In high-temperature brazing, an exceptionally wide range of materials can be successfully joined, including advanced superalloys, refractory metals, and even ceramics. The process is not limited by the base materials themselves, but rather by the ability of a filler metal (the braze alloy) to "wet" and bond to their surfaces in a controlled, oxide-free environment.
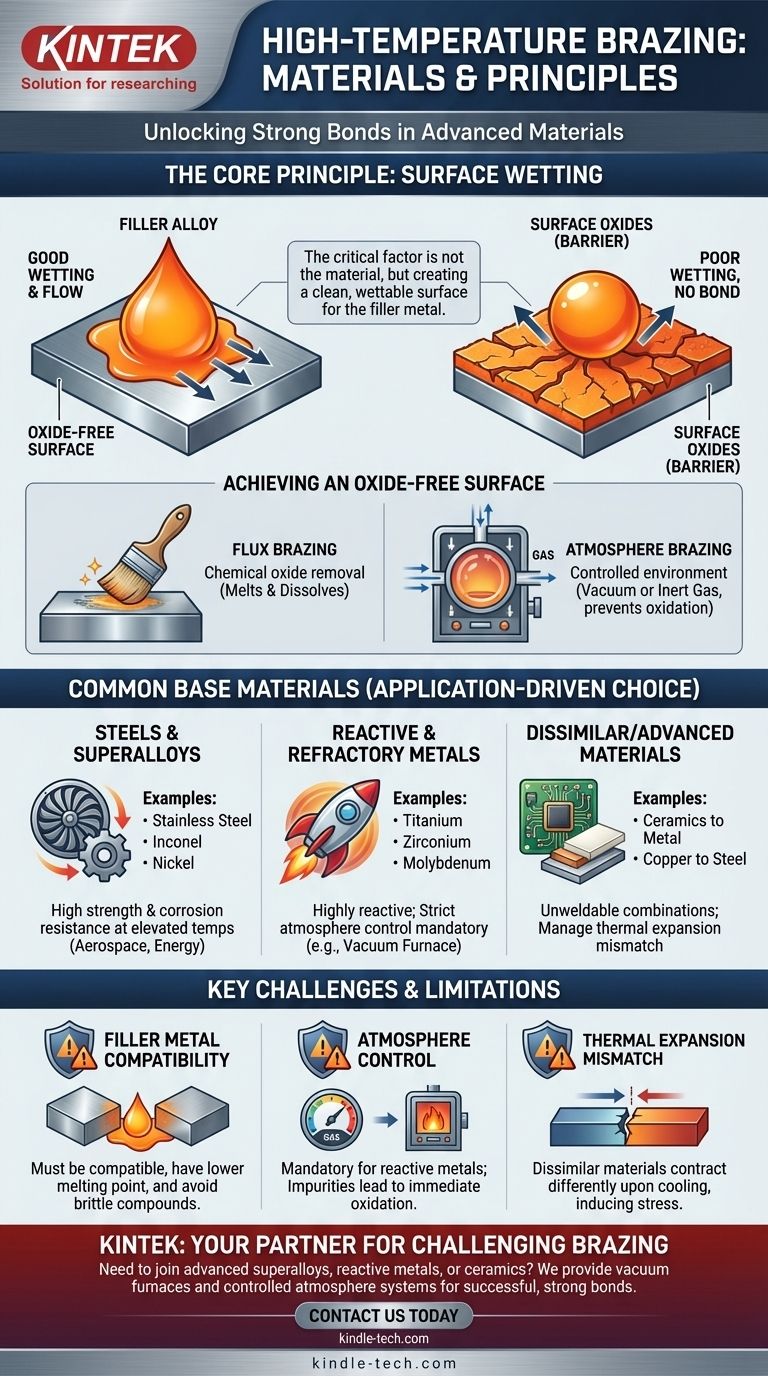
The critical factor for successful high-temperature brazing is not the specific material being joined, but the creation of an oxide-free surface that allows the molten filler alloy to form a strong, metallurgical bond.

The Guiding Principle: Surface Wetting
The entire brazing process is governed by a single, fundamental concept: wetting. Understanding this is key to selecting and preparing materials.
What is "Wetting"?
Wetting is the ability of the liquid braze alloy to flow over and adhere to the surfaces of the base materials. A successful braze requires excellent wetting to ensure the filler metal is drawn into the joint via capillary action, creating a continuous, strong bond upon cooling.
The Obstacle: Surface Oxides
Nearly all metals form a thin layer of oxide on their surface when exposed to air. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the molten filler alloy from making direct contact with the base metal, thus inhibiting wetting and blocking the formation of a bond.
Achieving an Oxide-Free Surface
The primary challenge in brazing is removing this oxide layer and preventing it from re-forming. This is typically accomplished in two ways:
- Flux Brazing: A chemical compound called flux is applied to the joint. When heated, the flux melts and dissolves the oxides, protecting the surface until the braze alloy flows.
- Atmosphere Brazing: The process is conducted inside a furnace with a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum or inert gas. This environment either removes the oxygen (preventing oxidation) or contains active elements that reduce existing oxides.
Common Base Materials for High-Temperature Applications
High-temperature brazing is essential for joining materials that must perform in demanding environments. The choice of material is driven entirely by the final application's requirements.
Steels and Nickel-Based Superalloys
Materials like stainless steel, alloy steels, nickel, and Inconel are frequently brazed for high-performance applications in aerospace and energy. Their inherent strength and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures make them ideal candidates for this joining method.
Reactive and Refractory Metals
Brazing is often the preferred method for joining titanium, zirconium, niobium, and molybdenum. These materials are highly reactive with oxygen at high temperatures, making controlled-atmosphere furnace brazing the only viable option to ensure a clean, strong joint.
Advanced and Dissimilar Materials
One of the greatest strengths of brazing is its ability to join materials that cannot be welded. This includes joining metals to ceramics, or joining metals with vastly different melting points, like copper to steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, high-temperature brazing requires careful engineering consideration to avoid potential failures.
Filler Metal Compatibility
The chosen braze alloy is as critical as the base materials. It must have a melting point lower than the base materials but be capable of withstanding the final service conditions. Its chemistry must also be compatible to ensure a proper metallurgical bond without creating brittle intermetallic compounds.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
For reactive metals like titanium or superalloys containing aluminum, atmosphere control is not optional—it is mandatory. An inadequate vacuum or impure inert gas will result in a failed joint due to the immediate formation of oxides at brazing temperatures.
Thermal Expansion Mismatch
When joining dissimilar materials, such as a metal to a ceramic, their different rates of thermal expansion must be managed. As the assembly cools from the brazing temperature, mismatched contraction rates can induce stress, potentially cracking the joint or the materials themselves.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct materials and process is a matter of aligning them with your primary engineering objective.
- If your primary focus is structural strength at high temperatures: Nickel-based superalloys (like Inconel) and high-strength stainless steels are your best candidates, typically joined in a vacuum furnace.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (like steel to ceramic): Brazing is an ideal choice, but you must carefully design the joint and select a ductile filler metal to accommodate thermal expansion stresses.
- If your primary focus is lightweighting with reactive metals: Titanium and aluminum alloys can be reliably joined with brazing, but this requires an impeccably clean process and a tightly controlled furnace atmosphere.
Ultimately, successful high-temperature brazing depends on a holistic understanding of the base materials, the filler alloy, and the precise control of the processing environment.
Summary Table:
| Base Material Category | Common Examples | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Steels & Superalloys | Stainless Steel, Inconel, Nickel | High strength & corrosion resistance at temperature. |
| Reactive & Refractory Metals | Titanium, Zirconium, Molybdenum | Requires strict atmosphere control (e.g., vacuum). |
| Dissimilar/Advanced Materials | Ceramics, Copper to Steel | Ideal for unweldable combinations; manage thermal stress. |
Need to braze challenging materials for a high-performance application? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support needed for successful high-temperature brazing. Our vacuum furnaces and controlled atmosphere systems are designed to meet the stringent requirements for joining superalloys, reactive metals, and ceramics. Let our team help you achieve strong, reliable bonds for your most demanding projects.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific brazing needs and explore our solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















