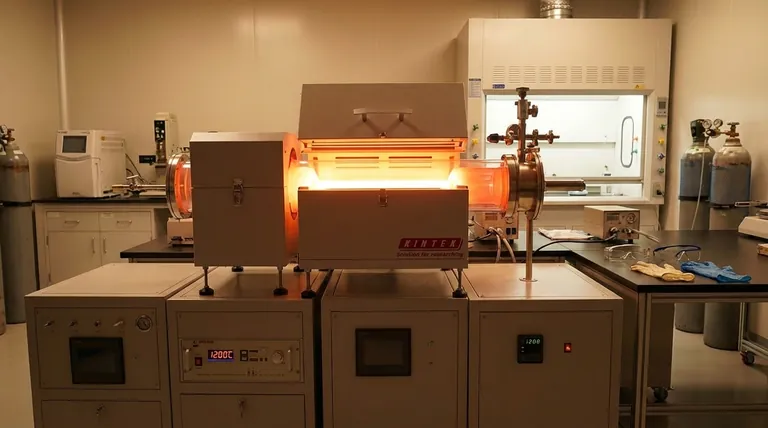
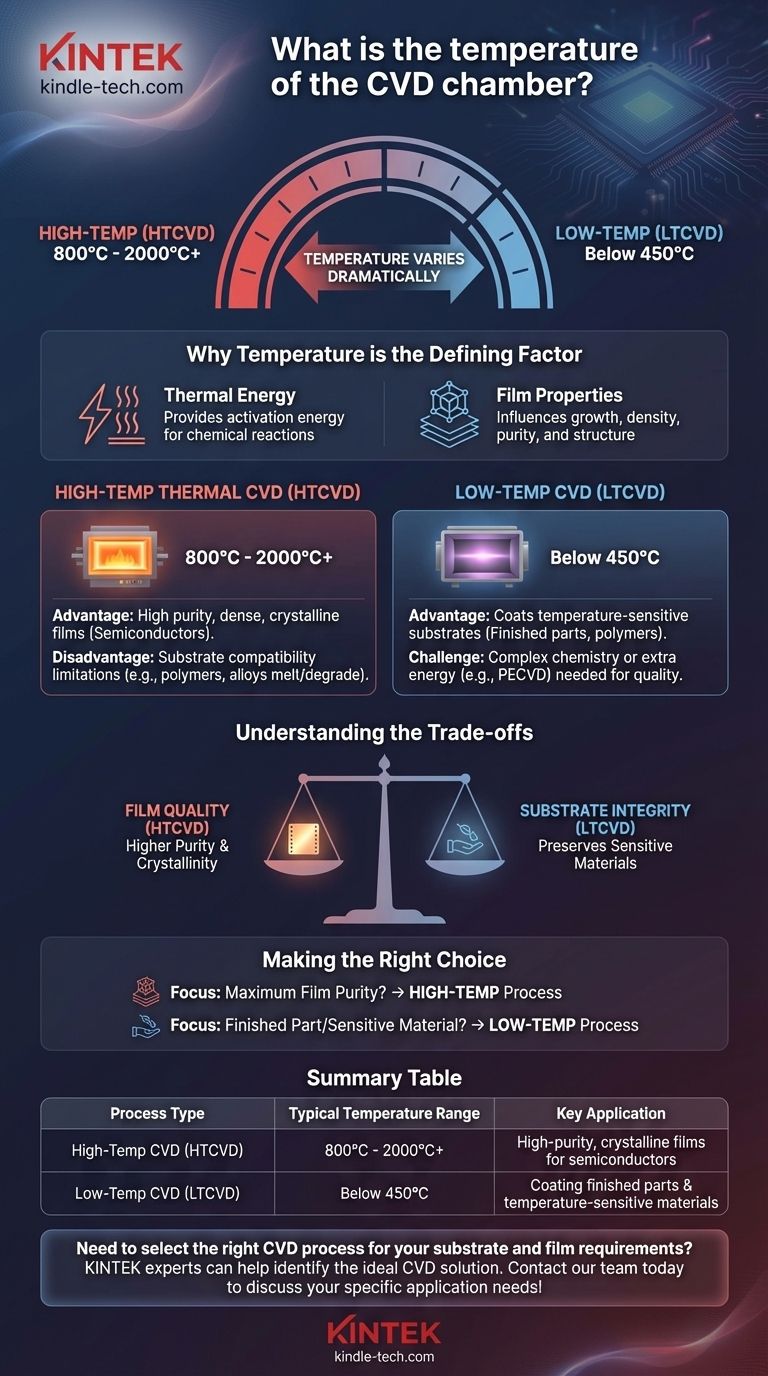
The temperature of a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) chamber is not a single value but varies dramatically depending on the specific process and desired outcome. While traditional thermal CVD operates at very high temperatures, often between 800°C and 2000°C, specialized low-temperature processes exist that run below 450°C to accommodate sensitive materials.
The core concept to grasp is that temperature is the primary control parameter in CVD. It is intentionally varied to manage the chemical reaction, control the properties of the final coating, and ensure compatibility with the object being coated (the substrate).

Why Temperature is the Defining Factor in CVD
Temperature is not just a background condition; it is the engine that drives the entire CVD process. It provides the activation energy required for the chemical reactions to occur on the substrate surface.
The Role of Thermal Energy
The fundamental goal of CVD is to decompose a precursor gas into a solid material that deposits as a thin film. This decomposition requires a significant amount of energy, which is most commonly supplied by heat.
Higher temperatures provide more thermal energy, causing the gas molecules to break down more effectively and bond to the substrate.
Impact on Film Properties
The chamber temperature directly influences the final film's characteristics. Factors like growth rate, density, purity, and crystal structure are all highly dependent on the heat applied during the deposition process.
Unpacking the Different CVD Temperature Regimes
The wide range of temperatures cited for CVD reflects the existence of different process types, each designed for specific applications and materials.
High-Temperature Thermal CVD (HTCVD)
This is the classic form of CVD, typically operating from 800°C to over 1200°C. Some demanding applications can even push temperatures toward 2000°C.
These high temperatures are necessary to create highly pure, dense, and often crystalline films, such as those used in the semiconductor and advanced materials industries.
Low-Temperature CVD (LTCVD)
To overcome the limitations of high heat, proprietary low-temperature CVD processes have been developed. These can operate at temperatures below 450°C.
This innovation is critical because it allows for the coating of materials that would otherwise be damaged, warped, or lose their essential mechanical properties at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Heat vs. Substrate Integrity
The choice between high- and low-temperature CVD is a classic engineering trade-off between achieving the ideal film properties and preserving the substrate material.
The High-Temperature Advantage
Generally, higher process temperatures yield films with superior quality. This can mean better crystallinity, higher density, and greater purity, as the high thermal energy drives the chemical reactions more completely.
The High-Temperature Disadvantage
The primary limitation of HTCVD is substrate compatibility. Many materials, including certain polymers, alloys, and finished mechanical components, cannot withstand temperatures exceeding 1000°C without degrading, melting, or losing their engineered properties.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
The clear benefit of LTCVD is its ability to coat temperature-sensitive substrates. This opens up CVD technology to a much broader range of applications, allowing complex, pre-fabricated parts to receive advanced coatings without being damaged.
The Low-Temperature Challenge
Achieving high-quality films at lower temperatures is more complex. It often requires carefully engineered precursor chemistry or the use of other energy sources (like plasma in a process called PECVD) to assist in breaking down the precursor gases effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct CVD process requires a clear understanding of your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity and crystallinity: A high-temperature process is likely necessary, provided your substrate material can tolerate the extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is coating a finished part or a temperature-sensitive material: You must seek out a specialized low-temperature CVD process to ensure the substrate's integrity is preserved.
Ultimately, understanding the role of temperature allows you to select the precise CVD process that meets your specific material and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp CVD (HTCVD) | 800°C - 2000°C+ | High-purity, crystalline films for semiconductors |
| Low-Temp CVD (LTCVD) | Below 450°C | Coating finished parts & temperature-sensitive materials |
Need to select the right CVD process for your substrate and film requirements?
KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processes. Our experts can help you identify the ideal CVD solution—whether for high-purity film growth or low-temperature coating of sensitive components—ensuring your laboratory achieves optimal results.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques


















