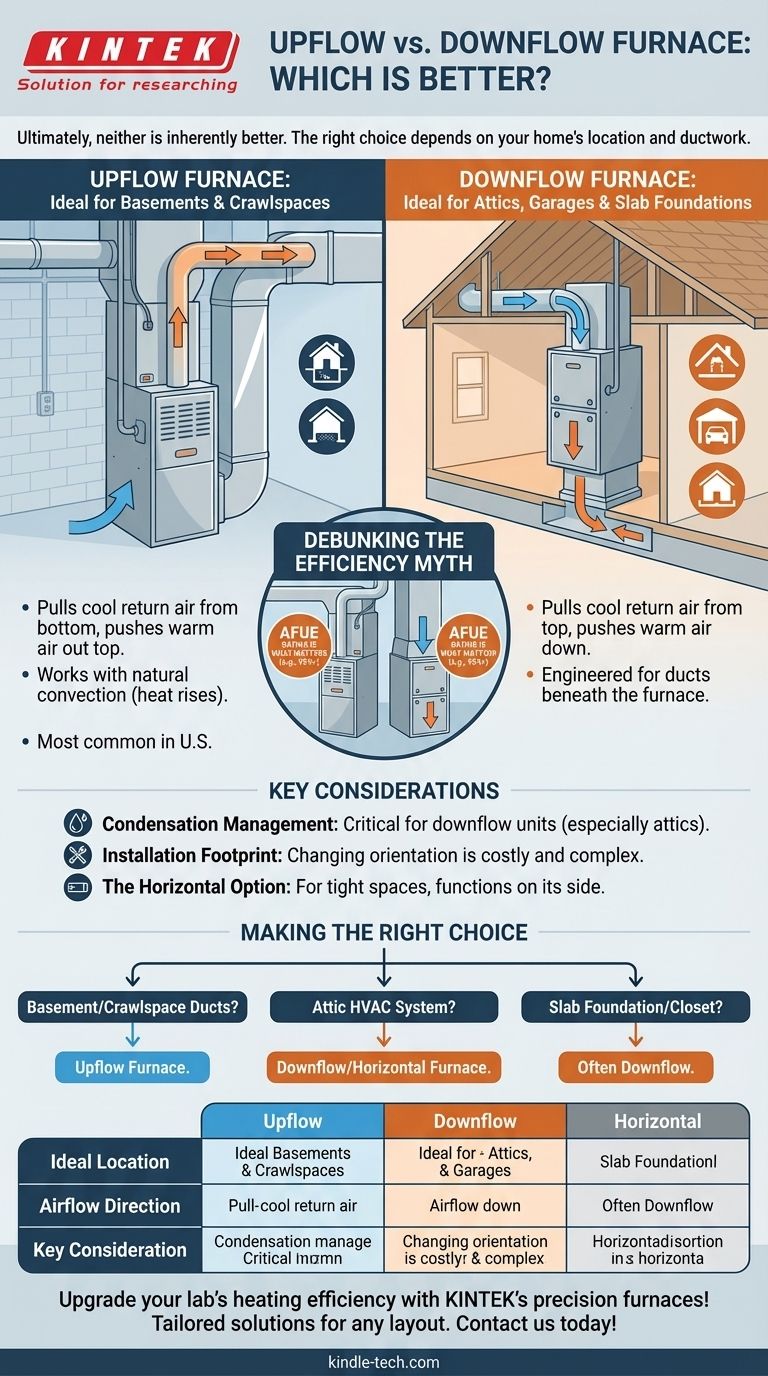
Ultimately, neither an upflow nor a downflow furnace is inherently better. The right choice is determined entirely by its installation location within your home. Upflow furnaces are the most common type in the U.S. simply because many homes are built with basements, the ideal location for an upflow design that leverages the natural tendency of heat to rise.
The "upflow vs. downflow" debate isn't about which technology is superior, but which configuration correctly matches your home's ductwork and layout. Choosing the wrong one for your location will lead to significant inefficiency, regardless of the furnace's quality.

The Fundamental Difference: Airflow Direction
The name of each furnace type describes the direction it moves air. Understanding this simple principle is the key to selecting the correct unit for your home.
How an Upflow Furnace Works
An upflow furnace pulls cool return air in through the bottom of the unit. It then heats the air and pushes the warm, conditioned air out of the top, where it is distributed into your home's ductwork.
This design works with physics, not against it. Since hot air naturally rises, this configuration is highly effective when the furnace is placed in the lowest level of a home.
Ideal Location for Upflow
The ideal and most common location for an upflow furnace is a basement or a crawlspace. The furnace sits on the floor and pushes heat upwards into the living spaces above.
How a Downflow Furnace Works
A downflow furnace, sometimes called a counterflow furnace, does the exact opposite. It pulls cool return air in from the top, heats it, and then pushes the warm air down into the ductwork below.
This design is specifically engineered for situations where the ductwork is located beneath the furnace, such as in the floor or a crawlspace, but the furnace itself is not in a basement.
Ideal Location for Downflow
Downflow furnaces are necessary for installations in attics, garages, or first-floor utility closets in homes built on a slab foundation. In these cases, the furnace is above the ductwork it needs to feed.
Debunking the Efficiency Myth
A common point of confusion is whether one furnace type is more energy-efficient than the other. The answer is tied to proper application, not the technology itself.
Configuration vs. Inherent Efficiency
While an upflow furnace in a basement takes advantage of natural convection (rising heat), the actual energy efficiency of a modern furnace is determined by its AFUE rating, not its airflow direction.
AFUE Rating Is What Matters
AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) measures how much fuel a furnace converts into usable heat. A furnace with a 95% AFUE rating converts 95 cents of every dollar of fuel into warmth for your home.
Both upflow and downflow models are available in high-efficiency ratings of 95% or higher. A high-efficiency downflow unit is far superior to a low-efficiency upflow unit.
The Real Source of Inefficiency
The biggest efficiency losses occur when the wrong type of furnace is installed in the wrong location. Trying to force an upflow furnace to work in an attic would require convoluted, inefficient ducting that negates any potential benefits. Proper installation is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While both types can be highly effective when installed correctly, there are a few practical considerations to keep in mind.
Condensation Management in Downflow Units
High-efficiency furnaces produce condensation as a byproduct of combustion. In a downflow unit, particularly one in a cold attic, managing this condensate is critical to prevent water damage and operational issues. The drainage system must be installed perfectly.
Installation Footprint and Ductwork
In most cases, you are replacing an existing furnace with one of the same orientation. Changing from an upflow to a downflow configuration (or vice-versa) is a major project that requires significant and costly ductwork modifications.
The Horizontal Option
For very tight spaces like narrow attics or constricted crawlspaces, a horizontal furnace is also an option. It functions similarly but lies on its side, pulling air from one end and pushing it out the other, making it a versatile problem-solver for unique layouts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
Forget asking which furnace is "better" and instead ask which one your home's layout requires.
- If your home has a basement or main-floor furnace room with crawlspace ducting: You will almost certainly need an upflow furnace.
- If your HVAC system is located in the attic: You will need a downflow or horizontal furnace to properly distribute heat to the floors below.
- If your home is on a slab foundation with the furnace in a closet: The correct choice depends on where the ducts run, but it is often a downflow configuration.
Focus on matching the furnace's orientation to your ductwork, then select the unit with the highest AFUE rating your budget allows.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Ideal Location | Airflow Direction | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upflow Furnace | Basement, Crawlspace | Pulls air from bottom, pushes heated air out top | Leverages natural heat rise; most common in homes with basements |
| Downflow Furnace | Attic, Garage, Slab Foundation | Pulls air from top, pushes heated air down | Requires precise condensate management; ideal for attic installations |
| Horizontal Furnace | Tight spaces (e.g., narrow attics) | Airflow from one side to the other | Solves unique layout challenges; versatile for constrained areas |
Upgrade your lab's heating efficiency with KINTEK's precision furnaces!
Whether your laboratory requires a compact horizontal design for tight spaces or a high-performance upflow/downflow configuration, KINTEK delivers reliable, energy-efficient solutions tailored to your specific layout and workflow. Our furnaces are engineered for precise temperature control, durability, and seamless integration with your existing setup.
Contact us today to discuss your lab's heating needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your research and testing capabilities. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- Why is a hydrogen atmosphere furnace necessary for W-Cu composite? Unlock Superior Infiltration and Density
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is hydrogen atmosphere heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Purity & Brightness
- What is hydrogen annealing? Achieve Superior Material Properties with Bright Annealing



















