This network of microscopic pores gives a small amount of carbon the surface area of a football field.
The Saturation Point
Over time, this immense surface area becomes completely covered with contaminants. At this point, the carbon is considered "spent" or saturated and can no longer effectively remove impurities from a liquid or gas stream.
The Role of High Temperature
The purpose of regeneration is to reverse the adsorption process. Applying significant thermal energy breaks the physical bonds holding the adsorbed compounds to the carbon, causing them to turn into a gas (volatilize) and leave the carbon's pores.
Deconstructing the Regeneration Process
Step 1: Heating and Volatilization
The first and longest phase involves heating the spent carbon in a low-oxygen environment to approximately 1000°F (540°C). This step is designed to bake off and vaporize the majority of the adsorbed organic compounds.
This initial heating is highly effective, typically removing 75% to 90% of the adsorbed material.
Step 2: Steam Injection and Reactivation
After the initial volatilization, a carbonaceous "char" residue from the contaminants often remains, blocking the finest pores. To remove this, high-temperature steam is injected into the furnace.
The steam triggers a chemical reaction with the residual char, gasifying it and clearing out the blocked pores. This is the crucial "reactivation" step that restores the carbon's porous structure and prepares it for reuse.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Inevitable Carbon Loss
The high temperatures and oxidative conditions of regeneration are harsh. Each cycle typically results in a 5-10% loss of the carbon material itself, which turns into fine dust or ash. This means the carbon cannot be regenerated indefinitely.
Energy and Cost
Heating large quantities of carbon to such high temperatures is an energy-intensive process. The cost of fuel, equipment maintenance, and handling must be weighed against the cost of purchasing new, or "virgin," activated carbon.
Off-Gas Treatment
The volatilized contaminants do not simply disappear. They form an "off-gas" that must be treated, often in a thermal oxidizer or afterburner, to destroy the hazardous compounds before they can be released into the atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Regenerating activated carbon is a strategic decision that balances cost, logistics, and environmental impact.
- If your primary focus is cost savings: Regeneration is often more economical than purchasing virgin carbon, especially for large-volume users, despite the energy costs involved.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Regeneration is a superior choice as it promotes a circular economy, reduces landfill waste, and lowers the carbon footprint associated with producing and transporting new material.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity: Using a third-party regeneration service can be ideal, as it offloads the complexity of managing on-site furnaces and air pollution control equipment.
Understanding the principles of regeneration allows you to effectively manage your activated carbon as a reusable asset rather than a disposable commodity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Regeneration Temperature | 1000°F (approx. 540°C) |
| Process Goal | Volatilize adsorbed contaminants |
| Key Second Step | Steam injection for pore reactivation |
| Typical Contaminant Removal (Step 1) | 75-90% |
| Typical Carbon Loss Per Cycle | 5-10% |
Optimize your activated carbon management with KINTEK!
Managing your activated carbon effectively is key to controlling costs and supporting sustainability. KINTEK specializes in providing the robust lab equipment and consumables needed for analyzing and optimizing processes like thermal regeneration. Whether you're testing regeneration efficiency or sourcing high-quality carbon, our solutions help you treat activated carbon as a reusable asset.
Let our expertise enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and discover how we can support your goals for cost savings and environmental responsibility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the role of a quartz tube in the preparation of Mo2Ga2C powder precursors? Essential Synthesis Benefits
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















