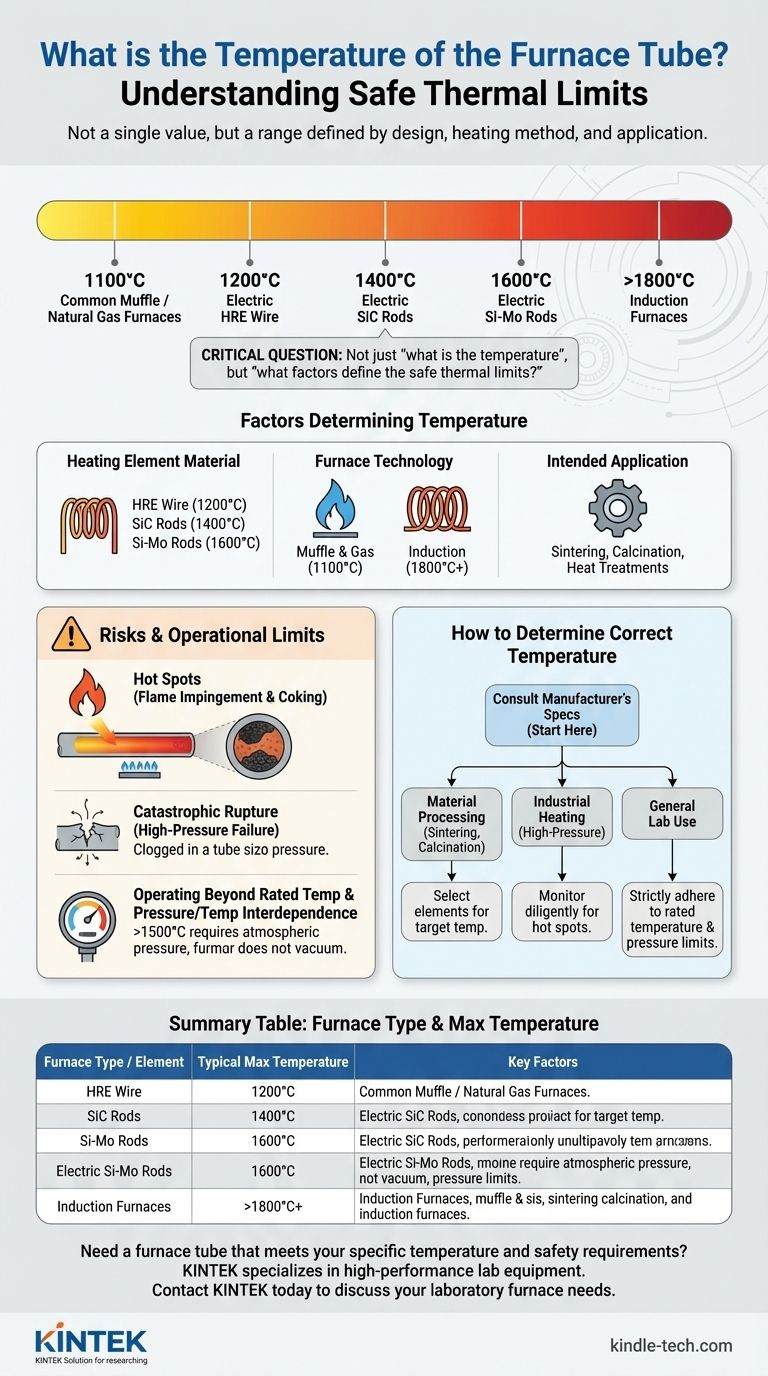
The temperature of a furnace tube is not a single value but varies significantly based on the furnace's design, heating method, and intended application. Temperatures can range from around 1100°C (2000°F) for common muffle or natural gas furnaces to 1600°C for specialized electric tube furnaces, with some induction furnaces capable of exceeding 1800°C. The specific materials used for the heating elements and the tube itself are the primary factors that determine its maximum safe operating temperature.
The critical question is not simply "what is the temperature," but "what factors define the safe thermal limits for a specific furnace tube?" The maximum temperature is dictated by the furnace's fundamental design, but catastrophic failure often occurs well below that limit due to localized "hot spots."

Factors Determining Furnace Tube Temperature
The term "furnace tube" can apply to many different systems, each with its own thermal capabilities. The maximum achievable temperature is a direct result of the technology used to generate the heat.
The Role of the Heating Element Material
For electric tube furnaces, the material of the resistance heating element is the main determinant of the maximum temperature.
- HRE Resistance Wire: These elements typically allow for maximum furnace temperatures around 1200°C.
- Silicon Carbon Rods: Furnaces using these rods can achieve higher temperatures, generally up to 1400°C.
- Silicon-Molybdenum Rods: For even more demanding applications, these elements enable furnaces to reach 1600°C.
The Type of Furnace Technology
Different heating methods produce vastly different thermal environments and are used for different applications.
- Muffle & Natural Gas Furnaces: These common furnace types typically operate in the 1090°C to 1100°C (approx. 2000°F) range.
- Induction Furnaces: These systems use inductive heating and can reach extreme temperatures of 1800°C or higher, depending on the design and the material being heated.
The Intended Application
The temperature is chosen to suit a specific process. Applications like high-temperature sintering, calcination of materials, and specialized heat treatments all require precise and stable temperature control at these elevated levels.
Understanding the Risks and Operational Limits
Simply knowing the maximum temperature is insufficient for safe operation. The real-world performance and safety of a furnace tube depend on maintaining uniform conditions and respecting its designed limitations.
The Danger of "Hot Spots"
A "hot spot" is a localized area on the tube that is significantly hotter than the surrounding surfaces. These are a primary cause of unexpected tube failure.
Hot spots can develop from external factors, like flame impingement, where a burner's flame directly touches the tube. They can also result from internal issues, such as coking, where carbon deposits build up on the inner wall, acting as an insulator and causing heat to accumulate in the tube metal.
Catastrophic Tube Rupture
In high-pressure industrial furnaces (operating above 1,500 psig), the consequence of a hot spot can be a tube rupture. This failure is not a simple leak; it can be an explosion powerful enough to extend outside the furnace firebox, representing a significant safety hazard.
Operating Beyond Rated Temperature
Every furnace has a rated temperature specified by the manufacturer. Attempting to operate the furnace beyond this limit, even for short periods, can compromise the structural integrity of the tube and heating elements, leading to premature failure.
Temperature and Pressure Interdependence
Operational parameters are often linked. For example, in some systems, when the furnace body temperature exceeds 1500°C, the furnace tube must be kept at normal atmospheric pressure. Operating it in a vacuum state under these conditions is prohibited, as it can create unsafe stresses on the tube material.
How to Determine the Correct Temperature for Your Application
Always begin by consulting the manufacturer's specifications for your specific furnace model. From there, your operational focus will depend on your goal.
- If your primary focus is material processing (sintering, calcination): Your required process temperature will dictate the type of furnace you need, specifically one with heating elements (like silicon-molybdenum) that can safely reach and sustain your target.
- If your primary focus is industrial heating (e.g., in a high-pressure system): Your priority must be diligent monitoring for hot spots caused by coking or flame impingement to prevent catastrophic tube failure.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory use: Always operate strictly within the "rated temperature" and be aware of all special conditions noted by the manufacturer, such as pressure limitations at very high temperatures.
Understanding the factors that define your furnace's limits is the key to safe, effective, and repeatable high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type / Element | Typical Max Temperature | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle / Natural Gas | ~1100°C (2000°F) | Common for general heating |
| Electric (HRE Wire) | ~1200°C | Good for standard lab applications |
| Electric (SiC Rods) | ~1400°C | Higher temperature capability |
| Electric (Si-Mo Rods) | ~1600°C | For demanding processes |
| Induction Furnace | 1800°C+ | Extreme heat for specialized uses |
Need a furnace tube that meets your specific temperature and safety requirements?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including tube furnaces with precise temperature control and robust safety features. Whether your application involves sintering, calcination, or general laboratory heating, our experts can help you select the right system to ensure efficient, safe, and repeatable results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory furnace needs and discover the right solution for your research or production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















