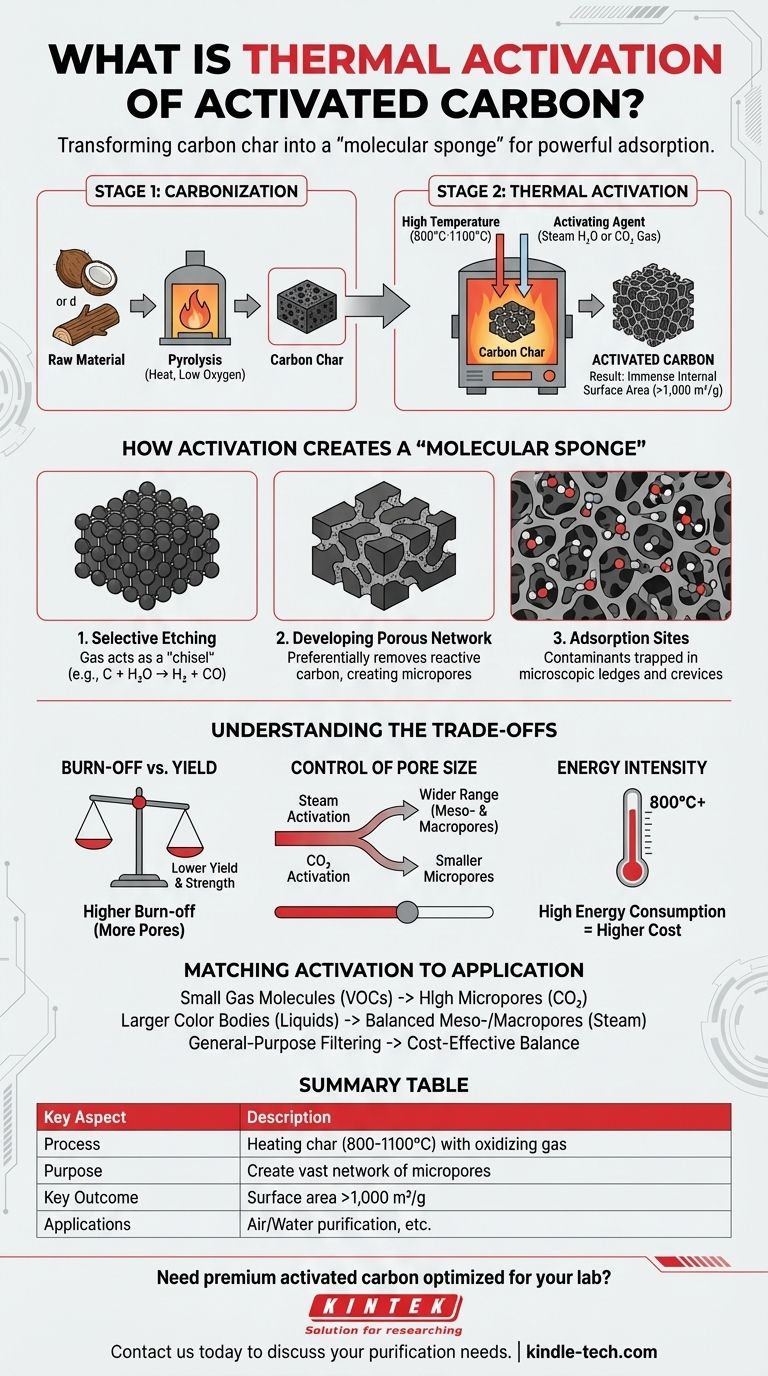
At its core, thermal activation is a high-temperature process used to transform a basic carbon char into the highly porous structure known as activated carbon. This method, also called physical activation, involves heating the carbonized material to extreme temperatures, typically between 800°C and 1100°C. In this environment, a controlled stream of an oxidizing gas, such as steam or carbon dioxide, selectively erodes the carbon, creating a vast network of microscopic pores.
The purpose of thermal activation is not simply to heat carbon, but to use high temperature and a reactive gas to strategically develop an immense internal surface area. This engineered network of pores is what gives activated carbon its powerful ability to adsorb, or trap, molecules.

The Two-Step Journey to Activation
The creation of activated carbon is not a single action but a carefully controlled two-stage process. Thermal activation is the critical second step.
Step 1: Carbonization
Before activation can occur, a raw, carbon-rich material (like coconut shells, wood, or coal) must be carbonized.
This is done by heating the material to high temperatures in an environment with very little or no oxygen. This process, known as pyrolysis, drives off most non-carbon elements, leaving behind a carbon-dense char with a rudimentary pore structure.
Step 2: Activation with Heat and Gas
This is the thermal activation stage. The carbonized char is brought into a furnace or kiln and heated to the activation temperature range of 800°C to 1100°C.
An activating agent—an oxidizing gas like steam (H₂O) or carbon dioxide (CO₂)—is then introduced. This gas reacts with the carbon, effectively "gasifying" or burning away a portion of the structure in a controlled manner.
How Activation Creates a "Molecular Sponge"
The magic of activation lies in how the carbon is removed. It's a selective etching process that carves out an intricate internal structure.
The Role of Temperature and Gas
High temperature provides the necessary energy for the chemical reaction between the carbon atoms and the oxidizing gas.
The gas acts as the "chisel." For example, with steam, the reaction is primarily C + H₂O → H₂ + CO. The carbon atom is removed from the solid structure and converted into a gas.
Developing the Porous Network
This reaction doesn't happen uniformly. It preferentially attacks and removes the more disorganized and reactive carbon atoms within the char.
This process widens the existing, undeveloped pores from the carbonization step and creates a massive number of entirely new micropores. The result is a complex, three-dimensional labyrinth of pores within each carbon particle.
The Result: Immense Surface Area
The primary outcome of thermal activation is a dramatic increase in surface area. A single gram of properly activated carbon can have an internal surface area of over 1,000 square meters.
This vast surface area, composed of countless microscopic ledges and crevices, provides the sites where contaminant molecules from a liquid or gas can be trapped via adsorption.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal activation is a process of balancing competing factors. It is not simply a matter of "more is better."
Burn-off vs. Yield
The longer the activation or the more aggressive the conditions, the more pores are created. However, this also means more carbon is gasified and lost.
Operators must manage the "burn-off" percentage carefully. Over-activation increases porosity but lowers the final product yield and can weaken the carbon's physical structure, eventually turning it to ash.
Control of Pore Size
The specific activating agent and temperature directly influence the final pore size distribution.
Steam activation generally creates a wider range of pore sizes, including larger meso- and macropores. CO₂ activation tends to produce a structure dominated by smaller micropores. The choice depends entirely on the target application.
Energy Intensity
Maintaining temperatures over 800°C is extremely energy-intensive. This makes thermal activation a costly process, which is directly reflected in the price of high-performance activated carbon.
Matching the Activation to the Application
The parameters of thermal activation are tuned to produce a material optimized for a specific purification task.
- If your primary focus is removing small gas molecules (like VOCs from air): You need carbon with a high volume of micropores, often best achieved with CO₂ activation.
- If your primary focus is filtering larger color bodies from liquids: You may need a balance of meso- and macropores to allow for faster diffusion, which can be favored by steam activation.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general-purpose filtering: A moderately activated carbon that balances performance against production yield is the most practical choice.
Ultimately, thermal activation is the critical engineering step that transforms simple carbon into a high-performance material for purification.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating carbonized char (800-1100°C) with an oxidizing gas (steam/CO₂). |
| Purpose | To create a vast network of micropores for high adsorption capacity. |
| Key Outcome | Increases internal surface area to over 1,000 m² per gram. |
| Applications | Air purification (VOCs), water treatment, decolorization, and more. |
Need high-performance activated carbon tailored for your specific purification needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying premium lab equipment and consumables, including activated carbon products optimized for various applications. Our expertise ensures you get the right material for maximum efficiency—whether for gas adsorption, liquid filtration, or general-purpose use. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's purification processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C



















