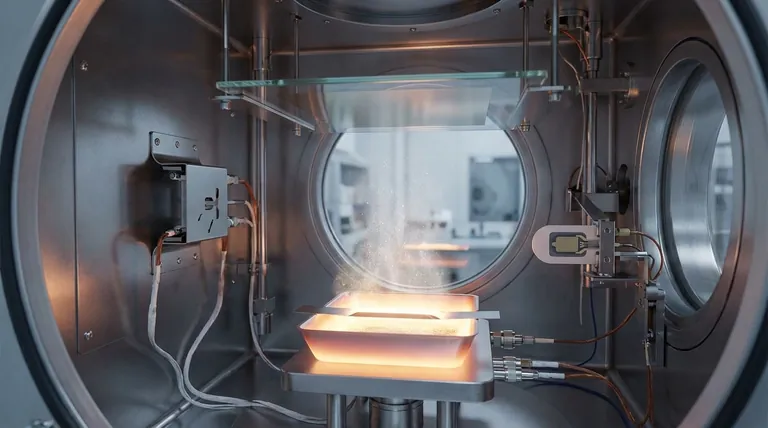
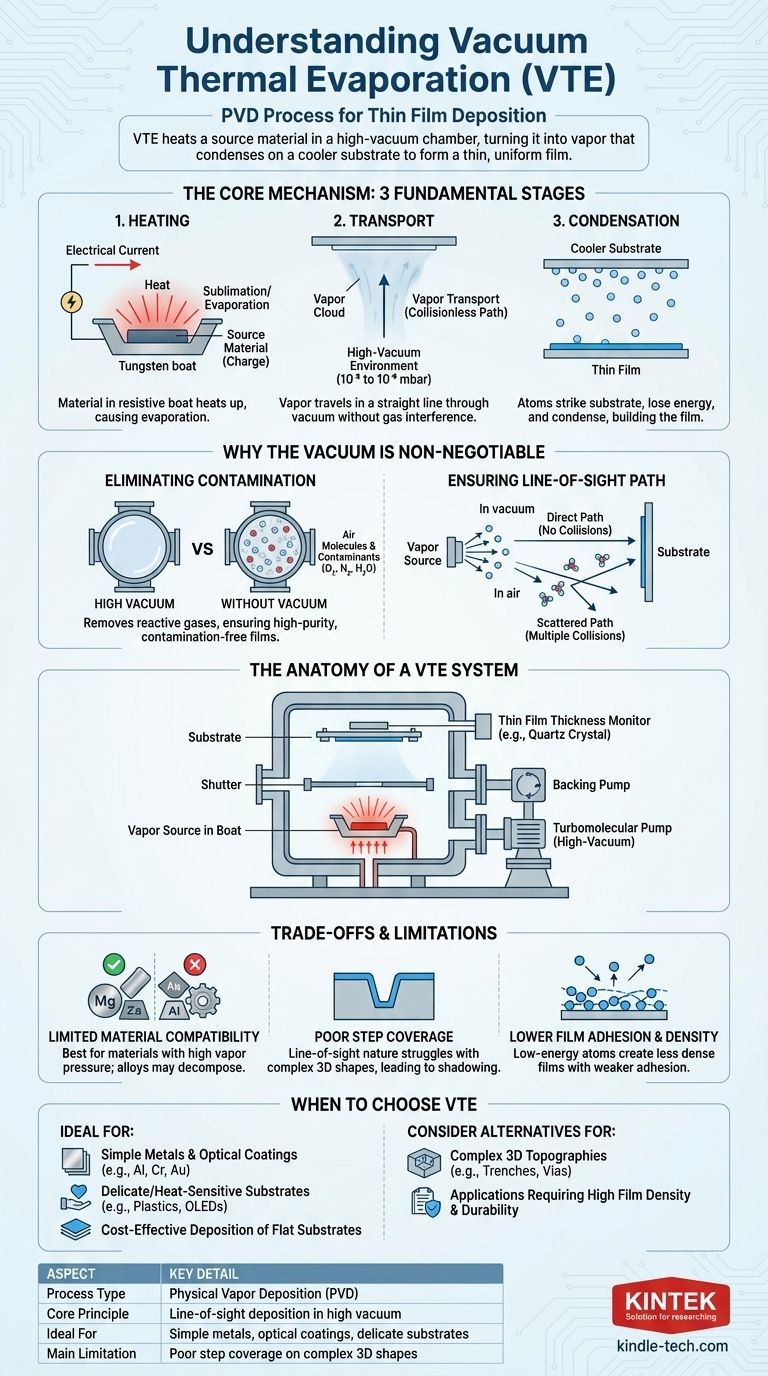
At its core, Vacuum Thermal Evaporation (VTE) is a coating process where a source material is heated inside a high-vacuum chamber until it vaporizes. Also known as resistance evaporation, this method is a type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The resulting vapor travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, to form an exceptionally thin and uniform film.
The defining characteristic of VTE is its reliance on a high-vacuum environment. This vacuum is not just an afterthought; it is the critical element that eliminates contaminants and allows vaporized atoms to travel a direct, unimpeded path to the substrate, ensuring a high-purity coating.

The Core Mechanism: From Solid to Thin Film
To understand VTE, it's best to break it down into its three fundamental stages: heating, transport, and condensation.
The Source Material and Heating Method
The process begins with a solid source material, often called the "charge." This material is placed into an electrically resistive container, such as a crucible or a "boat," typically made from a material with a much higher melting point, like tungsten or molybdenum.
An electrical current is passed through this container, causing it to heat up rapidly due to its resistance. This heat is transferred to the source material, raising its temperature until it begins to sublimate or evaporate.
Evaporation and Vapor Transport
As the source material reaches its evaporation point, it transitions into a gaseous state, creating a vapor cloud within the chamber.
Because the chamber is held at a high vacuum (from 10⁻⁵ down to 10⁻⁹ millibar), there are very few air or other gas molecules present. This creates a long "mean free path," allowing the evaporated atoms to travel in a straight line without colliding with other particles.
Condensation on the Substrate
This stream of vaporized atoms travels until it strikes a cooler surface—the substrate—which is strategically placed above the source.
Upon contact with the cooler substrate, the atoms rapidly lose their thermal energy and condense back into a solid state. This slow, atom-by-atom accumulation builds the desired thin film on the substrate's surface.
Why the Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
The quality and integrity of the final film are entirely dependent on the quality of the vacuum. The vacuum serves two primary, indispensable purposes.
Eliminating Film Contamination
Atmospheric air contains reactive gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. If present during deposition, these gases would react with the hot vapor atoms and become incorporated into the film, creating impurities that degrade its electrical, optical, or mechanical properties.
A high vacuum removes these potential contaminants, ensuring the deposited film is composed almost purely of the intended source material.
Ensuring a "Line-of-Sight" Path
The vacuum enables what is known as collisionless transport. Without a vacuum, evaporated atoms would constantly collide with air molecules, scattering them in random directions and preventing them from ever reaching the substrate efficiently.
By removing these obstacles, the vacuum ensures the vapor travels in a direct "line of sight" from the source to the substrate. This principle is key to achieving a uniform and predictable coating.
The Anatomy of a VTE System
A typical VTE system integrates several key components to achieve this controlled process.
The Vacuum Chamber and Pumps
The entire process occurs within a sealed chamber. A series of pumps work to create the high-vacuum environment. First, a backing pump (like a rotary vane or dry scroll pump) removes the bulk of the air.
Then, a high-vacuum pump, typically a turbomolecular pump, takes over to reduce the pressure to the required low levels, often in the 300–1000 l/s range.
Process Control Components
To manage the deposition, a shutter is placed between the source and substrate. This allows the source to be brought to a stable evaporation rate before the shutter is opened to begin coating, ensuring process stability.
A thin film thickness monitor, often a quartz crystal microbalance, is used to measure the film thickness in real-time. It provides the precise feedback needed to stop the deposition once the target thickness is reached.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, VTE is not the solution for every application. Its "line-of-sight" nature creates clear trade-offs.
Limited Material Compatibility
VTE works best with materials that have a reasonably high vapor pressure and that evaporate without decomposing. Some alloys can be difficult to deposit because their constituent elements evaporate at different rates, changing the film's composition.
Poor Step Coverage
Because atoms travel in straight lines, VTE is poor at coating complex, 3D shapes with high aspect ratios like trenches or vias. The top surfaces receive a thick coating, but the sidewalls and bottom corners receive very little material, a phenomenon known as shadowing.
Lower Film Adhesion and Density
Compared to higher-energy processes like sputtering, the atoms in VTE arrive at the substrate with relatively low kinetic energy. This can result in films that are less dense and have weaker adhesion to the substrate, which may be unsuitable for applications requiring high durability.
When to Choose Vacuum Thermal Evaporation
Based on its principles and limitations, VTE is the ideal choice for specific applications where its advantages shine.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of simple metals or optical coatings: VTE is excellent for depositing materials like aluminum, chromium, gold, or anti-reflection coatings onto relatively flat substrates due to its simplicity and high deposition rates.
- If your primary focus is coating delicate or heat-sensitive substrates: The low energy of the depositing atoms makes VTE suitable for coating plastics, organic electronics (OLEDs), or other materials that could be damaged by higher-energy deposition techniques.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D topographies: You should strongly consider alternative methods like sputtering or Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), as VTE's line-of-sight nature results in poor, non-conformal coverage.
Ultimately, mastering VTE is about leveraging its power to create exceptionally pure films in a simple, highly controlled, line-of-sight process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Principle | Line-of-sight deposition in a high vacuum |
| Ideal For | Simple metals (Al, Au, Cr), optical coatings, delicate substrates |
| Main Limitation | Poor step coverage on complex 3D shapes |
Ready to achieve high-purity thin films for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for your vacuum deposition needs. Whether you're working on optical coatings, electronics, or delicate materials, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for precise, contamination-free results.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's thin film projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition



















