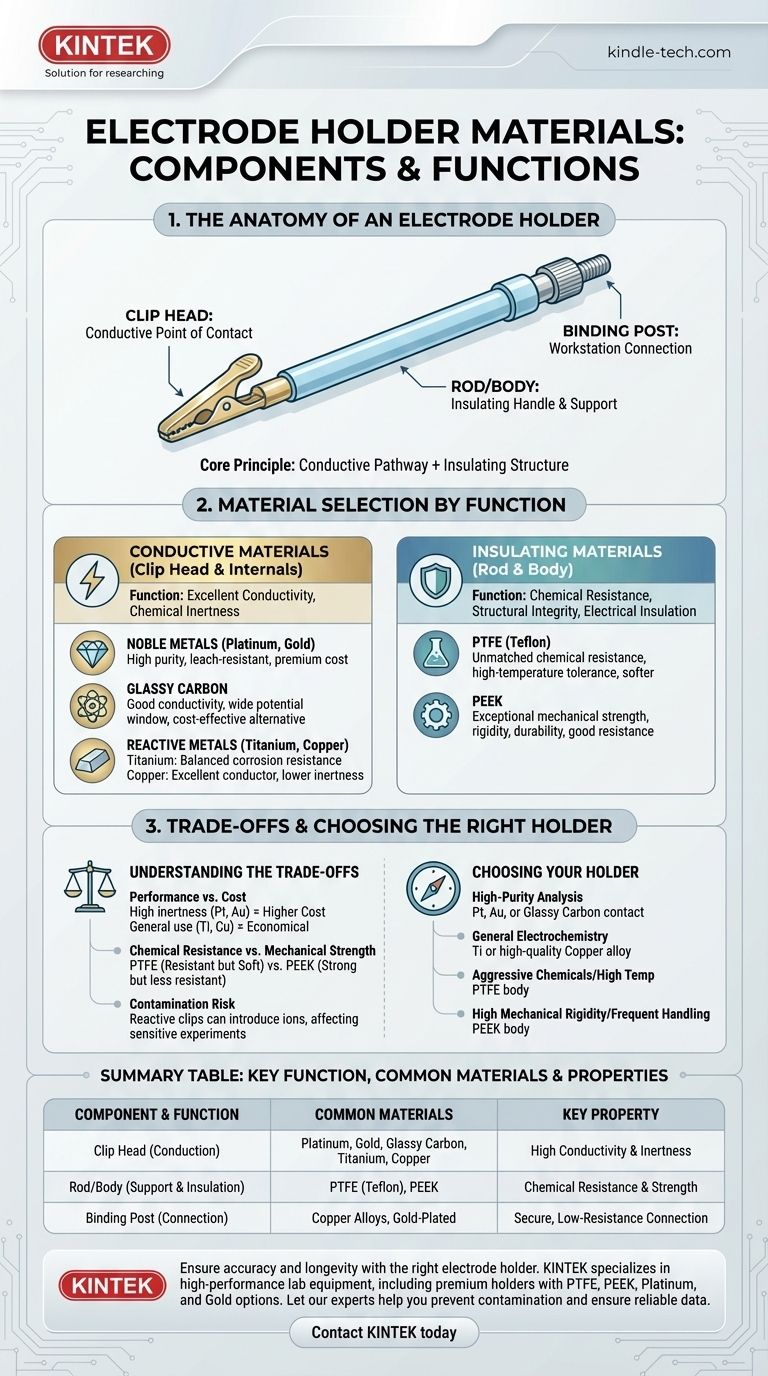
The materials for an electrode holder are specifically chosen to match the distinct function of each part, balancing electrical conductivity with chemical inertness and structural integrity. The conductive contact points are typically made from materials like platinum, gold, glassy carbon, titanium, or copper, while the main body or rod is almost always a chemically resistant polymer such as PTFE or PEEK.
The core principle behind an electrode holder's design is a strategic separation of duties: using highly conductive and chemically inert materials for the electrical pathway, while employing durable, insulating polymers for the structural body to ensure safety, stability, and experimental integrity.

The Anatomy of an Electrode Holder
An electrode holder's primary job is to securely grip a sample (the working electrode) and provide a stable, reliable electrical connection to an electrochemical workstation. This requires a few key components working in concert.
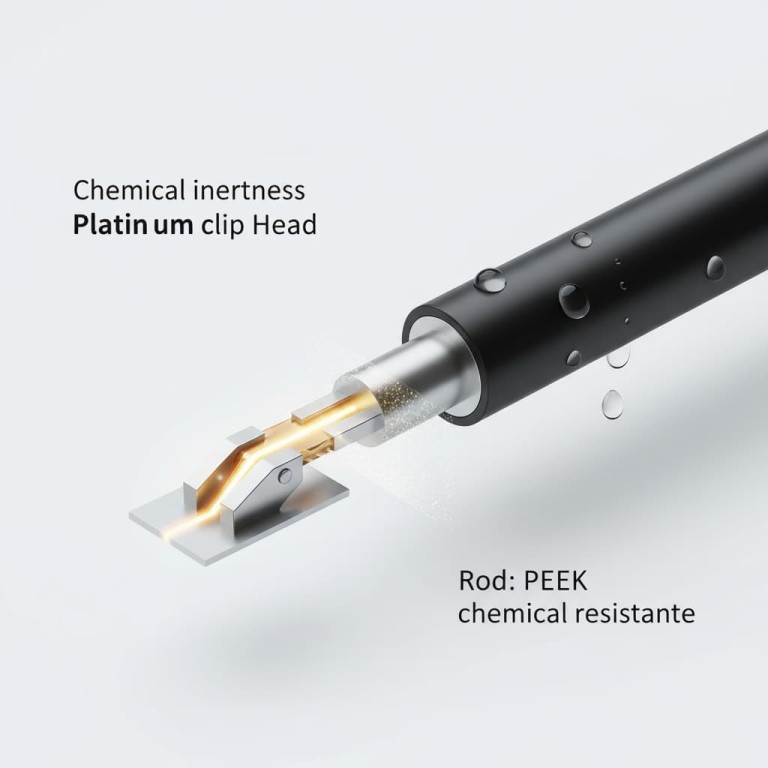
The Clip Head: The Point of Contact
The clip head is the business end of the holder. Its purpose is to physically clamp the sample and transfer the electrical signal with minimal interference or signal loss.
The Rod or Body: The Insulating Handle
The rod forms the main body of the holder. It must be a robust electrical insulator to protect the operator and prevent short circuits. It also provides the structural frame and a handle for manipulation.
The Binding Post: The Workstation Connection
This is the terminal at the opposite end of the holder. It allows for a secure connection to the cables leading to the potentiostat or electrochemical workstation, completing the circuit.
Material Selection by Component Function
The choice of material for each part is not arbitrary; it is dictated entirely by its role. The design requires a perfect marriage of conductive and insulating properties.
Conductive Materials (The Clip Head & Internals)
The material that touches your sample is critical, as it must be an excellent conductor without reacting with your electrolyte or contaminating your experiment.
- Noble Metals (Platinum, Gold): These are the premium choices. They offer excellent conductivity and are highly inert, meaning they are unlikely to corrode or leach ions into your solution, ensuring data purity.
- Glassy Carbon: This material provides good conductivity and is chemically inert across a wide potential window, often serving as a cost-effective alternative to platinum or gold.
- Reactive/Base Metals (Titanium, Copper): Copper is an exceptional conductor and is often used for internal wiring and less critical components due to its low cost. Titanium offers a good balance of conductivity and corrosion resistance, superior to copper but less inert than gold or platinum.
Insulating Materials (The Rod & Body)
The body must be chemically resistant to spills and fumes while providing strong mechanical support and electrical insulation.
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): Commonly known by the trade name Teflon, PTFE offers unmatched chemical resistance to nearly all acids, bases, and solvents. It also has a high-temperature tolerance, making it a standard for harsh lab environments.
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK): PEEK is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional mechanical strength, rigidity, and hardness. While its chemical resistance is excellent, it is chosen over PTFE in applications where greater structural integrity and wear resistance are required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an electrode holder involves balancing performance requirements with practical constraints. There is no single "best" material for all situations.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between chemical inertness and cost. A gold or platinum-tipped holder provides the highest data integrity for sensitive experiments but comes at a significant price premium. For general applications, a titanium or copper-based holder is far more economical.
Chemical Resistance vs. Mechanical Strength
The two most common body materials, PTFE and PEEK, present a clear trade-off. PTFE is the champion of chemical resistance but is a relatively soft material. PEEK provides far greater mechanical strength and rigidity but may not be suitable for the most extremely corrosive chemical environments.
The Risk of Contamination
The material of the conductive clip can directly influence your results. Using a copper clip in a sensitive corrosion study, for instance, could introduce copper ions into the electrolyte, creating experimental artifacts and invalidating the data.
Choosing the Right Holder for Your Application
Your experimental goal should always guide your material selection.
- If your primary focus is high-purity electroanalysis: Choose a holder with a platinum, gold, or glassy carbon contact to eliminate the risk of sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is general electrochemistry in non-corrosive solutions: A holder with a titanium or high-quality copper alloy contact is often a cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If you are working with highly aggressive chemicals or at high temperatures: Ensure the holder body is made from PTFE for maximum chemical stability.
- If your application requires high mechanical rigidity or involves frequent handling: A holder with a PEEK body will provide superior durability and a longer service life.
Ultimately, selecting the correct materials is fundamental to ensuring the accuracy of your results and the longevity of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials | Key Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clip Head / Contact | Electrical conduction to sample | Platinum, Gold, Glassy Carbon, Titanium, Copper | High Conductivity & Chemical Inertness |
| Rod / Body | Structural support & electrical insulation | PTFE (Teflon), PEEK | Chemical Resistance & Mechanical Strength |
| Binding Post | Connection to workstation | Copper Alloys, Gold-Plated | Secure, Low-Resistance Connection |
Ensure the accuracy and longevity of your electrochemical experiments with the right electrode holder. The materials you choose are critical to your results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including electrode holders with premium contacts (platinum, gold) and durable polymer bodies (PTFE, PEEK) tailored for your specific application—from high-purity analysis to demanding industrial environments. Let our experts help you select the perfect holder to prevent contamination and ensure reliable data. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Sample Support Body for Electrochemical Tests
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is a flat cell for corrosion testing? Achieve Non-Destructive, In-Situ Analysis
- How should the PTFE electrode stand be adjusted to fit the electrolytic cell? Ensure Maximum Stability for Your Experiments
- How should an electrode holder be cleaned as part of regular maintenance? Ensure Reliable Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the steps for post-experiment procedures after using the cell with a conventional aqueous solution? Ensure Accuracy and Reproducibility
- How can auxiliary equipment be installed on the PTFE electrode stand? Ensure Stable & Interference-Free Setup



















