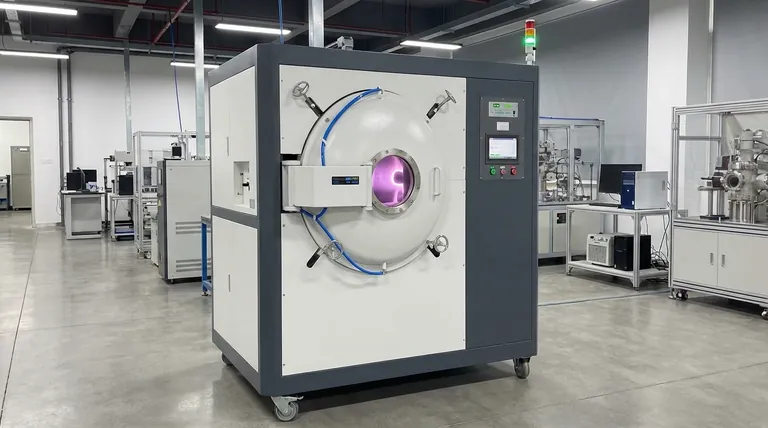
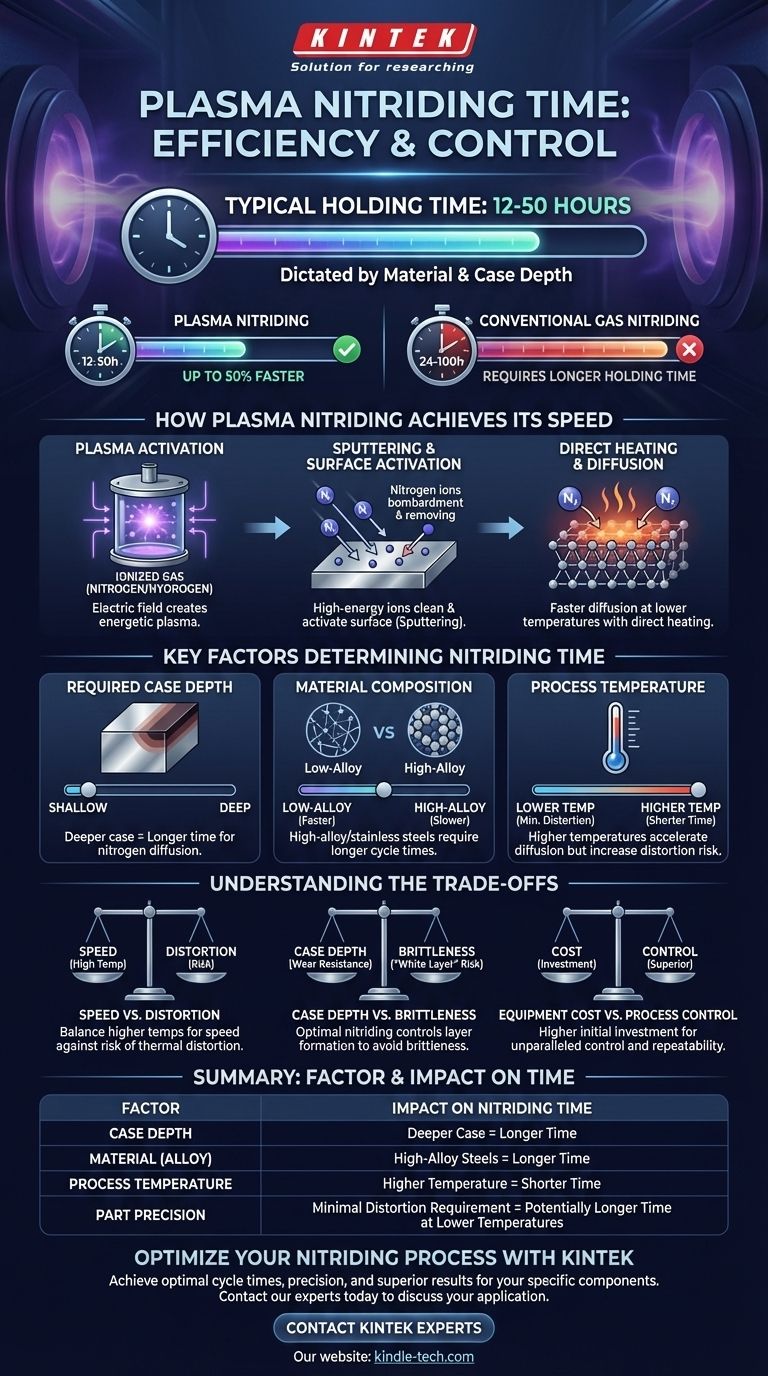
In plasma nitriding, the holding time typically ranges from 12 to 50 hours. This duration is primarily dictated by the specific material being treated and the required case depth for the component. A key advantage is its efficiency; plasma nitriding often requires only about half the holding time compared to conventional gas nitriding to achieve a similar result.
While the 12-to-50-hour cycle time provides a baseline, the true advantage of plasma nitriding lies in its efficiency and control. The process uses ionized gas in a vacuum to directly activate the material's surface, enabling faster nitrogen diffusion at lower temperatures and delivering superior results with minimal distortion.

How Plasma Nitriding Achieves Its Speed
The efficiency of plasma nitriding stems from its unique physical mechanism, which differs fundamentally from traditional gas or salt bath methods.
The Role of Plasma Activation
Plasma nitriding is a vacuum-assisted process. The parts to be treated are loaded into a chamber and form the cathode (negative electrode), while the furnace wall acts as the anode (positive electrode).
After evacuating the chamber, a precise mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen gas is introduced. An applied electric field ionizes this gas, creating a glowing, energized state of matter known as plasma.
Sputtering and Surface Activation
Nitrogen ions within the plasma are accelerated by the electric field and strike the workpiece's surface with high energy. This bombardment, known as sputtering, cleans the surface at an atomic level.
This cleaning effect is critical. It removes passive layers, such as the thin oxide film on stainless steel, that would otherwise inhibit or prevent nitriding. This surface activation creates a perfectly receptive surface for nitrogen diffusion.
Direct Heating and Diffusion
The constant ion bombardment also serves as the primary heating mechanism, heating only the workpiece, not the entire furnace. This is highly energy-efficient.
Once the surface is activated and heated, nitrogen atoms readily diffuse into the material, forming the hard, wear-resistant nitrided layer. The active plasma environment significantly accelerates this diffusion rate compared to conventional methods.
Key Factors That Determine Nitriding Time
The specific duration of a plasma nitriding cycle is not a fixed number; it is a carefully calculated variable dependent on several factors.
Required Case Depth
The most significant factor is the desired depth of the hardened layer, or "case." A deeper case requires more time for nitrogen to diffuse further into the material.
Material Composition
Different steel alloys absorb nitrogen at different rates. High-alloy materials, such as tool steels or certain stainless steels, often require longer cycle times to achieve the desired hardness and depth compared to simple low-alloy steels.
Process Temperature
Nitriding kinetics are exponentially affected by temperature. Higher temperatures increase the rate of nitrogen diffusion, shortening the process time.
However, plasma nitriding's ability to run at very low temperatures (as low as 350°C) is a major advantage for minimizing distortion in finished parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right parameters involves balancing competing priorities. Plasma nitriding offers a wide process window, but understanding the trade-offs is essential for success.
Speed vs. Distortion
Operating at higher temperatures will significantly shorten the cycle time. However, this increases the risk of thermal distortion, which can be unacceptable for high-precision components like gears or dies. Using a lower temperature preserves dimensional stability but extends the process time.
Case Depth vs. Brittleness
While a deep case is often desired for wear resistance, excessive nitriding can lead to the formation of a brittle surface layer known as the "white layer." Plasma nitriding offers superior control over the formation and composition of this layer compared to other methods, but it is a factor that must be managed.
Equipment Cost vs. Process Control
Plasma nitriding systems are a larger capital investment than traditional gas nitriding furnaces. The trade-off is unparalleled control, repeatability, and the ability to process a wider range of materials (like titanium and nickel alloys) that are difficult or impossible to treat with other methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Optimizing plasma nitriding time depends entirely on the goal for your specific component.
- If your primary focus is maximum speed for low-alloy steels: You can operate at the higher end of the temperature range (e.g., ~520°C) to significantly reduce cycle time compared to gas methods.
- If your primary focus is minimal distortion on high-precision parts: Utilize the lower temperature capabilities of plasma nitriding (e.g., 350-450°C), accepting a potentially longer cycle to preserve dimensional integrity.
- If your primary focus is treating high-alloy or stainless steels: Plasma nitriding is the superior choice, as its sputtering effect automatically removes passive oxide layers, ensuring a uniform and high-quality nitrided case where other methods would fail.
Ultimately, understanding these factors empowers you to leverage plasma nitriding not just for its speed, but for its precision and control.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Nitriding Time |
|---|---|
| Case Depth | Deeper case = Longer time |
| Material (Alloy) | High-alloy steels = Longer time |
| Process Temperature | Higher temperature = Shorter time |
| Part Precision | Minimal distortion requirement = Potentially longer time at lower temperatures |
Ready to optimize your plasma nitriding process for speed, precision, and superior results?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced thermal processing solutions for laboratories and manufacturing. Whether you are working with high-alloy steels, precision components requiring minimal distortion, or need to achieve a specific case depth, our expertise and equipment can help you achieve optimal cycle times and unparalleled quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















