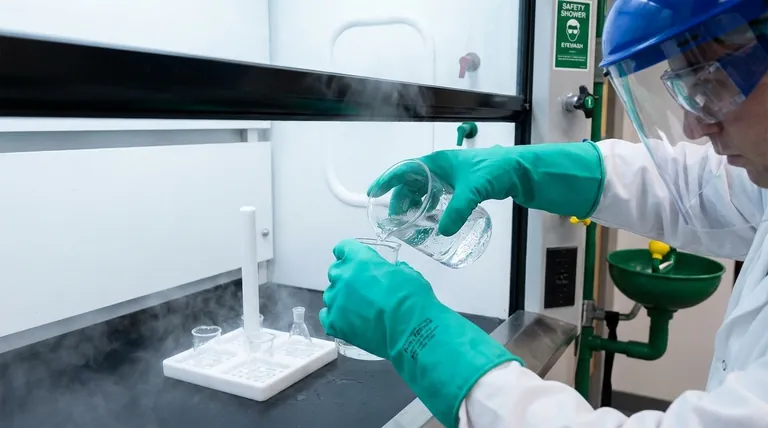
At a minimum, you must use acid and alkali-resistant gloves, chemical splash goggles, and a properly functioning fume hood when handling corrosive electrolytes. These requirements form the baseline for protecting yourself from immediate chemical splashes, skin contact, and the inhalation of hazardous fumes.
The core principle of laboratory safety is not just wearing protective gear, but implementing a Hierarchy of Controls. This means prioritizing engineering solutions like fume hoods first, followed by safe work practices, with Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) serving as the final, essential barrier between you and the hazard.

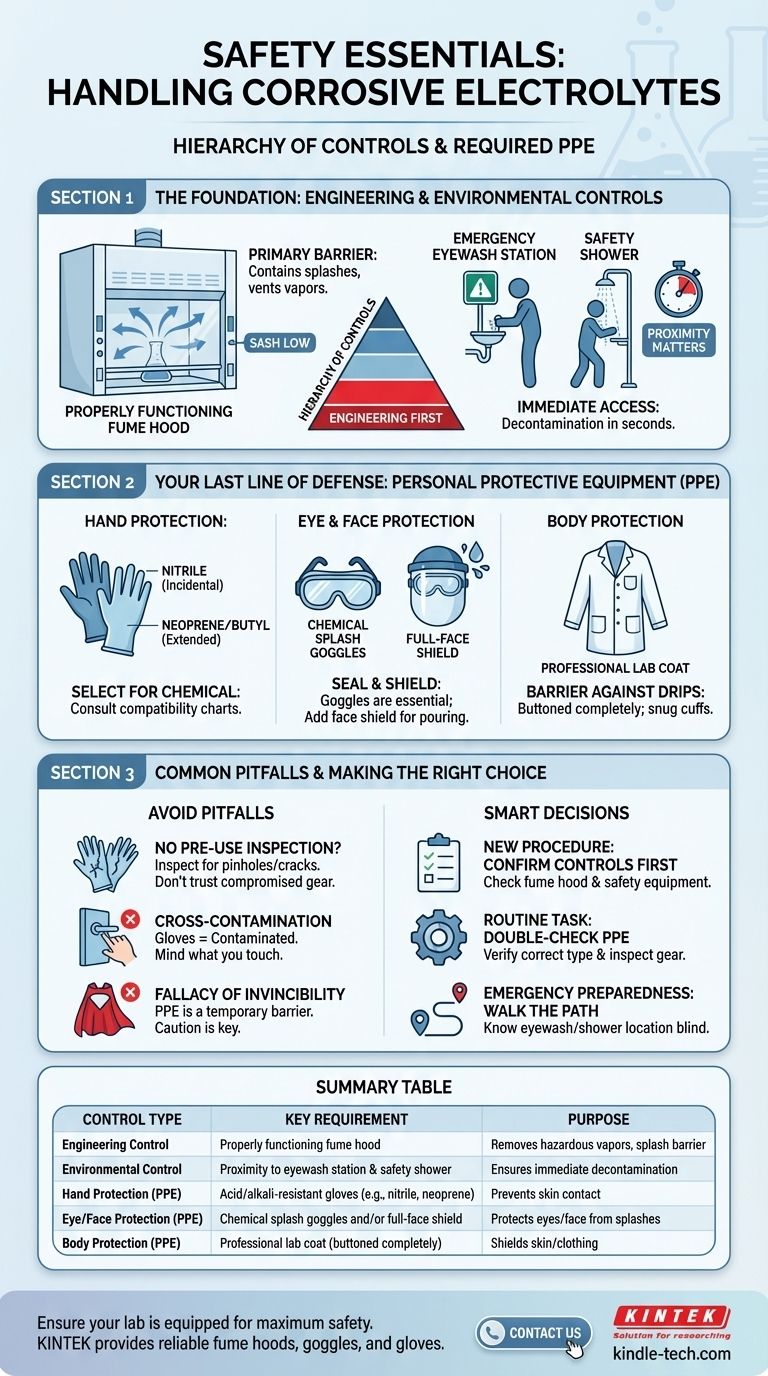
The Foundation: Engineering and Environmental Controls
Before you even select your gloves, you must ensure the environment itself is designed for safety. These controls protect everyone in the lab, not just the individual operator.
Why a Fume Hood is Non-Negotiable
A fume hood is your primary engineering control. Its purpose is twofold: it provides a physical barrier against splashes and explosions, and its ventilation system constantly pulls hazardous vapors or aerosols away from your breathing zone.
All handling of open containers of corrosive electrolytes should occur deep within the hood with the sash at the lowest practical height.
Proximity to Emergency Equipment
Accidents can happen despite the best precautions. Your workspace must be located within a few seconds of an eyewash station and a safety shower. Know their exact location and how to operate them before you handle the first container.
Your Last Line of Defense: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE is critical, but it is the last line of defense after engineering controls and safe procedures have been established. It protects your body from any hazardous materials that breach the primary controls.
Hand Protection: Choosing the Right Glove
The term "acid and alkali-resistant" is a general category. The chemical resistance of gloves varies significantly by material. Always consult a glove compatibility chart for the specific electrolyte you are handling.
Common choices include nitrile for incidental contact and more robust materials like neoprene or butyl rubber for extended handling or highly corrosive substances.
Eye and Face Protection: Goggles Are Essential
Standard safety glasses are not sufficient. You must wear chemical splash goggles that form a seal around your eyes to protect against splashes from any angle.
When there is a significant risk of splashing during pouring or mixing, a full-face shield should be worn over your chemical splash goggles for an added layer of protection.
Body Protection: The Professional Lab Coat
Wear a lab coat made of an appropriate material, buttoned completely. This protects your skin and personal clothing from drips and splashes. Ensure cuffs are snug and not loose-fitting.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Relying on a single safety measure is a common and dangerous mistake. A holistic system is the only way to ensure true protection.
The Fallacy of "Invincibility"
PPE does not make you immune to hazards. It only provides a temporary barrier. The goal is to avoid contact altogether through careful technique. Never let the presence of PPE lead to a decrease in caution.
Forgetting Pre-Use Inspection
Always inspect your gloves for pinholes, cracks, or signs of degradation before each use. A compromised glove provides a false sense of security and can trap hazardous material against your skin.
Misunderstanding Contamination
Once you handle a chemical container, your gloves are considered contaminated. Be mindful of what you touch afterward—avoid contact with your face, pens, notebooks, or door handles to prevent cross-contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to safety should be deliberate and systematic. Always begin with a risk assessment for your specific procedure.
- If your primary focus is setting up a new procedure: Confirm the availability and proper function of engineering controls like the fume hood, eyewash, and shower before you bring any chemicals into the workspace.
- If your primary focus is performing a routine task: Double-check that you have the correct type of PPE for the specific electrolyte and conduct a visual inspection of your gear before you begin.
- If your primary focus is emergency preparedness: Walk the path to the eyewash and safety shower so you can do it with your eyes closed, and confirm the location of the appropriate chemical spill kit.
Ultimately, safety is an active process, not a passive checklist.
Summary Table:
| Control Type | Key Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering Control | Properly functioning fume hood | Removes hazardous vapors and provides a splash barrier |
| Environmental Control | Proximity to eyewash station and safety shower | Ensures immediate decontamination in case of exposure |
| Hand Protection (PPE) | Acid/alkali-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile, neoprene) | Prevents skin contact with corrosive substances |
| Eye/Face Protection (PPE) | Chemical splash goggles and/or full-face shield | Protects eyes and face from chemical splashes |
| Body Protection (PPE) | Professional lab coat (buttoned completely) | Shields skin and clothing from drips and splashes |
Ensure your lab is equipped for maximum safety when handling corrosive materials. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, including fume hoods, safety goggles, and chemical-resistant gloves, to meet all your laboratory safety needs. Don't compromise on protection—contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's safety protocols and provide the right solutions for your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What material is a PTFE cleaning basket made of? Unlocking Superior Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What inspection should be performed on a PTFE cleaning basket before use? A 3-Step Protocol for Safe, Effective Cleaning
- How should a PTFE cleaning basket be cleaned before its initial use? A Critical First Step for Process Integrity
- What should be monitored during the cleaning process when using a PTFE cleaning basket? Ensure Reliable Results & Prevent Damage
- What is the maximum operating temperature for a PTFE cleaning basket? Avoid Catastrophic Failure at 260°C



















