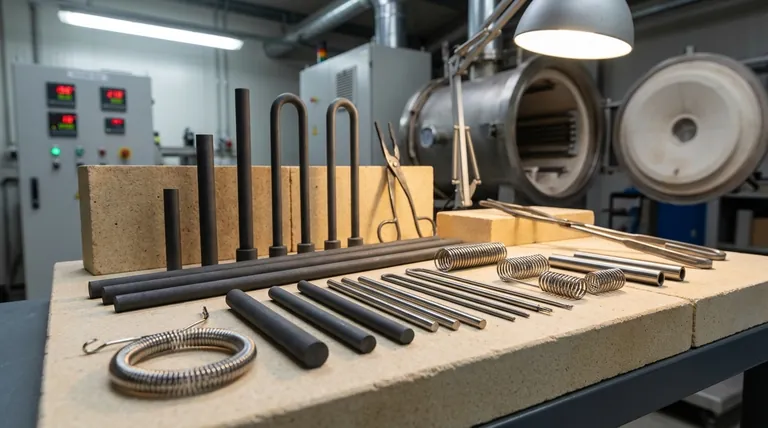
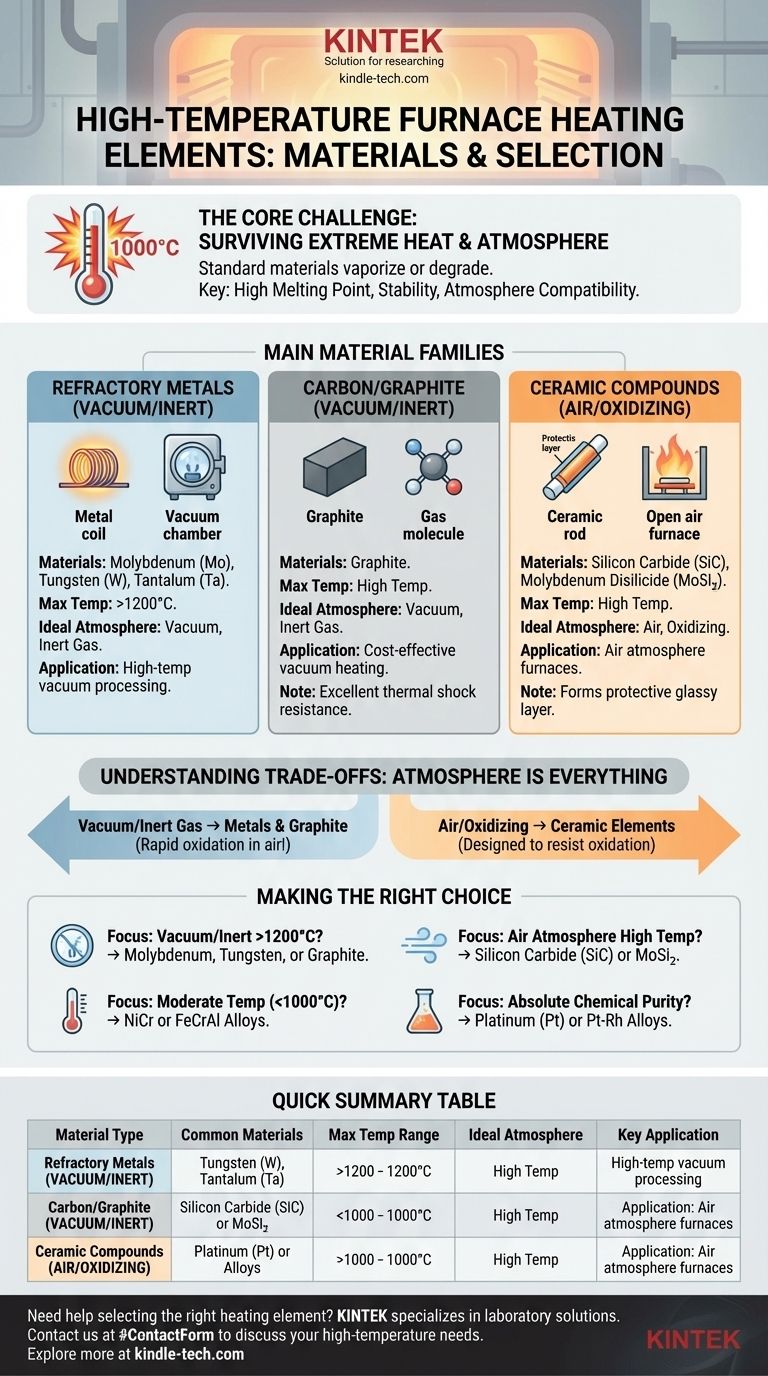
For high-temperature furnaces, the heating elements are made from a select group of materials capable of withstanding extreme conditions without melting or degrading. The most common choices are refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten, non-metallic elements like graphite, and ceramic compounds such as silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂). The specific material used is determined by the furnace's maximum operating temperature and, most importantly, its internal atmosphere.
The choice of a heating element is not just about heat resistance; it's a critical decision dictated by the furnace's operating atmosphere. Metals like molybdenum and graphite are ideal for vacuum environments, while ceramic compounds are required for furnaces that operate in air.

The Core Challenge: Surviving Extreme Heat
Standard conductor materials like copper or aluminum would instantly vaporize at the temperatures required in high-temperature industrial and laboratory processes. The goal is to find a material that not only has an exceptionally high melting point but also remains structurally stable and electrically reliable over many heating cycles.
Why Standard Materials Fail
At temperatures exceeding 1000°C, most common metals begin to soften, deform, and rapidly oxidize (or "burn") when exposed to air. This makes them completely unsuitable for generating controlled, sustained heat at these levels.
The Properties of a High-Temperature Element
A successful heating element must possess a high melting point, resistance to chemical reactions with the furnace atmosphere and the product, and good mechanical strength at high temperatures. This is why material selection is so specialized.
A Breakdown of High-Temperature Elements
High-temperature heating elements are generally divided into three main families: refractory metals, carbon/graphite, and ceramic compounds. Each has a distinct role based on its properties.
Refractory Metals: The Workhorses of Vacuum
Refractory metals are defined by their extremely high melting points. Molybdenum (Mo), tungsten (W), and tantalum (Ta) are the most common choices for high-temperature furnace elements.
These metals are excellent for applications in vacuum furnaces or environments filled with an inert gas. They provide stable and uniform heat at temperatures often exceeding 1200°C.
Carbon/Graphite: The Versatile Choice
Graphite is a popular, cost-effective material for heating elements, particularly in vacuum furnaces.
It offers several key advantages, including excellent resistance to thermal shock, high-temperature stability, and ease of machining into complex shapes. Like refractory metals, it must be used in a non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Ceramic Compounds: Masters of Air Furnaces
When a furnace must operate in an air atmosphere, metals are not an option. This is where ceramic compounds excel.
Silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) are the primary materials used. They form a protective glassy layer on their surface that prevents oxygen from destroying the element, allowing them to function effectively in open-air applications.
Precious Metals: For Specialized Applications
In certain niche applications, such as glass manufacturing or high-purity laboratory research, platinum (Pt) and its alloys with rhodium (Rh) are used. While exceptionally stable, their high cost limits their use to situations where chemical inertness is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere is Everything
The single most important factor dictating the choice between these materials is the furnace atmosphere. Using the wrong element in a given atmosphere will lead to immediate and catastrophic failure.
The Vacuum vs. Air Distinction
Refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten, along with graphite, will rapidly oxidize and disintegrate if operated at high temperatures in the presence of oxygen. They are strictly for vacuum or inert gas environments.
Conversely, ceramic elements like MoSi₂ are specifically designed to resist oxidation, making them the default choice for furnaces that heat products in an air atmosphere.
The Cost-Performance Balance
Graphite is often a cost-effective choice for vacuum applications. Refractory metals provide excellent performance but can be more expensive.
Ceramic elements carry a higher initial cost but are essential for air operation, a cost that is unavoidable for those processes. Precious metals represent the peak of both performance and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating element is fundamental to furnace design and successful operation. Your choice should be guided by your primary technical requirement.
- If your primary focus is heating in a vacuum or inert gas above 1200°C: Your best options are molybdenum, tungsten, or graphite elements.
- If your primary focus is heating in an air atmosphere at high temperatures: You must use an oxidation-resistant ceramic element like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂).
- If your primary focus is moderate-temperature heating (below 1000°C): Cost-effective alloys like nickel-chromium (NiCr) or iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) are the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical purity and avoiding contamination: You may need to invest in precious metal elements like platinum or platinum-rhodium.
Understanding these material properties and their relationship to the operating environment empowers you to design and manage a reliable high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Materials | Max Temp Range | Ideal Atmosphere | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refractory Metals | Molybdenum, Tungsten | > 1200°C | Vacuum, Inert Gas | High-temp vacuum processing |
| Carbon/Graphite | Graphite | High Temp | Vacuum, Inert Gas | Cost-effective vacuum heating |
| Ceramic Compounds | SiC, MoSi₂ | High Temp | Air, Oxidizing | Air atmosphere furnaces |
| Precious Metals | Platinum, Pt-Rh Alloys | Moderate-High | Various | High-purity, specialized labs |
Need help selecting the right heating element for your high-temperature furnace?
At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to match the perfect heating element to your specific temperature requirements and furnace atmosphere. Whether you need refractory metals for vacuum applications or ceramic elements for air atmospheres, our team ensures optimal performance and longevity for your lab processes.
Contact us today at #ContactForm to discuss your high-temperature heating needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application



















