At its core, a vacuum furnace is a specialized type of furnace that heats materials inside a strong, sealed chamber from which nearly all the air has been removed. By operating in a near-vacuum, it creates an extremely controlled environment, preventing the unwanted chemical reactions—like oxidation—that occur when heating materials in the presence of air. This process is critical for advanced manufacturing, metallurgy, and material science.
A vacuum furnace's primary function is not just to generate heat, but to do so in a pristine, low-pressure environment. This prevents surface contamination and allows for thermal processes that result in superior material purity, strength, and integrity.

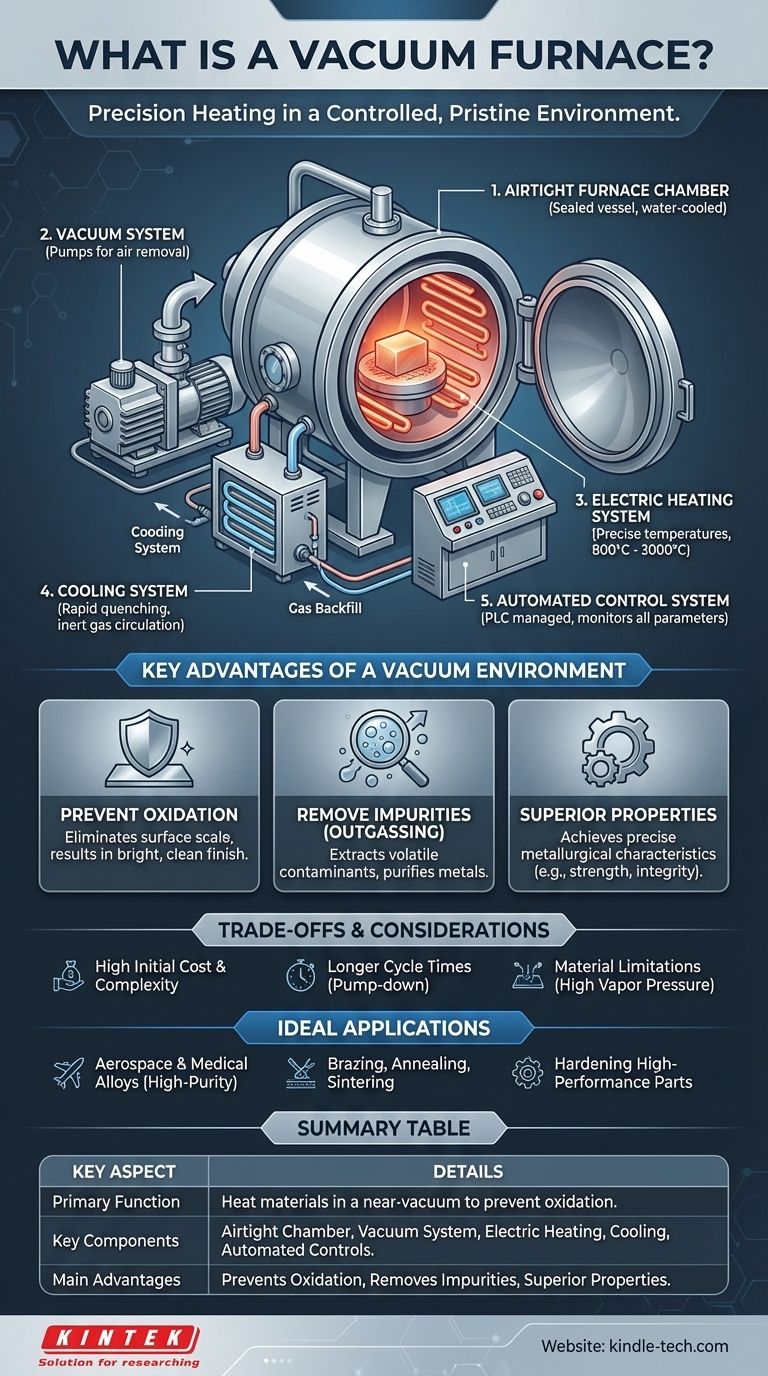
How a Vacuum Furnace Works: Key Components
A vacuum furnace is a system of integrated components, each with a critical role in creating and maintaining the desired processing conditions. Understanding these parts reveals how it achieves its unique capabilities.
The Airtight Furnace Chamber
The process begins with the furnace chamber (or shell). This is a robust, sealed vessel, typically constructed from high-strength steel and often featuring a double-walled, water-cooled design to manage the intense internal heat and maintain structural integrity under high vacuum.
The Vacuum System
This is the heart of the furnace. It's a multi-stage system of pumps, valves, and gauges designed to remove air and other gases from the chamber. It typically includes mechanical pumps for initial evacuation and more powerful diffusion or Roots pumps to achieve the final high-vacuum level required for processing.
The Electric Heating System
Inside the chamber, electric heating elements generate precise and uniform temperatures, which can range from 800°C to over 3,000°C. The absence of air allows for highly efficient radiant heat transfer, ensuring the material is heated evenly without hot spots.
The Cooling System
A critical component is the cooling system. This often involves an internal pure water circuit that cools the furnace walls and seals. For rapid cooling (quenching) of the processed material, the system can backfill the chamber with a high-purity inert gas like nitrogen or argon, which is then circulated to extract heat quickly.
The Automated Control System
Modern vacuum furnaces are managed by a comprehensive Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). This system automates and precisely monitors all critical parameters—including temperature, vacuum level, gas flow, and cycle time—ensuring process accuracy and repeatability.
The Key Advantages of a Vacuum Environment
Using a vacuum instead of a conventional atmosphere provides distinct and powerful benefits for treating advanced materials.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
This is the most significant advantage. By removing oxygen, a vacuum furnace completely prevents the formation of oxides (scale) on the material's surface. The result is a clean, bright finish that requires no subsequent cleaning and preserves the material's integrity.
Removing Impurities (Outgassing)
The low-pressure environment actively pulls volatile substances and contaminants out of the material itself. This process, known as outgassing, is crucial for purifying metals and ensuring the final product meets stringent quality standards.
Achieving Superior Metallurgical Properties
The precise control over the entire thermal cycle—from heating to soaking to rapid gas quenching—allows engineers to achieve specific and repeatable metallurgical properties. This is essential for processes like hardening, brazing, annealing, and sintering high-performance alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are specialized tools with specific considerations that make them unsuitable for every application.
High Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are sophisticated, high-precision machines. Their initial purchase price, installation, and ongoing maintenance costs are significantly higher than those of conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Longer Overall Cycle Times
The need to pump down the chamber to the required vacuum level before the heating cycle can begin adds time to the overall process. This "pump-down time" can make it less efficient for high-volume, low-margin production.
Material Limitations
Certain materials with high vapor pressures are not suitable for vacuum processing. At high temperatures and low pressures, these materials can begin to vaporize or "sublimate," leading to a loss of key alloying elements.
When is a Vacuum Furnace the Right Tool?
Choosing a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the material requirements and the desired outcome of the thermal process.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and brightness: A vacuum furnace is essential, as it completely prevents the oxidation that darkens and scales materials processed in air.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing: The vacuum environment is non-negotiable for removing contaminants and by-products from sensitive materials like titanium, superalloys, or medical implants.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific metallurgical properties: The precise control over heating and rapid gas quenching makes it superior for creating advanced alloys with exacting structural requirements.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace provides an unparalleled level of environmental control, enabling the creation of materials with properties that are simply unattainable in a conventional atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Heat materials in a near-vacuum environment to prevent oxidation and contamination. |
| Key Components | Airtight chamber, vacuum pump system, electric heating elements, cooling system, automated controls. |
| Main Advantages | Prevents oxidation, removes impurities (outgassing), achieves superior metallurgical properties. |
| Ideal Applications | High-purity processing (e.g., aerospace alloys, medical implants), brazing, annealing, sintering, hardening. |
| Considerations | Higher initial cost, longer cycle times, not suitable for materials with high vapor pressure. |
Ready to Achieve Unparalleled Material Purity?
Does your laboratory or manufacturing process demand the highest levels of material integrity and contamination-free results? The precise control of a vacuum furnace is essential for advanced applications in aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and materials science.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnace solutions tailored to your specific needs. We provide the technology and expertise to help you:
- Eliminate surface oxidation and achieve bright, clean finishes.
- Purify sensitive materials like titanium and superalloys through effective outgassing.
- Gain repeatable, precise control over critical thermal processes like hardening and brazing.
Let's discuss how a vacuum furnace can solve your specific thermal processing challenges. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite generally used as a refractory material for lining electric furnaces? Unmatched Performance & Efficiency
- What temperature do you braze aluminium? Master the Critical Temperature Window for Strong Joints
- What is the density of a sinter? It's a Variable, Engineered Property
- What is the function of high-temperature vacuum furnaces in EUROFER steel development for nuclear fusion reactors?
- What role does a high-temperature furnace play in Inconel 718 homogenization? Ensure Microstructural Precision
- Why is a vacuum welding system used for sealing zirconium alloy cladding? Ensure Precise Surface Oxidation Results
- What is the primary function of a high vacuum furnace in heat treating stainless steel? Precision Microstructural Control
- What is the atmosphere of a brazing furnace? Control Gases for Perfect Metal Joining



















