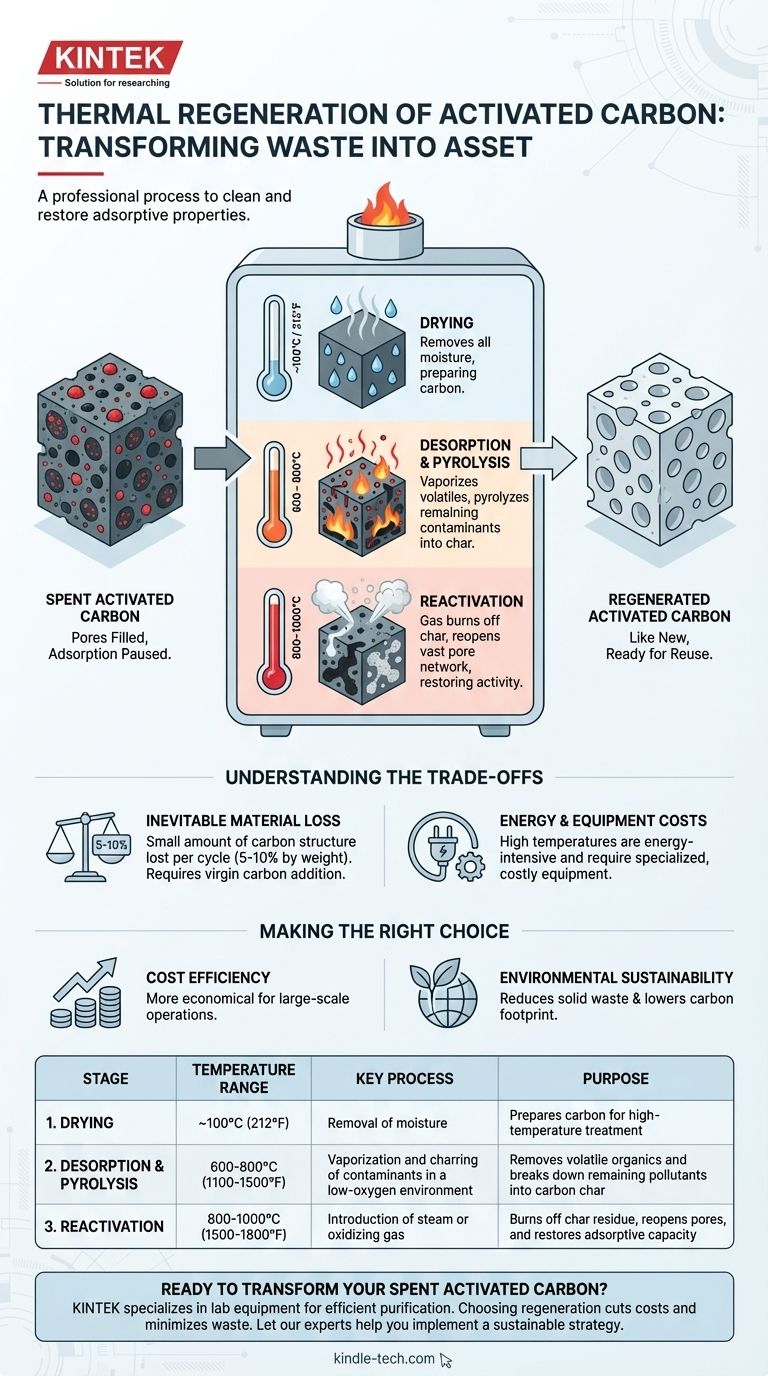
In essence, thermal regeneration is a high-temperature process used to clean and restore the adsorptive properties of used, or "spent," activated carbon. This controlled heating process effectively destroys and removes the contaminants that have accumulated on the carbon's surface, allowing the material to be reused in purification applications.
The core purpose of thermal regeneration is to convert spent activated carbon from a waste product back into a functional asset. By burning off trapped pollutants, the process reopens the carbon's vast network of pores, renewing its ability to capture new contaminants.
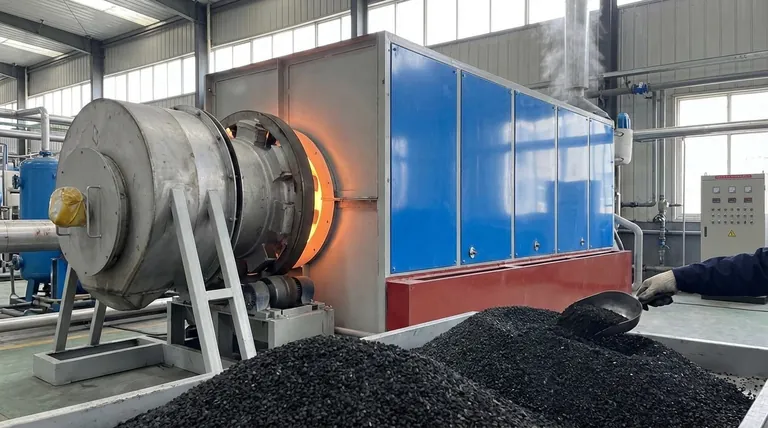

The Problem: When Activated Carbon Gets "Full"
To understand regeneration, we must first understand how activated carbon works and what happens when it stops working.
The Power of Adsorption
Activated carbon is an incredibly porous material. A single gram can have a surface area equivalent to a football field, created by a vast network of microscopic pores.
This immense surface area allows it to adsorb molecules, meaning it attracts and holds contaminants on its surface as liquids or gases pass through it.
Reaching Saturation
Over time, these pores become filled with the adsorbed contaminants. At this point, the carbon is considered "spent" or "saturated" and can no longer effectively purify the stream it is treating. This leaves two options: disposal or regeneration.
The Three Stages of Thermal Regeneration
Thermal regeneration is a meticulous, multi-stage process typically performed in a high-temperature furnace.
Stage 1: Drying (~100°C / 212°F)
The first step is to gently heat the spent carbon to remove all water and moisture trapped within its pores. This is a critical preparatory stage.
Stage 2: Desorption & Pyrolysis (600-800°C / 1100-1500°F)
Next, the carbon is heated further in a low-oxygen environment. This heat vaporizes and boils off the more volatile adsorbed organic compounds.
Any remaining organic compounds that don't vaporize are "pyrolyzed," or baked, which breaks them down into a char of elemental carbon. At the end of this stage, the original contaminants are gone, but the pores are now clogged with this carbonaceous char.
Stage 3: Reactivation (800-1000°C / 1500-1800°F)
In the final and most critical stage, steam or another oxidizing gas is introduced at very high temperatures. This gas selectively reacts with the char residue, converting it to a gas and clearing it out.
This unblocks the microscopic pores, restoring the carbon's original surface area and making it "active" once again. The regenerated carbon is then cooled and is ready for reuse.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, thermal regeneration is not a perfect process. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Inevitable Material Loss
Each regeneration cycle causes a small amount of the carbon structure to burn off along with the char residue. Typically, about 5-10% of the carbon by weight is lost during each cycle. This loss must be compensated for by adding an equivalent amount of new, or "virgin," carbon.
Energy and Equipment Costs
The high temperatures required for regeneration make it an energy-intensive process. It requires significant capital investment in specialized equipment like rotary kilns or multiple-hearth furnaces, which is why it is often performed by specialized service companies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to regenerate or dispose of spent carbon depends on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is large-scale cost efficiency: Thermal regeneration is almost always more economical than purchasing and disposing of single-use activated carbon.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Reusing carbon through regeneration dramatically reduces solid waste and lowers the carbon footprint associated with producing and transporting virgin material.
Ultimately, thermal regeneration transforms activated carbon from a disposable consumable into a reusable, long-term asset for purification.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Drying | ~100°C (212°F) | Removal of moisture | Prepares carbon for high-temperature treatment |
| 2. Desorption & Pyrolysis | 600-800°C (1100-1500°F) | Vaporization and charring of contaminants in a low-oxygen environment | Removes volatile organics and breaks down remaining pollutants into carbon char |
| 3. Reactivation | 800-1000°C (1500-1800°F) | Introduction of steam or oxidizing gas | Burns off char residue, reopens pores, and restores adsorptive capacity |
Ready to transform your spent activated carbon from a waste product into a reusable asset?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that power efficient purification processes. By choosing regeneration, you can significantly cut long-term costs and minimize environmental waste for your laboratory.
Let our experts help you implement a sustainable, cost-effective strategy for your activated carbon needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your purification goals and discover the right solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the regeneration temperature of activated carbon? Optimize Your Process with the Right Method
- What are the materials used in the refractory lining of kilns? Choose the Right Lining for Maximum Durability
- What are the benefits of microwave pyrolysis? Achieve Faster, More Efficient Waste-to-Value Conversion
- What are the disadvantages of rotary kiln incinerator? High Costs and Operational Complexities
- What is the calcining zone in the kiln? The Key to Efficient Chemical Transformation
- What is the influence of calcination temperature? Mastering the Key to Material Properties
- What is the chemical reaction of calcination? A Guide to Thermal Decomposition Processes
- What is the temperature range of a rotary kiln incinerator? Optimize Waste Destruction & Efficiency



















