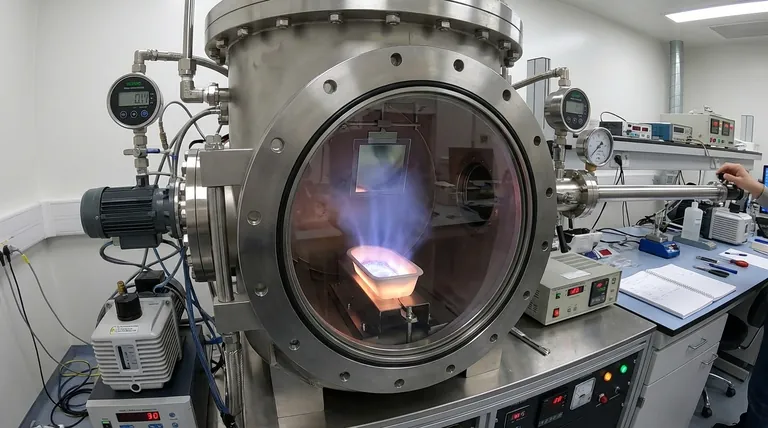
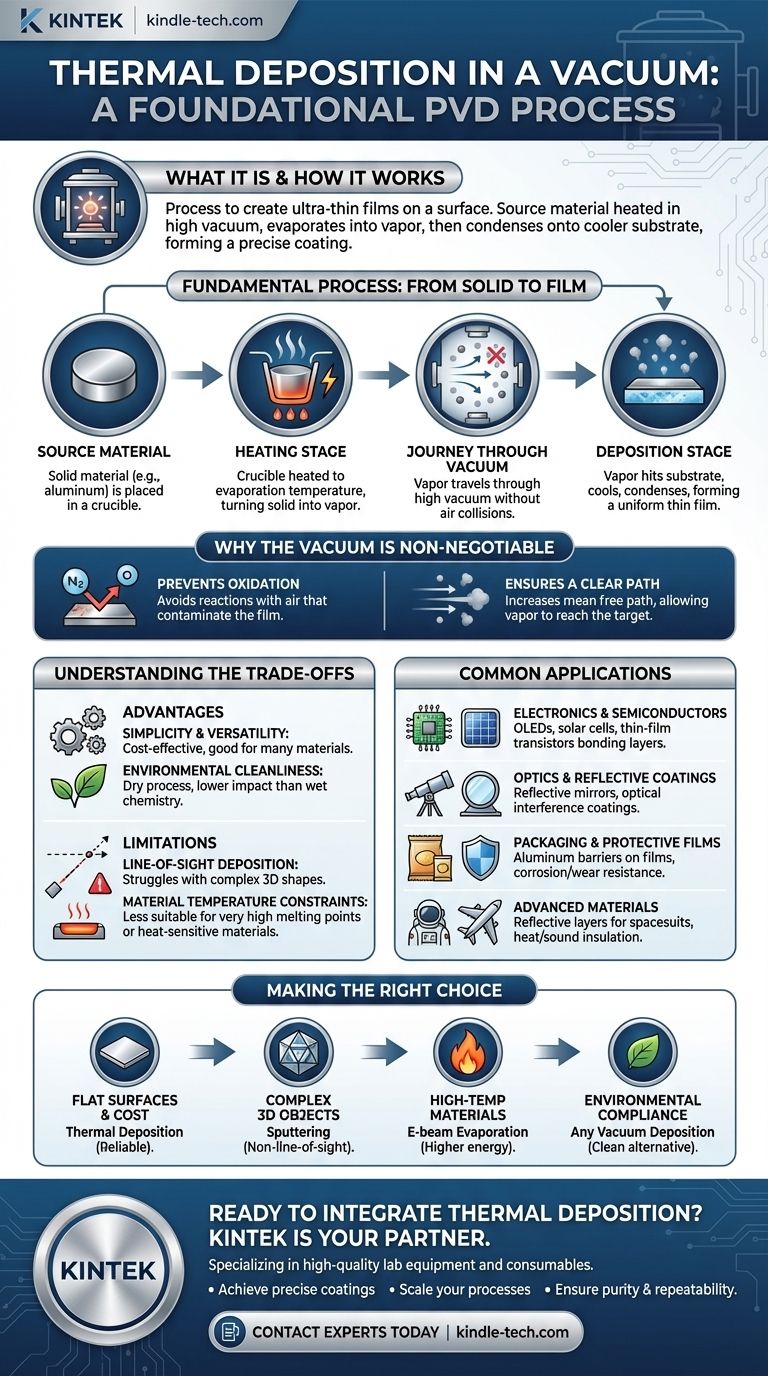
In short, thermal deposition in a vacuum is a process used to create ultra-thin films on a surface. It works by heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it evaporates into a vapor; this vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler target object, known as a substrate, forming a precise and uniform coating.
The core principle to grasp is that the vacuum is not merely an empty space—it is an active and essential component of the process. It prevents the hot material from reacting with air and clears the path for vapor molecules to travel directly to the target, which would be impossible at normal atmospheric pressure.

The Fundamental Process: From Solid to Film
Thermal deposition, a type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), is a foundational technique in materials science and manufacturing. The process can be broken down into a few key stages.
The Source Material
The process begins with the material you intend to deposit, often a metal like aluminum or gold. This source material typically starts as a solid, in forms like wire, pellets, or shot.
The Heating Stage
This solid material is placed into a holder, often a ceramic or semi-metal container called a "boat" or a "crucible." An electric current heats the boat, which in turn heats the source material to its evaporation temperature, turning it from a solid directly into a gas (vapor).
The Journey Through Vacuum
Once evaporated, a cloud of vapor forms above the source. Because this occurs in a high-vacuum environment, the vapor molecules can travel long distances in a straight line without colliding with air molecules.
The Deposition Stage
The vapor travels until it strikes the cooler substrate, which is strategically placed in its path. Upon contact, the vapor rapidly cools, condenses, and adheres to the surface, building up layer by layer to form a thin, solid film.
Why the Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
Performing this process at atmospheric pressure would fail for two critical reasons. The vacuum is not optional; it is fundamental to success.
Prevents Oxidation and Contamination
Most materials, when heated to their evaporation point, would instantly react with the oxygen and other gases present in the air. This would create oxides and other compounds, contaminating the final film and preventing the deposition of a pure material.
Ensures a Clear Path to the Target
At normal atmospheric pressure, the average distance a vapor molecule can travel before hitting an air molecule (its mean free path) is extremely short—less than a millimeter. The vapor would never reach the substrate. A vacuum increases this mean free path dramatically, allowing the vapor to travel unimpeded from the source to the target.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal deposition is not a universal solution. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: Simplicity and Versatility
Compared to other PVD methods, thermal evaporation is relatively simple and cost-effective. It works well for a wide range of materials, especially metals with lower boiling points, making it a go-to choice for many applications.
Advantage: Environmental Cleanliness
As a "dry process" that occurs entirely within a sealed chamber, vacuum deposition has a significantly lower environmental impact than "wet" chemical processes like electroplating, which often involve hazardous materials.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Deposition
The vapor travels in a straight line. This means thermal deposition is a line-of-sight process, which excels at coating flat or simple surfaces. It struggles, however, to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with hidden surfaces or sharp angles.
Limitation: Material Temperature Constraints
The process relies on heating to cause evaporation. This makes it less suitable for materials with extremely high melting points or for materials that decompose when heated. Other methods, such as electron-beam evaporation or sputtering, are often used for these more demanding materials.
Common Applications Across Industries
The ability to create precise, functional thin films makes thermal deposition a critical process in numerous fields.
Electronics and Semiconductors
It is used to create the thin metal bonding layers required in devices like OLEDs, solar cells, and thin-film transistors.
Optics and Reflective Coatings
The technique is essential for producing highly reflective mirror coatings and complex optical interference coatings that selectively filter light.
Packaging and Protective Films
A common application is depositing a thin layer of aluminum onto polymer films for food packaging. This creates a permeation barrier that protects against moisture and oxygen. It is also used for corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant coatings.
Advanced Materials
The technology is used to create reflective layers in high-performance textiles for NASA spacesuits and firefighter uniforms, as well as for heat and sound insulation in aircraft.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right deposition method depends entirely on your material, substrate, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coatings on flat surfaces: Thermal deposition is an excellent and highly reliable choice, especially for common metals like aluminum.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D objects uniformly: You should investigate non-line-of-sight methods like sputtering, which can provide more consistent coverage on intricate geometries.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-temperature or composite materials: It is wise to explore higher-energy processes like electron-beam evaporation, which can handle materials that are unsuitable for simple thermal heating.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Any vacuum deposition process is a strong candidate, offering a clean alternative to traditional chemical plating.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently determine where thermal deposition fits within your technical toolkit.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Principle | Heating a material in a vacuum to evaporate and condense it onto a substrate. |
| Key Advantage | Simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and environmental cleanliness. |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight nature; struggles with complex 3D shapes. |
| Common Applications | Electronics (OLEDs, solar cells), optical coatings, and protective packaging films. |
Ready to Integrate Thermal Deposition into Your Lab Workflow?
Understanding the theory is the first step. Implementing it effectively requires the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your vacuum deposition needs.
We provide reliable thermal evaporation systems and expert support to help you:
- Achieve precise, uniform coatings for your R&D or production.
- Scale your processes with robust and easy-to-use machinery.
- Ensure material purity and process repeatability with our trusted consumables.
Serving laboratories and material scientists worldwide, KINTEK is your partner in advanced materials processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect thermal deposition solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which features of vacuum hot pressing equipment are utilized by the dual-step vacuum hot press process? Optimize AlMgTi
- Why is a vacuum hot-pressing furnace preferred for C_fiber/Si3N4 composites? Achieve High Density & Fiber Protection
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process
- Why is a heated laboratory hydraulic press necessary for composite laminates? Achieve Void-Free Structural Integrity



















