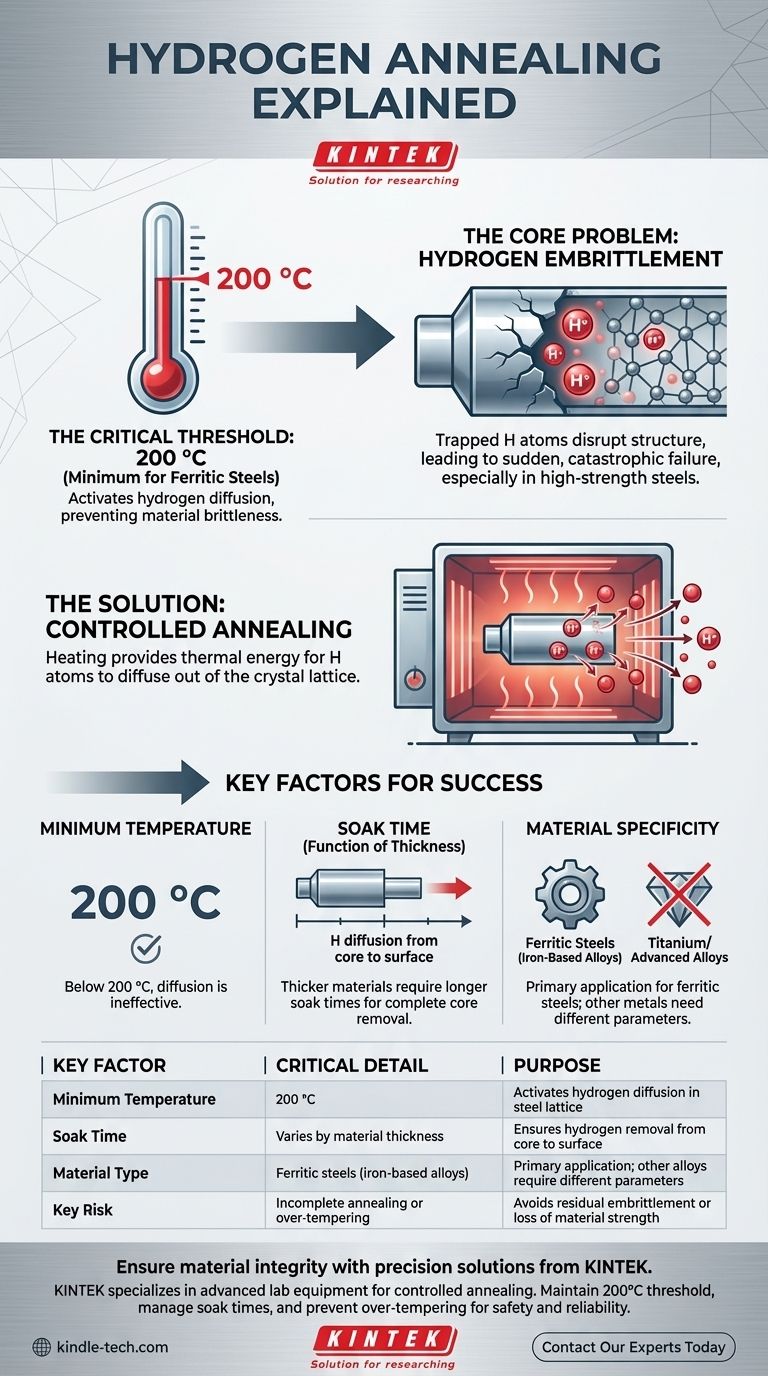
The minimum temperature required for effective low hydrogen annealing is 200 °C. This specific temperature provides the necessary thermal energy for trapped hydrogen atoms to diffuse out of the crystal lattice of materials like iron and certain stainless steels, which is the entire purpose of the process.
The core challenge is not just knowing the temperature, but understanding why that temperature is critical. Hydrogen annealing is a diffusion process designed to remove trapped hydrogen that causes material brittleness; 200 °C is the threshold where this diffusion becomes effective in common steels.
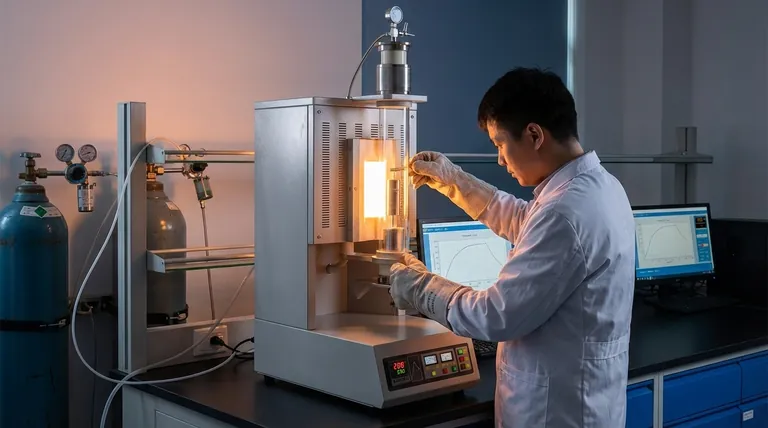

The Core Problem: Hydrogen Embrittlement
Hydrogen embrittlement is a primary cause of premature and catastrophic failure in metallic components, especially high-strength steels.
How Hydrogen Gets Trapped
During manufacturing processes like welding, electroplating, or casting, individual hydrogen atoms (protons) can be introduced into the metal. Being extremely small, they easily permeate the metal's crystal lattice.
Once trapped inside, these atoms disrupt the structure, significantly reducing the material's ductility and making it brittle and susceptible to cracking under stress.
The Consequence: Reduced Integrity
A component suffering from hydrogen embrittlement can fail suddenly and without warning, even when subjected to loads far below its designed capacity. This makes removing trapped hydrogen a critical step for ensuring safety and reliability.
The Solution: How Annealing Works
Annealing is a controlled heat treatment process. By heating the material, we give the trapped hydrogen atoms enough thermal energy to move, or diffuse, through the metal's structure until they escape from the surface.
Why 200 °C is the Critical Threshold
For iron and many common steels, 200 °C represents the minimum temperature at which hydrogen atoms gain sufficient mobility to diffuse effectively. Below this temperature, the atoms remain largely locked in place, and the annealing process is ineffective.
Annealing is a Function of Time and Temperature
Reaching 200 °C is only the first step. The component must be held at this temperature for a sufficient duration, known as the soak time.
The required time depends heavily on the thickness of the material. A thicker section requires a longer soak time to allow hydrogen from the core of the component to diffuse all the way to the surface.
Understanding the Key Factors
Simply heating a part to 200 °C does not guarantee success. The process must be carefully controlled to be effective without causing unintended harm.
Risk of Incomplete Annealing
If the temperature is too low or the soak time is too short, hydrogen will only be removed from the surface layers. The core of the component will remain embrittled, leaving it vulnerable to internal crack initiation and failure.
Risk of Over-Tempering
While higher temperatures can accelerate hydrogen diffusion, they can also negatively alter the material's fundamental properties. Exceeding the specified annealing temperature can reduce the strength and hardness (temper) of the steel, compromising its design characteristics. Low hydrogen annealing at 200 °C is specifically designed to avoid this.
Material Specificity
The 200 °C threshold is primarily relevant for ferritic steels (iron-based alloys). Other metals, such as titanium or certain advanced alloys, have different diffusion characteristics and require entirely different annealing parameters.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your approach to hydrogen annealing should be dictated by your material and the criticality of the component.
- If your primary focus is preventing failure in high-strength steel: You must strictly adhere to the specified 200 °C minimum and ensure soak times are adequate for the component's thickest section.
- If your primary focus is ensuring complete hydrogen removal in thick components: Your critical variable is time. You must calculate the appropriate soak time to allow for diffusion from the core, as merely reaching the temperature is insufficient.
- If your primary focus is on a material other than standard steel: You must consult material-specific data sheets, as the 200 °C benchmark does not apply universally and could be ineffective or damaging.
Ultimately, controlling hydrogen annealing is a critical step in guaranteeing the structural integrity and long-term reliability of your components.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Critical Detail | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Temperature | 200 °C | Activates hydrogen diffusion in steel lattice |
| Soak Time | Varies by material thickness | Ensures hydrogen removal from core to surface |
| Material Type | Ferritic steels (iron-based alloys) | Primary application; other alloys require different parameters |
| Key Risk | Incomplete annealing or over-tempering | Avoids residual embrittlement or loss of material strength |
Ensure your lab's material integrity with precision hydrogen annealing solutions from KINTEK.
Hydrogen embrittlement poses a silent threat to high-strength steel components, leading to unpredictable failures. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables designed to deliver precise, controlled annealing processes. Our solutions help you maintain the critical 200°C threshold, manage soak times accurately, and prevent over-tempering—ensuring your materials meet the highest standards of safety and reliability.
Whether you're working with ferritic steels or specialized alloys, KINTEK provides the tools and expertise to safeguard your components against hydrogen-related failures. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific annealing needs and enhance your lab's capability to produce durable, trustworthy results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















