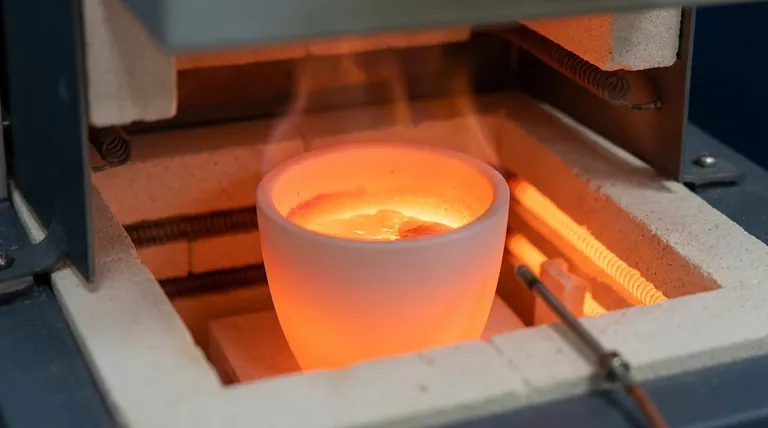
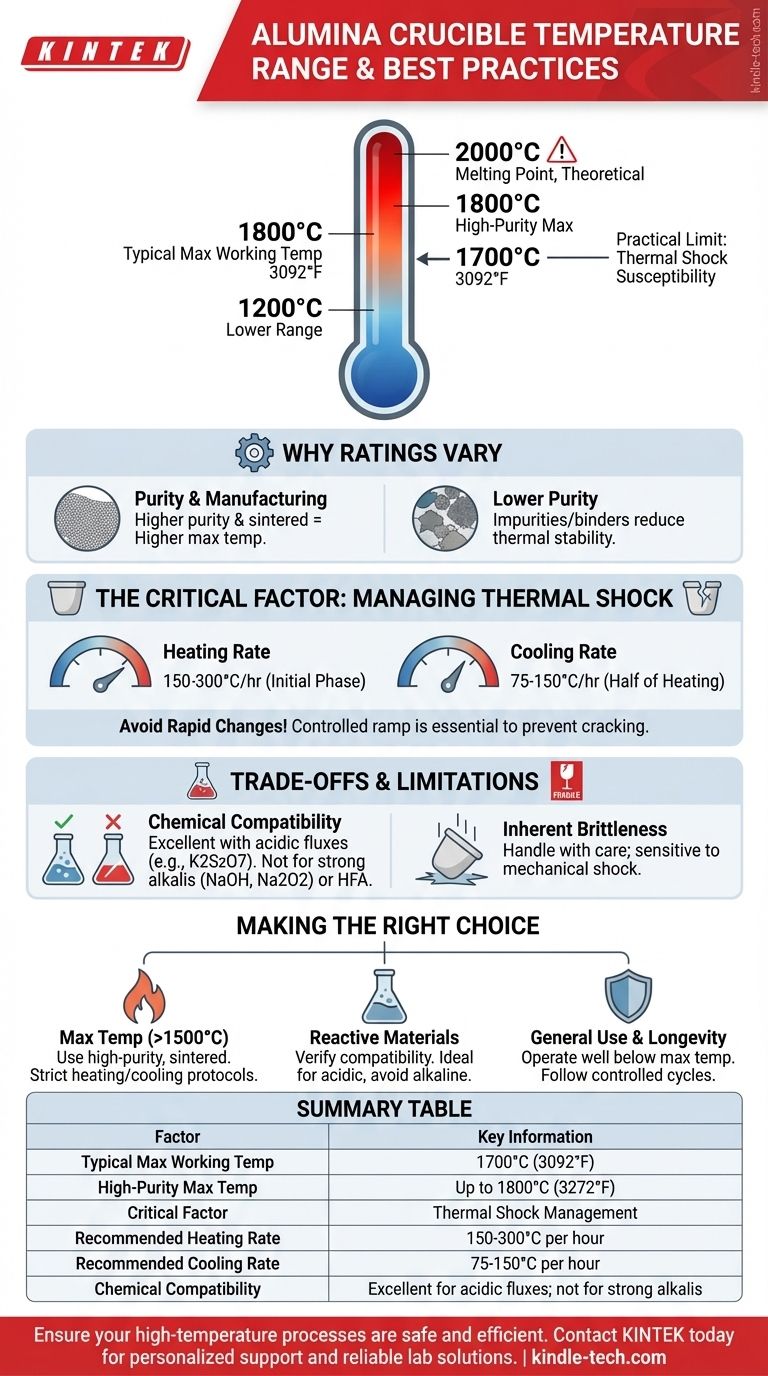
The maximum working temperature for an alumina crucible is typically around 1700°C (3092°F). However, this figure is not absolute; the safe operating range depends heavily on the crucible's purity, manufacturing process, and specific application. Some specialized, high-purity alumina products can even reach a maximum of 1800°C, while others are rated for lower temperatures near 1200°C.
While alumina has a very high melting point near 2000°C, its practical temperature limit is defined by its susceptibility to thermal shock. The key to successfully using an alumina crucible at its maximum temperature is not just reaching the heat, but controlling the rate of heating and cooling.

Why Temperature Ratings Vary
The term "alumina crucible" can describe products with different performance characteristics. Understanding what influences the temperature rating is key to selecting the right tool and using it correctly.
The Impact of Purity and Manufacturing
Not all alumina is created equal. A sintered, high-purity alumina crucible will have a higher and more reliable maximum service temperature, often at or above 1700°C.
Crucibles with lower purity or different manufacturing methods may have lower temperature limits due to the presence of binding agents or impurities that reduce their thermal stability.
Working Temperature vs. Melting Point
The melting point of alumina is around 2000°C, but this is a theoretical maximum. The maximum working temperature (e.g., 1700-1800°C) is the highest temperature at which the crucible maintains its structural integrity and chemical stability for practical use. Operating near the melting point is never recommended.
The Critical Factor: Managing Thermal Shock
Alumina is a strong ceramic, but it is sensitive to rapid temperature changes, a phenomenon known as thermal shock. This is the single most common cause of crucible failure.
Recommended Heating Rates
To prevent cracking, the furnace and crucible must be heated slowly and evenly. A controlled ramp rate is essential.
A general guideline is to heat at a rate of 150-300°C per hour, especially during the initial phase. This minimizes the thermal stress on the material.
Controlled Cooling
Cooling is just as critical as heating. The cooling rate should be gradual, typically half of the heating rate (75-150°C per hour).
If possible, avoid removing a crucible from a very hot furnace directly into room temperature air. Let the furnace cool down significantly first.
Best Practices for Handling
When you must pour molten material, make the process as brief as possible to minimize the crucible's exposure to a sudden temperature drop. If running consecutive melts, keeping the furnace hot between runs can extend the crucible's life.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Beyond temperature, you must consider the chemical environment and physical handling of the crucible for successful operation.
Chemical Incompatibility
Alumina exhibits excellent resistance to acidic substances. It is well-suited for use with acidic fluxes like K2S2O7.
However, it is not suitable for use with alkaline substances such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), sodium peroxide (Na2O2), or sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), as these will corrode the ceramic at high temperatures. It must also be kept away from hydrofluoric acid (HFA).
Inherent Brittleness
Like all ceramics, alumina crucibles are hard but brittle. They can be damaged by mechanical shock, such as being dropped or having material dropped into them. Always handle them with care.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to match your procedure to the crucible's capabilities.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature operation (above 1500°C): Prioritize a high-purity, sintered alumina crucible and implement strict, slow heating and cooling protocols.
- If your primary focus is melting highly reactive materials: Verify chemical compatibility first; alumina is ideal for acidic samples but will fail with strong alkaline substances.
- If your primary focus is general use and longevity: Operate well below the stated maximum temperature (e.g., 100-150°C below) and always follow controlled heating and cooling cycles.
Properly managed, an alumina crucible is an exceptionally reliable tool for high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Typical Max Working Temp | 1700°C (3092°F) |
| High-Purity Max Temp | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) |
| Critical Factor | Thermal Shock Management |
| Recommended Heating Rate | 150-300°C per hour |
| Recommended Cooling Rate | 75-150°C per hour |
| Chemical Compatibility | Excellent for acidic fluxes; not for strong alkalis |
Ensure your high-temperature processes are safe and efficient with the right lab equipment. Selecting the correct crucible is critical for your results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a range of alumina crucibles suited for various temperature needs and chemical applications. Our experts can help you choose the ideal product for your specific laboratory requirements. Contact KINTEK today for personalized support and reliable solutions for all your lab needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the function of an alumina crucible in NaSICON synthesis? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Reactions
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- Why are high-alumina crucibles selected for Cs-zeolite heat treatment? Ensure Sample Purity at 1100 °C
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production



















