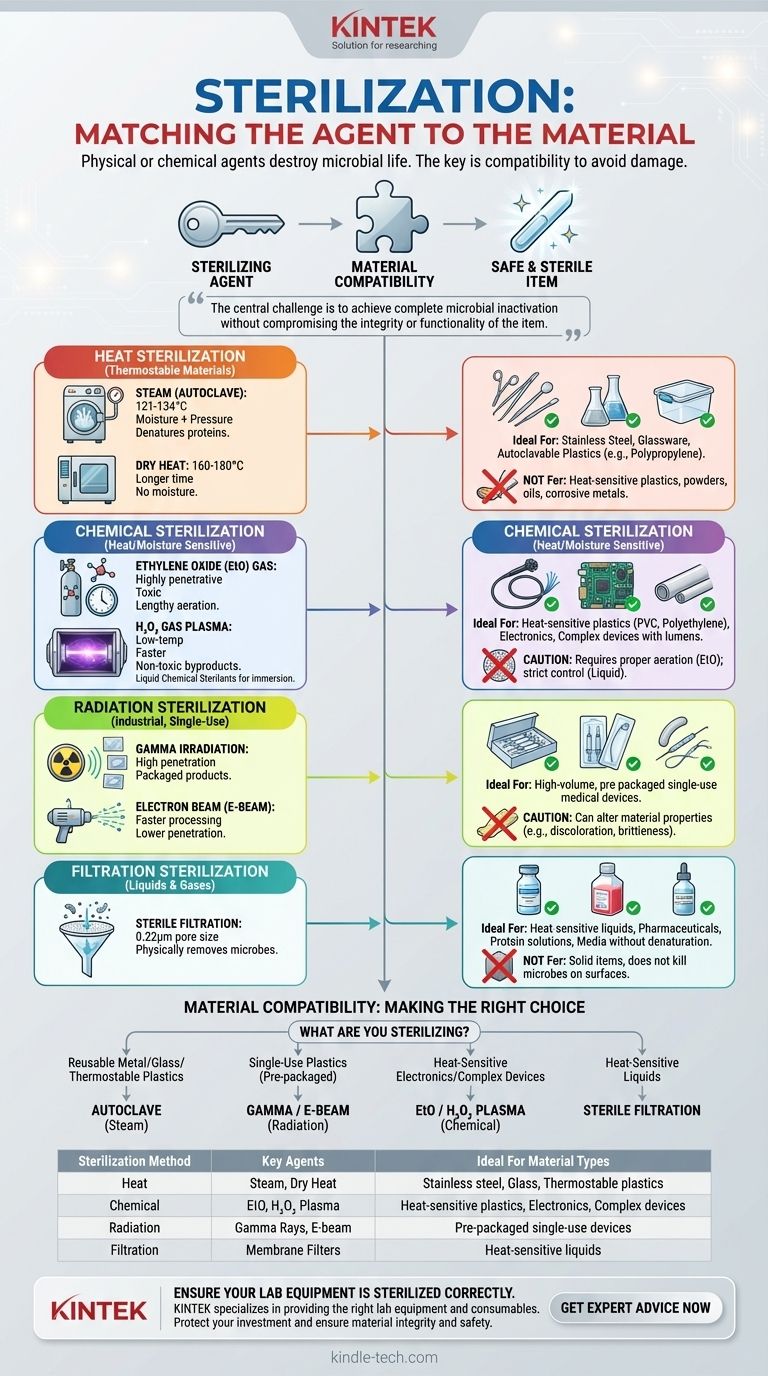
The materials used in sterilization are not materials themselves, but rather physical or chemical agents chosen based on their ability to destroy all microbial life. The primary methods fall into four categories: high-temperature heat (steam and dry heat), chemical agents (gases and liquids), radiation (gamma and electron beam), and sterile filtration for liquids. The choice of agent is dictated entirely by the material composition of the object being sterilized, as an incompatible method can cause melting, degradation, or other critical damage.
The core principle of sterilization is not about finding one superior method, but about matching the correct sterilizing agent to the material being processed. The central challenge is to achieve complete microbial inactivation without compromising the integrity or functionality of the item.

Understanding Sterilization Methods by Agent
The effectiveness of any sterilization process depends on its ability to kill or remove all forms of microbial life, including highly resistant bacterial spores. Each method uses a different mechanism of action, making it suitable for a specific set of materials.
Heat Sterilization
Heat is the most common, reliable, and cost-effective sterilization method, but it is only suitable for thermostable materials.
-
Steam (Autoclave): This method uses pressurized steam at high temperatures (typically 121°C or 134°C). The moisture is critical as it efficiently transfers heat and denatures microbial proteins. It is the gold standard for sterilizing surgical instruments (stainless steel), laboratory glassware, and autoclavable plastics like polypropylene.
-
Dry Heat: Performed in an oven, this method uses higher temperatures (160-180°C) for much longer periods than autoclaving. Because dry air is less efficient at heat transfer, it is reserved for materials that cannot be exposed to moisture, such as powders, oils, and certain metal instruments that might be susceptible to corrosion.
Chemical Sterilization
Chemical methods are essential for sterilizing items that are sensitive to heat or moisture.
-
Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Gas: EtO is a highly effective and penetrative gas that can sterilize complex devices with long lumens, even when pre-packaged. It is the method of choice for many single-use medical devices, electronics, and plastics (like PVC and polyethylene) that would be damaged by heat or radiation. However, EtO is toxic and requires a lengthy aeration period to remove residual gas.
-
Hydrogen Peroxide (H₂O₂) Gas Plasma: This low-temperature method vaporizes hydrogen peroxide, which is then energized into a plasma state to kill microorganisms. It is faster than EtO and its byproducts (water and oxygen) are non-toxic, eliminating the need for long aeration. It is commonly used for heat-sensitive instruments like endoscopes and electrical probes.
-
Liquid Chemical Sterilants: Solutions like glutaraldehyde and peracetic acid can be used for "cold sterilization" by immersing items. This is often applied to semi-critical medical devices that cannot withstand heat, though achieving true sterility requires strict control of immersion time and concentration.
Radiation Sterilization
Radiation is a high-efficiency, low-temperature method used primarily for the large-scale, industrial sterilization of single-use medical products.
-
Gamma Irradiation: This process uses Cobalt-60 as a source to emit high-energy gamma rays. These rays have excellent penetration power, allowing for the sterilization of fully sealed and packaged products like syringes, catheters, implants, and sutures.
-
Electron Beam (E-beam): E-beam uses a stream of high-energy electrons to sterilize products. Its penetration is lower than gamma, but the processing time is significantly faster (seconds vs. hours). It is ideal for high-volume, relatively low-density products.
Filtration Sterilization
Unlike other methods that kill microbes, filtration physically removes them from liquids or gases.
- Sterile Filtration: This technique passes a solution through a filter with a pore size small enough (typically 0.22 micrometers) to trap bacteria. It is the only viable method for sterilizing heat-sensitive liquids, such as pharmaceuticals, protein solutions, and cell culture media, without denaturing the active components.
The Critical Factor: Material Compatibility
The most important decision is selecting a sterilization method that will not degrade the material of the item. An incorrect choice can render a device useless or unsafe.
- Metals (e.g., Stainless Steel): Extremely durable and ideal for steam autoclaving.
- Glass: Highly resistant to heat, making it perfect for both autoclaving and dry heat sterilization.
- Plastics & Polymers: This is the most complex category. Some, like polypropylene and polycarbonate, can withstand autoclaving. Many others, including polyethylene and PVC, will melt or warp and require low-temperature methods like EtO or radiation. Radiation can, however, alter the physical properties of some plastics, causing discoloration or brittleness.
- Electronics & Complex Devices: These items are highly sensitive to both heat and moisture. Low-temperature gas methods like EtO or H₂O₂ gas plasma are the only suitable options.
- Liquids & Biologicals: For stable aqueous solutions like saline, autoclaving works well. For heat-labile pharmaceuticals or growth media, sterile filtration is the essential choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Item
The optimal sterilization method is a function of your item's material composition and its intended use.
- If your primary focus is reusable surgical instruments or lab glassware: Autoclaving (steam sterilization) is the industry standard due to its unmatched reliability, speed, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is single-use plastic medical devices (e.g., syringes, catheters): Gamma or E-beam irradiation is the preferred method for industrial-scale, pre-packaged sterilization.
- If your primary focus is heat-sensitive electronic equipment (e.g., endoscopes, probes): Low-temperature methods like Ethylene Oxide (EtO) or Hydrogen Peroxide gas plasma are necessary to prevent damage.
- If your primary focus is heat-sensitive liquids (e.g., pharmaceuticals, culture media): Sterilizing-grade filtration is the only method that removes microbes without degrading the solution.
Ultimately, selecting the correct sterilization method is a critical decision that directly impacts material integrity, patient safety, and product efficacy.
Summary Table:
| Sterilization Method | Key Agents | Ideal For Material Types |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Sterilization | Steam, Dry Heat | Stainless steel, glass, thermostable plastics (e.g., polypropylene) |
| Chemical Sterilization | Ethylene Oxide, H₂O₂ Plasma | Heat-sensitive plastics (e.g., PVC), electronics, complex devices |
| Radiation Sterilization | Gamma Rays, E-beam | Pre-packaged single-use devices (e.g., syringes, catheters) |
| Filtration Sterilization | Membrane Filters | Heat-sensitive liquids (e.g., pharmaceuticals, culture media) |
Ensure Your Lab Equipment is Sterilized Correctly
Choosing the wrong sterilization method can damage sensitive equipment, compromise your research, and lead to costly replacements. KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your specific sterilization needs, whether you're working with autoclaves, gas plasma systems, or filtration units.
We help you protect your investment and ensure material integrity and safety. Contact us today to find the perfect sterilization solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of autoclave in microbiology lab? Achieve Sterile Conditions with 121°C
- What are the do's and don'ts in using autoclave? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- What is an example of autoclave in laboratory? Essential Sterilization for Reliable Science
- What autoclave is used for sterilization? The Definitive Guide to Steam Sterilization
- Is an autoclave the same as a steam sterilizer? Understanding the Key to Reliable Sterilization



















