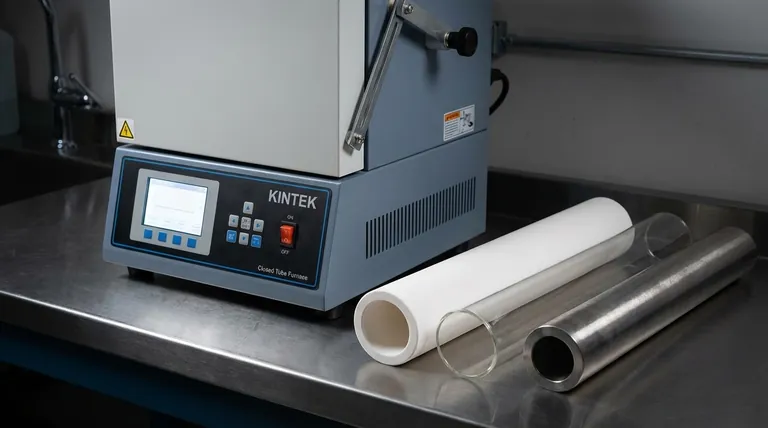
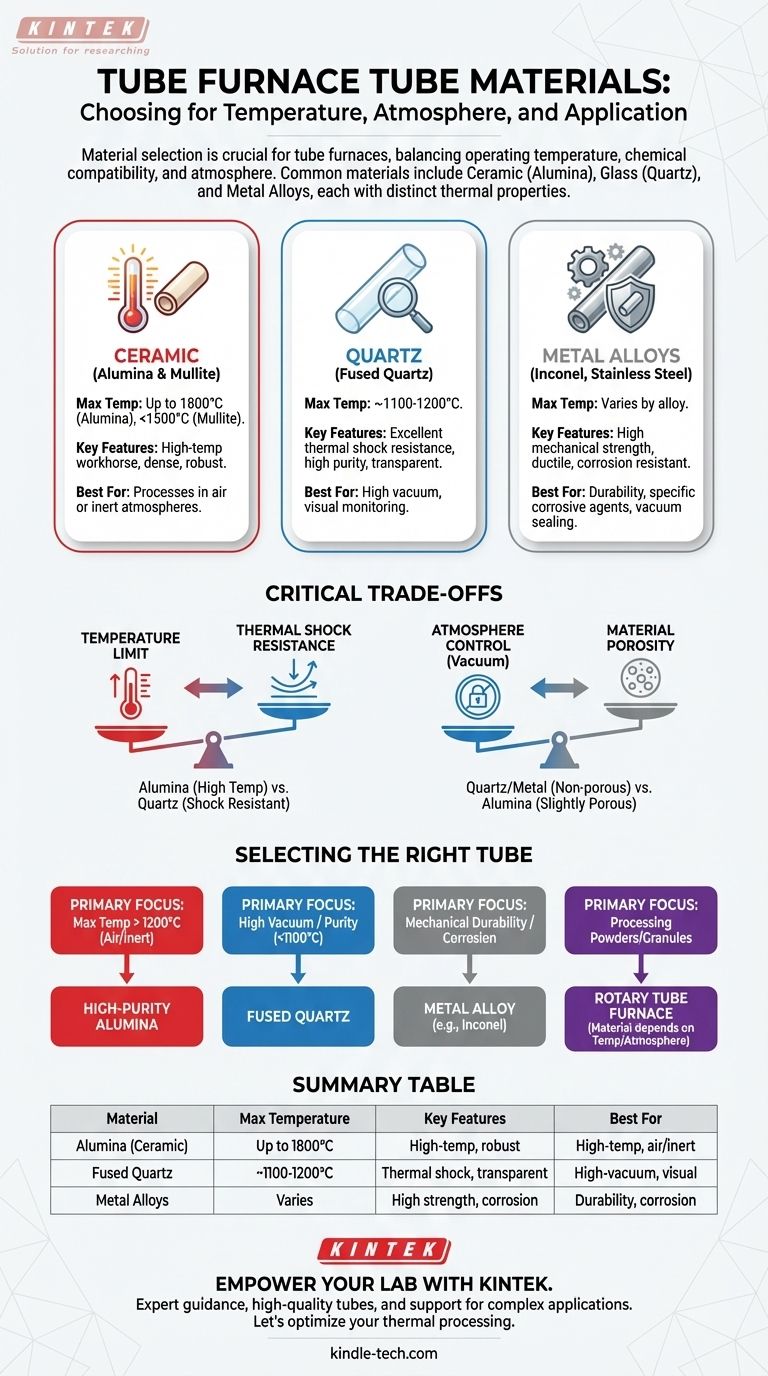
The material used for a tube furnace tube is selected based on its required operating temperature, chemical compatibility with the sample, and the type of atmosphere used during processing. The most common materials are high-purity alumina (a ceramic), fused quartz (a type of glass), and various metal alloys like stainless steel or Inconel. Each material offers a distinct set of properties tailored to specific thermal applications.
The choice of a tube furnace material is not about finding the single "best" option, but about making a strategic trade-off. You must align the material's properties—primarily its temperature limit, thermal shock resistance, and chemical inertness—with the precise demands of your process.

Matching the Material to the Application
A furnace tube is not a one-size-fits-all component. It is the core environment where your process occurs, and selecting the correct material is fundamental to achieving accurate and repeatable results. The decision rests on three primary factors: temperature, atmosphere, and the nature of the material being processed.
Ceramic Tubes (Alumina & Mullite)
High-purity alumina is the workhorse for high-temperature applications, often capable of withstanding temperatures up to 1700°C or even 1800°C. It is a dense, robust ceramic ideal for processing in air or inert atmospheres.
Mullite is another ceramic material, often used as a more cost-effective alternative to alumina for lower-temperature applications, typically below 1500°C.
Quartz Tubes (Fused Quartz)
Fused quartz is a form of high-purity glass known for its excellent thermal shock resistance and high purity. It is the standard choice for processes requiring a high vacuum, as its non-porous surface allows for a reliable seal.
Because it is transparent, a quartz tube also allows for direct visual observation of the sample during heating, which can be critical for process development and monitoring. However, its maximum service temperature is significantly lower than alumina, typically around 1100-1200°C.
Metal Alloy Tubes (Inconel, Stainless Steel, etc.)
Metal alloy tubes are valued for their mechanical strength and ductility, making them highly resistant to physical breakage. Alloys like Inconel are designed for high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance.
Tubes made from stainless steel are often used in vacuum systems where robust seals are paramount. For highly corrosive materials or specific vacuum sintering processes, specialized tubes made of heat-resistant alloys like tungsten or molybdenum may be required.
Specialized Furnace Configurations
It's important to note that the tube's function can also influence its design. For example, rotary tube furnaces are used to process powders or granular materials.
These furnaces use a rotating tube to ensure uniform heating, and the tube itself can be made from ceramic, quartz, or a metal alloy, depending on the process requirements.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing a material always involves balancing competing properties. Understanding these trade-offs is key to avoiding failed experiments and damaged equipment.
Temperature Limit vs. Thermal Shock Resistance
Alumina offers the highest temperature ceiling but is brittle and susceptible to thermal shock. Heating or cooling it too quickly can cause it to crack.
Quartz, conversely, has exceptional resistance to thermal shock but cannot be used at the extreme temperatures that alumina can withstand.
Atmosphere Control vs. Material Porosity
Achieving a high vacuum requires a tube material that is non-porous. Quartz and metal alloys are excellent for this, as they can be sealed effectively.
Ceramic tubes like alumina are slightly porous at a microscopic level, which makes them less suitable for high-vacuum applications without specialized glazing or system designs.
Chemical Compatibility vs. Contamination
The tube material must be inert to your sample and any process gases. Quartz offers very high purity, but certain materials (like alkali metals) can react with it at high temperatures.
For some applications, metal alloy tubes may be fitted with non-metallic inner liners to prevent volatiles from the sample from interacting with the metal, ensuring process purity and safety.
Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
Your choice should be a direct reflection of your primary process goal. A clear understanding of your priorities will lead you to the correct material.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature (above 1200°C) in air or an inert atmosphere: A high-purity alumina ceramic tube is the standard and most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is a high-vacuum environment or high sample purity below 1100°C: A fused quartz tube provides the necessary seal integrity and low contamination.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability or resistance to specific corrosive agents: A metal alloy tube, such as Inconel or stainless steel, offers the best performance.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granules uniformly: A rotary tube furnace is the correct equipment, and the tube material within it should be selected based on the temperature and atmosphere requirements above.
By matching the tube's properties to your specific goal, you empower your process for success.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Ceramic) | Up to 1800°C | High-temperature workhorse, robust | High-temp processes in air/inert atmospheres |
| Fused Quartz | ~1100-1200°C | Excellent thermal shock, high purity, transparent | High-vacuum environments, visual monitoring |
| Metal Alloys (e.g., Inconel) | Varies by alloy | High mechanical strength, corrosion resistant | Applications requiring durability & specific corrosion resistance |
Empower Your Lab with the Right Tube Furnace Solution
Selecting the correct tube material is critical for the success and safety of your thermal processes. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of tube furnace tubes tailored to your specific temperature, atmosphere, and application requirements.
We provide:
- Expert guidance to match the perfect tube material to your process.
- High-purity alumina, fused quartz, and metal alloy tubes from trusted manufacturers.
- Support for complex applications, including high-vacuum and corrosive environments.
Let's optimize your thermal processing together.
Contact our experts today to discuss your needs and ensure you have the right tube for precise, reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material



















