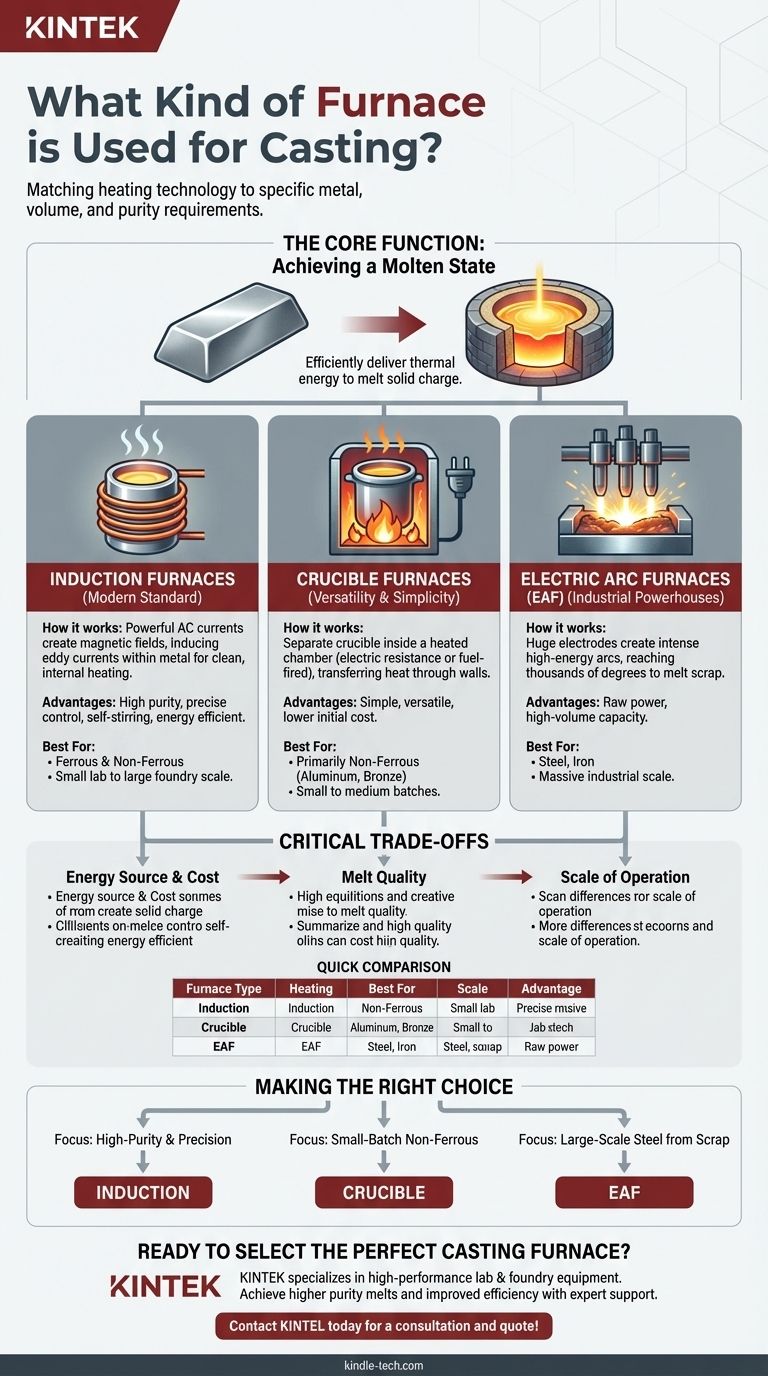
In metal casting, the furnace you use is defined by its heating method, with the most common and important types being induction, crucible (or resistance), and electric arc furnaces. While other specialized furnaces exist, these three designs cover the vast majority of applications, from small-scale artisanal work to massive industrial foundries.
The selection of a casting furnace is not about finding a single "best" type, but about matching the furnace's heating technology—be it induction, resistance, or electric arc—to the specific metal, production volume, and purity requirements of your operation.

The Core Function: How Casting Furnaces Work
Before comparing specific types, it's crucial to understand the fundamental purpose of any casting furnace. Its job is to efficiently and safely deliver enough thermal energy to a solid metal charge to raise its temperature beyond its melting point.
The Primary Goal: Achieving a Molten State
The entire process hinges on turning solid metal (ingots, scrap, etc.) into a liquid that can be poured into a mold. The furnace's efficiency, speed, and ability to control the final temperature of this molten metal are its most critical performance metrics.
Containing the Metal: The Crucible and Refractory Lining
Molten metal is highly reactive and incredibly hot. The furnace must contain it in a vessel that can withstand these conditions without failing or contaminating the melt. This is typically a crucible (a removable pot, often made of ceramic or graphite) or a furnace body lined with a durable refractory material like alumina or magnesia.
Key Types of Furnaces for Metal Casting
The primary differences between furnace types lie in how they generate and transfer heat to the metal charge.
Induction Furnaces: The Modern Standard
An induction furnace uses powerful alternating electric currents to create a strong magnetic field around the metal. This field "induces" eddy currents within the metal itself, causing it to heat up rapidly from the inside out due to its own electrical resistance.
This method is extremely clean as there is no direct contact between the heating element and the metal. The electromagnetic forces also create a natural stirring action, which ensures a uniform temperature and alloy composition in the melt.
Crucible Furnaces: Versatility and Simplicity
A crucible furnace is a simpler design where a separate crucible containing the metal is placed inside an insulated chamber. The chamber is then heated from the outside, and that heat is transferred through the crucible wall to the metal.
The heat source can vary. Electric resistance furnaces use heating elements similar to an electric oven, while fuel-fired furnaces use natural gas or oil burners. They are very common for smaller foundries and for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum and bronze.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF): Industrial Powerhouses
For melting massive quantities of iron and steel, the Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is dominant. These furnaces use huge graphite electrodes to create an incredibly high-energy electric arc that strikes the metal charge.
The intense heat of the arc—reaching thousands of degrees—rapidly melts scrap steel and other ferrous materials. EAFs are the cornerstone of modern "mini-mills" that specialize in recycling scrap metal into new steel products.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing four key factors: cost, quality, scale, and the specific metal you intend to melt.
Energy Source and Cost
Fuel-fired crucible furnaces often have a lower initial equipment cost but may have higher ongoing energy and maintenance costs. Induction and arc furnaces are entirely electric, and their operational cost is tied directly to electricity prices, but they are generally more energy-efficient.
Melt Quality and Contamination
Induction furnaces produce the highest quality, purest melts because the heating process is non-contact. Fuel-fired furnaces can introduce impurities from the combustion process into the melt, which may be unacceptable for certain high-specification alloys.
Scale of Operation
Crucible furnaces are ideal for small to medium batches, from a few kilograms to a few hundred. Induction furnaces scale well from small laboratory units to large foundry systems melting many tons. EAFs operate only at a massive industrial scale, often melting over 100 tons at a time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be aligned with the primary goal of your casting operation.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melts and precise temperature control: An induction furnace is the superior choice due to its clean, efficient, and self-stirring nature.
- If your primary focus is small-batch or non-ferrous casting (e.g., aluminum, brass): A crucible furnace, either electric resistance or gas-fired, offers the best balance of simplicity, cost, and versatility.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production from scrap: The Electric Arc Furnace is the undisputed industry standard for its raw power and high-volume capacity.
Understanding these fundamental differences in heating technology is the key to selecting the right furnace for any casting operation.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Heating Method | Best For Metals | Ideal Scale | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | Electromagnetic induction | Ferrous & Non-Ferrous | Small lab to large foundry | High purity, precise control, self-stirring |
| Crucible Furnace | External resistance or fuel-fired | Primarily Non-Ferrous (e.g., Aluminum, Bronze) | Small to medium batches | Simplicity, versatility, lower initial cost |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | High-energy electric arc | Steel, Iron | Massive industrial scale | High-volume scrap melting, raw power |
Ready to Select the Perfect Casting Furnace?
Choosing the right furnace technology is critical to the success of your casting operation. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab and foundry equipment, including crucible and induction furnaces tailored to your specific metal, purity, and production requirements.
We help you achieve:
- Higher Purity Melts: Our induction furnaces ensure clean, non-contact heating for superior metal quality.
- Improved Efficiency: Find the right balance of energy use, cost, and throughput for your scale.
- Expert Support: Get guidance on the best furnace type for your application, from R&D to full-scale production.
Let's discuss your project. Whether you're melting aluminum, brass, or high-specification alloys, we have the solution.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is the physical description of a tube furnace? A Detailed Breakdown of its High-Temperature Design
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















