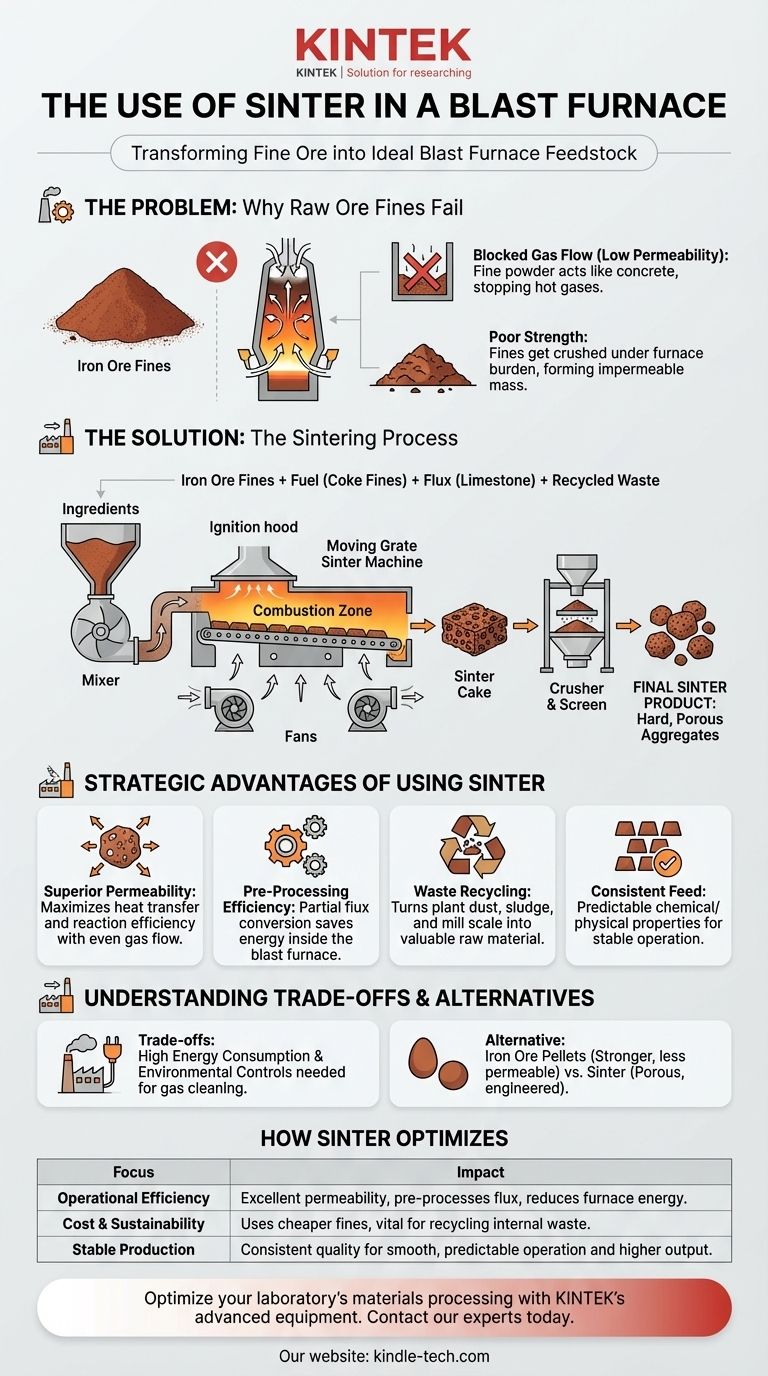
The primary use of sinter in a blast furnace is to act as a pre-processed, ideal feedstock for iron production. It is an engineered aggregate created by heating fine iron ore particles with flux and fuel until they fuse into a hard, porous mass. This process transforms otherwise unusable ore fines into a product with the perfect size, strength, and chemical properties needed for efficient blast furnace operation.
The core problem is that fine, dust-like iron ore cannot be fed directly into a blast furnace—it would clog the furnace and blow out the top. Sintering solves this by agglomerating these fines into a strong, permeable material that optimizes the entire iron-making process.

The Problem: Why Raw Ore Fines Fail in a Furnace
The "Fines" Dilemma
Iron ore mining and processing naturally generate a significant amount of fine, powder-like material. These "fines" are rich in iron but are physically unsuitable for direct use.
Blocked Gas Flow (Low Permeability)
A blast furnace relies on a continuous upward flow of extremely hot gases to heat and chemically reduce the iron ore. A bed of fine powders would act like concrete, blocking this crucial gas flow and preventing the furnace from functioning.
Poor Strength and Stability
The raw materials in a blast furnace form a massive column weighing thousands of tons. Fine particles lack the mechanical strength to support this weight and would be crushed into a dense, impermeable mass.
The Solution: How Sintering Creates the Ideal Feedstock
Combining the Ingredients
The sintering process begins by mixing iron ore fines with other essential, fine-grained materials:
- Fuel: Coke fines provide the heat for the fusion process.
- Flux: Limestone or dolomite fines are added to help remove impurities in the blast furnace later on.
- Recycled Materials: Dust, sludge, and mill scale from other parts of the steel plant are often included, making sintering an effective recycling process.
Fusing Particles with Heat
This carefully prepared mix is spread on a moving grate. The surface is ignited, and powerful fans pull air down through the bed. This creates a narrow, high-temperature combustion zone that moves through the material, heating the particles to around 1300-1400°C.
This temperature is hot enough to cause the surfaces of the particles to fuse together—a process called incipient fusion—without melting the entire mass.
Creating the Final Product
The result is a solid, fused sheet called a "sinter cake." This cake is then broken up, crushed, and screened to produce a final product with a consistent, controlled size and high porosity.
The Strategic Advantages of Using Sinter
1. Superior Permeability
The porous structure of sinter is its single most important physical property. It allows hot reducing gases to flow evenly throughout the furnace, maximizing heat transfer and the efficiency of the chemical reactions.
2. Pre-Processing for Efficiency
The sintering process accomplishes some of the chemical work before the material even enters the blast furnace. The limestone (calcium carbonate) is partially converted to lime (calcium oxide), a step that would otherwise consume valuable energy inside the furnace.
3. A Vehicle for Recycling
Sintering is the primary method for recycling iron-rich waste materials generated within a steel plant. This turns a costly disposal problem into a valuable raw material, improving both economic and environmental performance.
4. Consistent and Predictable Feed
By blending various raw materials, a sinter plant produces a feedstock with highly consistent chemical and physical properties. This consistency leads to a more stable, predictable, and controllable blast furnace operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
High Energy Consumption
A sintering plant is itself a major energy consumer. The process requires significant thermal and electrical energy to operate the fans and generate the heat needed for fusion.
Environmental Controls are Critical
The process can release pollutants like sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and dust. Modern sinter plants require extensive and costly gas cleaning systems to mitigate their environmental impact.
The Alternative: Pellets
The other primary form of agglomerated feedstock is iron ore pellets. Pellets are formed by rolling very fine ore concentrates into small balls and firing them in a kiln. While often stronger than sinter, they are typically less permeable. The choice between using sinter or pellets often depends on the quality of the available ore and the specific economics of the steel plant.
How Sinter Optimizes the Blast Furnace
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Sinter provides excellent permeability for gas flow and pre-processes the flux, reducing the energy needed inside the blast furnace.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction and sustainability: Sinter enables the use of cheaper iron ore fines and serves as a vital tool for recycling internal plant waste.
- If your primary focus is stable production: Sinter's consistent, engineered quality ensures a smooth and predictable furnace operation, leading to higher output and better hot metal quality.
Ultimately, sinter transforms a low-value industrial byproduct into a high-performance asset that is essential for modern, efficient ironmaking.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Impact on Blast Furnace Operation |
|---|---|
| Superior Permeability | Enables even gas flow for efficient heat transfer and chemical reactions. |
| Pre-Processed Flux | Reduces energy consumption by partially converting limestone to lime before entry. |
| Waste Recycling | Incorporates plant dust and sludge, turning waste into valuable raw material. |
| Consistent Quality | Provides stable, predictable feed for smoother furnace operation and higher output. |
Optimize your laboratory's materials processing with KINTEK's advanced equipment. Just as sinter enhances blast furnace efficiency, our lab furnaces, mills, and consumables are engineered to deliver precise, reliable results for your research and quality control. Whether you're testing raw materials or developing new processes, KINTEK provides the robust tools you need for success. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's unique challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is a magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- How mechanical properties are affected by sintering? Master the Trade-offs for Stronger Materials












