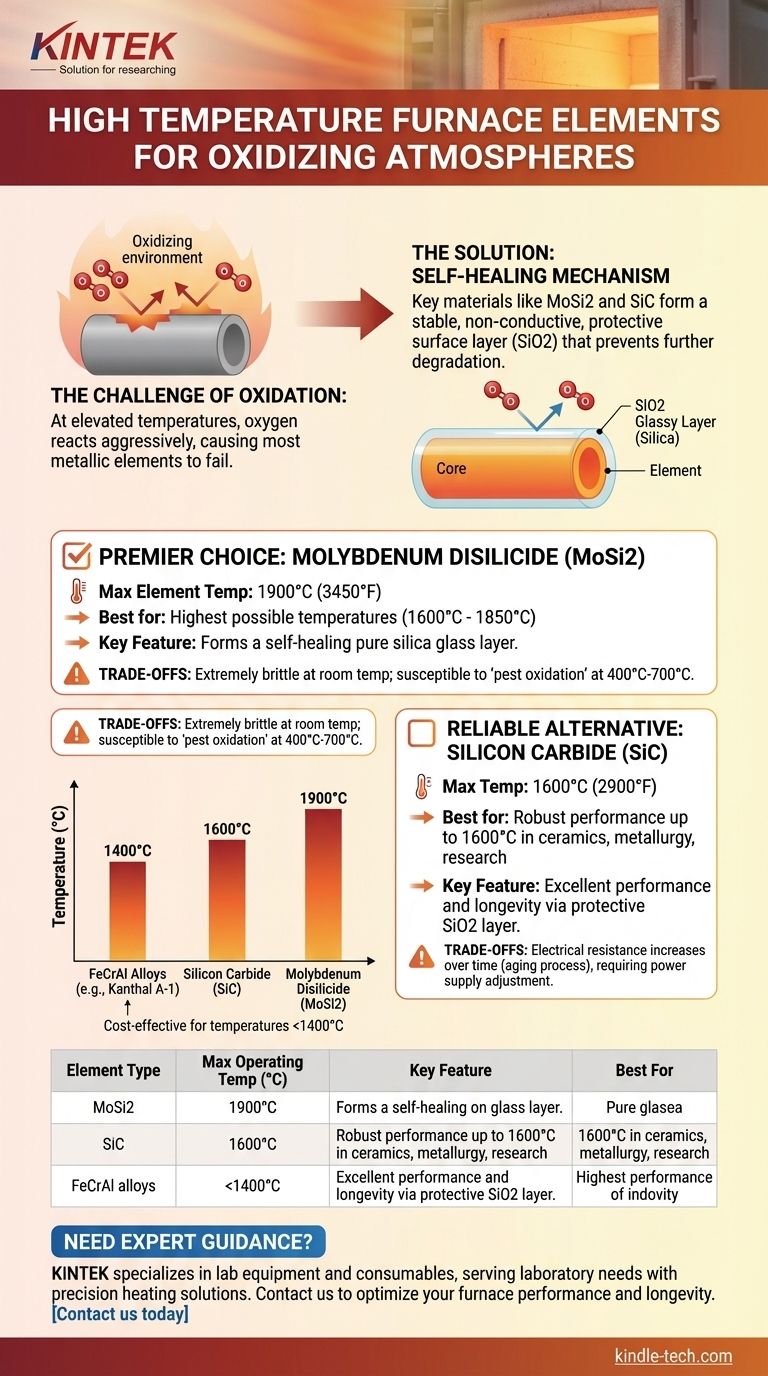
For the highest temperatures in an oxidizing atmosphere, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are the superior choice. These specialized ceramic-based elements are engineered to thrive in oxygen-rich environments, capable of reaching element temperatures as high as 1900°C by forming a protective, self-healing glass layer on their surface.
The key to high-temperature performance in an oxidizing atmosphere is not to resist oxidation, but to control it. The best materials, like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC), use the available oxygen to form a stable, non-conductive, and protective surface layer that prevents further degradation of the element.

Why Oxidizing Atmospheres Are a Challenge
At elevated temperatures, most materials react aggressively with oxygen. This process, known as oxidation, is the primary reason why standard metallic heating elements fail catastrophically in high-temperature air furnaces.
The Fundamental Problem of Oxidation
Think of oxidation as a form of controlled burning. For most metals, this process is destructive and continuous. The oxide layer that forms is often flaky and porous, offering no protection and allowing oxygen to continue consuming the material until the element breaks.
The Self-Healing Solution
The most successful high-temperature elements turn this problem into a solution. They are designed from materials that, when reacting with oxygen, form an impervious and stable protective layer. This layer effectively seals the core element from the atmosphere, stopping further oxidation.
The Premier Choice: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
When your process demands the highest possible operating temperatures in air or an oxygen-rich environment, MoSi2 is the industry-standard material.
How MoSi2 Works
The "magic" of MoSi2 lies in its silicon component. As the element heats up in the presence of oxygen, a thin layer of pure silica glass (silicon dioxide, SiO2) forms on the surface. This glassy layer is highly stable, non-conductive, and re-forms instantly if any cracks or flaws appear, making it "self-healing."
Maximum Operating Temperature
MoSi2 elements can achieve a maximum temperature of 1900°C (3450°F). It is critical to note this is the element's maximum rated temperature; the furnace's practical operating temperature will typically be slightly lower, often in the 1700°C to 1850°C range for long service life.
Key Characteristics
Beyond its temperature resistance, MoSi2 allows for very high power density. This means furnaces built with these elements can heat up extremely quickly, a significant advantage for many laboratory and production processes.
A Reliable Alternative: Silicon Carbide (SiC)
For a vast range of high-temperature applications that do not require the extreme heat of MoSi2, Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a robust and widely used alternative.
A Similar Protective Mechanism
Like MoSi2, SiC elements also form a protective silicon dioxide (SiO2) layer when heated in an oxidizing atmosphere. This gives them excellent performance and longevity in air.
Operating Temperature Range
SiC elements are generally used for furnace temperatures up to 1600°C (2900°F). While this is lower than MoSi2, it covers the requirements for a majority of high-temperature applications in ceramics, metallurgy, and research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right element is not just about the maximum temperature. You must consider the material's physical properties and potential failure modes.
The Brittleness of MoSi2
MoSi2 is a cermet (ceramic-metal composite) and is extremely brittle at room temperature. The elements must be handled with great care during installation and are susceptible to mechanical shock. They only gain ductility at very high temperatures.
MoSi2 "Pest" Oxidation
In a specific low-temperature range of roughly 400°C to 700°C, MoSi2 can undergo a destructive phenomenon known as "pest oxidation." If held in this range for extended periods, the element can rapidly disintegrate. Therefore, furnaces using MoSi2 must be designed to pass through this temperature range quickly.
SiC Element Aging
Over their service life, SiC elements gradually increase in electrical resistance. This is a natural aging process that must be managed. The power supply system must be ableto increase the voltage over time to maintain the required power output and furnace temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection must be guided by the specific temperature and operational demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures (1600°C to 1850°C): Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) is the definitive and often only choice.
- If your primary focus is robust performance up to 1600°C: Silicon Carbide (SiC) is an excellent, reliable, and mechanically tougher alternative to MoSi2.
- If your primary focus is on temperatures below 1400°C: High-performance metallic alloys like FeCrAl (e.g., Kanthal A-1) are the most cost-effective and dependable solution for oxidizing atmospheres.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating element is about matching the material's unique properties to the precise demands of your high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Element Type | Max Operating Temp (°C) | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | 1900°C | Self-healing silica layer | Highest temperature applications (1600-1850°C) |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1600°C | Protective SiO2 layer | Robust performance up to 1600°C |
| FeCrAl Alloys | 1400°C | Cost-effective | Temperatures below 1400°C |
Need expert guidance selecting the right heating elements for your specific high-temperature process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision heating solutions. Our team can help you choose between MoSi2, SiC, and other elements to optimize your furnace performance and longevity. Contact us today for personalized consultation and discover how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs



















