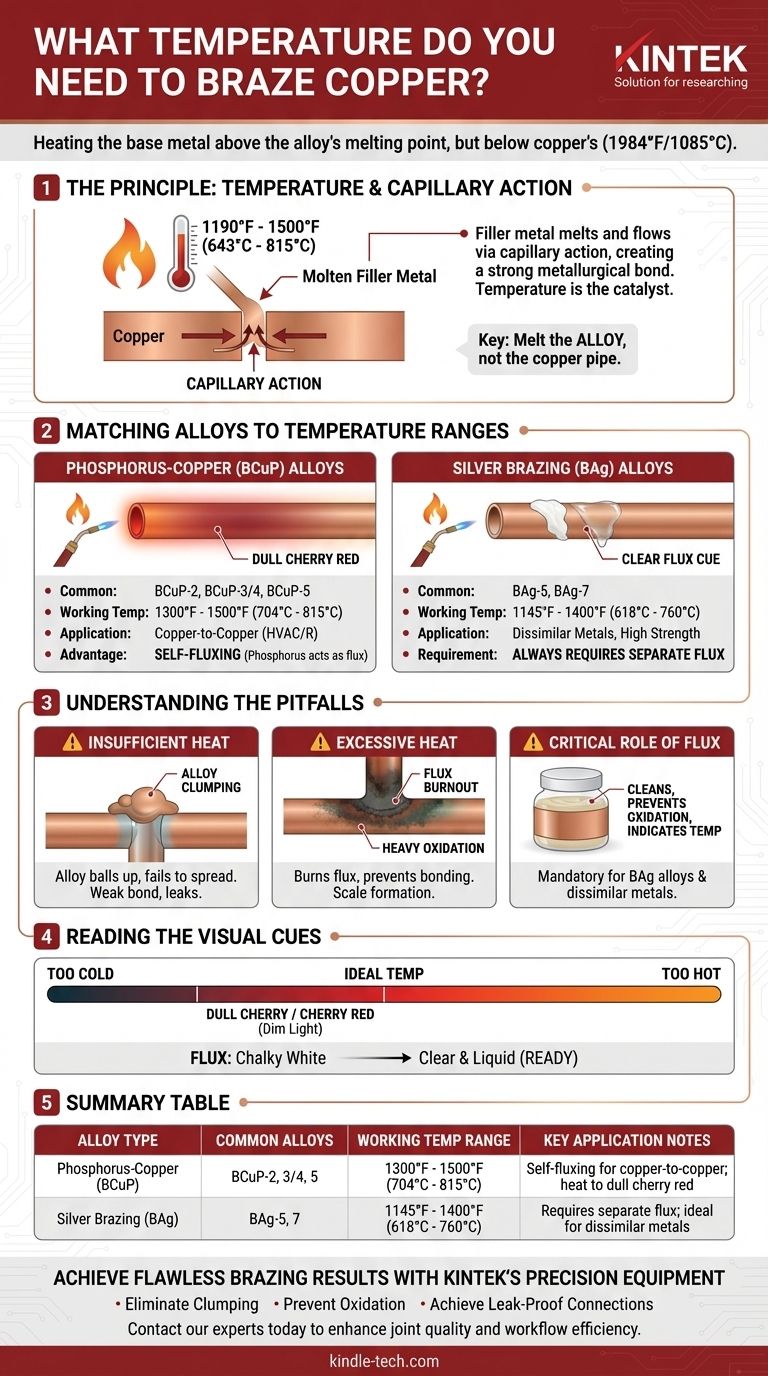
To braze copper, you must heat the base metal to a temperature that is above the melting point of your chosen brazing alloy, but below the melting point of the copper itself. This working temperature typically falls between 1190°F and 1500°F (643°C and 815°C), depending entirely on the specific filler metal you are using. The key is to melt the alloy, not the copper pipe.
The question isn't just "what temperature," but "what temperature is right for my specific brazing alloy?" The alloy dictates the target temperature, and achieving that precise heat is the difference between a perfect, leak-proof joint and a complete failure.

The Principle: Why Temperature Is More Than a Number
Brazing creates a metallurgical bond that is often stronger than the base metals being joined. This process relies on a principle called capillary action, where the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight gap between the two copper pieces. Temperature is the catalyst for this entire process.
The Role of the Filler Metal
Unlike welding, brazing does not melt the base metal (the copper). Instead, you only melt a filler metal, often called a brazing rod or alloy. Each alloy has a specific temperature range at which it becomes liquid and flows properly.
Achieving Capillary Action
For capillary action to work, the copper must be hot enough to instantly melt the brazing rod upon contact. If the copper is too cold, the alloy will "clump" and fail to penetrate the joint. The ideal temperature creates a "wetting" action, allowing the liquid alloy to spread evenly across the metal surfaces.
The Danger of Overheating
Copper's melting point is 1984°F (1085°C). While you are unlikely to melt the pipe with a standard torch, overheating is a common and serious mistake. Excessive heat causes heavy surface oxidation, which prevents the filler metal from bonding. It can also burn away the flux needed for the process and potentially weaken the copper itself.
Matching Brazing Alloys to Temperature Ranges
The specific alloy you choose is determined by your application (e.g., HVAC, plumbing, joining dissimilar metals). This choice then dictates your target temperature.
Phosphorus-Copper Alloys (BCuP)
These are the most common alloys for joining copper to copper, especially in HVAC and refrigeration. Their key advantage is that the phosphorus acts as a fluxing agent, meaning no separate flux is needed for copper-to-copper joints.
- Common Alloys: BCuP-2 (0% silver), BCuP-3/4 (5-6% silver), BCuP-5 (15% silver).
- Working Temperature: Typically 1300°F to 1500°F (704°C to 815°C).
- Visual Cue: Heat the copper until it glows a faint to dull cherry red.
Silver Brazing Alloys (BAg)
Often called "silver solder" (a technically incorrect but common term), these alloys are used for higher strength, vibration resistance, or joining copper to other metals like brass or steel. They contain varying percentages of silver.
- Common Alloys: BAg-5 (45% silver), BAg-7 (56% silver).
- Working Temperature: Generally lower, from 1145°F to 1400°F (618°C to 760°C).
- Note: These alloys always require a separate flux, even when joining copper to copper.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
A successful braze requires managing heat, cleanliness, and materials. Avoiding common mistakes is critical.
The Critical Role of Flux
Unless you are using a BCuP alloy on a copper-to-copper joint, flux is mandatory. Flux is a chemical paste that cleans the surface, prevents oxidation during heating, and indicates when the metal is at the correct temperature. Applying too little flux, or overheating and burning it away, will cause the joint to fail.
The Danger of Insufficient Heat
If the base metal is not hot enough, the filler rod will not flow into the joint. You will see it ball up and refuse to spread, resulting in a surface-level bond with no strength or seal. This is a common cause of leaks.
The Consequences of Excessive Heat
Applying too much heat is just as bad. You will burn away the flux, create heavy black scale (cupric oxide) on the copper, and prevent a bond from forming. This can also cause the filler metal to run right through the joint without properly sealing it.
Reading the Visual Cues
Your most important tool is your eye. Learning to read the color of the metal and the behavior of the flux is the key to mastering brazing.
- Color: For most copper brazing, you are looking for a dull cherry or cherry red color in a dimly lit environment. If the copper is bright orange or yellow, it is far too hot.
- Flux: When using flux, it will first dry and turn chalky white. As the temperature rises, it will become clear and liquid, like water. This "clear" phase is the sign that the base metal is ready for the brazing alloy.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your goal determines your tools and temperature. Select your approach based on the job's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is standard HVAC/R (copper-to-copper): Use a self-fluxing Phosphorus-Copper (BCuP) alloy and heat the joint evenly to a dull cherry red before applying the rod.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals (e.g., copper to brass): Use a silver-bearing (BAg) alloy with the correct white brazing flux, and watch for the flux to turn clear and liquid before introducing the alloy.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength or high vibration: Choose a high-silver content BAg alloy and focus on precise, even heating to avoid overheating the parts while ensuring full penetration.
Ultimately, successful brazing is not about hitting a magic number on a thermometer, but about understanding and controlling the relationship between your metal, your alloy, and your heat source.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Alloy Type | Common Alloys | Working Temperature Range | Key Application Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphorus-Copper (BCuP) | BCuP-2, BCuP-3/4, BCuP-5 | 1300°F to 1500°F (704°C to 815°C) | Self-fluxing for copper-to-copper joints; heat to dull cherry red |
| Silver Brazing (BAg) | BAg-5, BAg-7 | 1145°F to 1400°F (618°C to 760°C) | Requires separate flux; ideal for dissimilar metals and high strength |
Achieve Flawless Brazing Results with KINTEK's Precision Equipment
Whether you're working on HVAC systems, plumbing, or specialized metal joining, precise temperature control is non-negotiable for successful copper brazing. At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables that deliver the consistent, accurate heat required for perfect capillary action and strong metallurgical bonds.
Our brazing solutions help you:
- Eliminate clumping and failed joints with precise temperature control
- Prevent oxidation and flux burnout through even heat distribution
- Achieve leak-proof connections with reliable, repeatable results
We serve professionals in: HVAC/R, plumbing, metal fabrication, and research laboratories who demand equipment that matches their technical expertise.
Ready to transform your brazing process? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's specialized equipment can enhance your joint quality and workflow efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of brazing? Join Dissimilar Metals with Strong, Leak-Proof Bonds
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What is the basic of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Low-Heat Metal Joining
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















