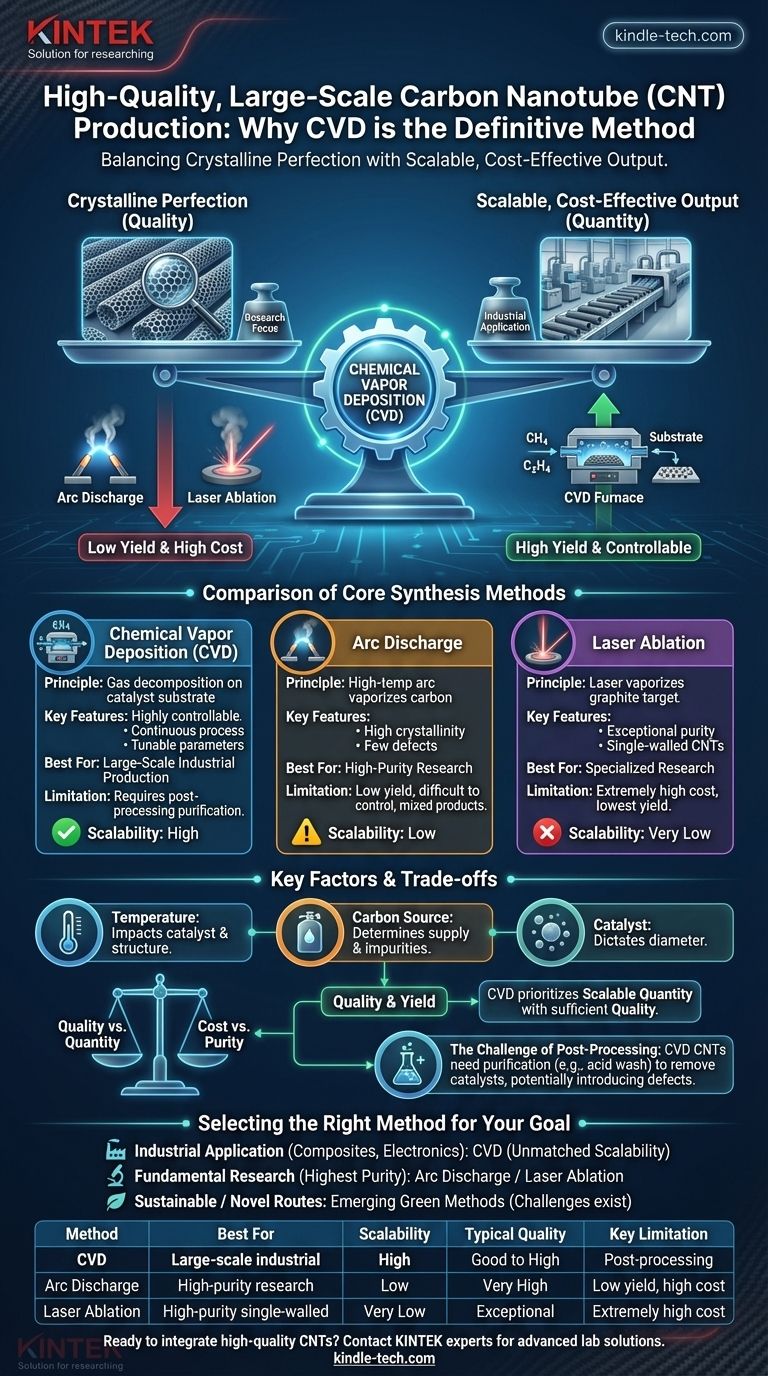
For producing high-quality carbon nanotubes (CNTs) at a large scale, the definitive method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While traditional methods like arc discharge and laser ablation can produce very high-purity CNTs, they fundamentally lack the scalability and cost-effectiveness required for commercial applications. CVD offers the most effective balance between tunable quality control and high-volume industrial output.
The central challenge in CNT production is balancing crystalline perfection with scalable, cost-effective output. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) has emerged as the industry standard because it provides the most viable and controllable pathway to large-scale production without a prohibitive sacrifice in quality.
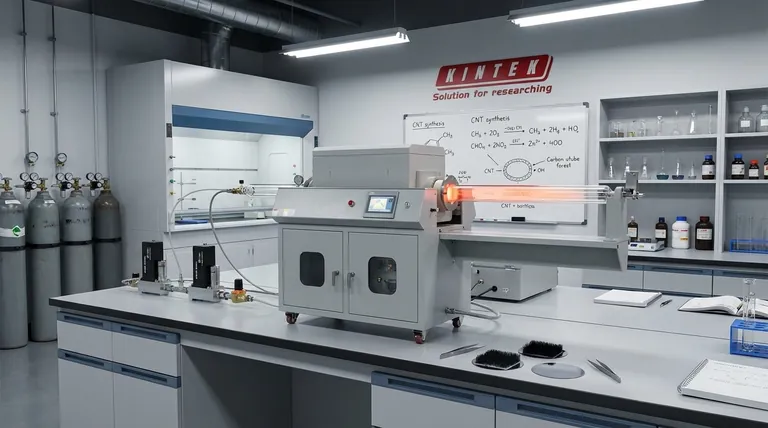

A Comparison of Core Synthesis Methods
To understand why CVD is the dominant choice, it's essential to compare it against its predecessors. Each method operates on a different principle, leading to distinct outcomes in quality, yield, and cost.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Scalable Workhorse
CVD involves introducing a hydrocarbon gas (like methane or ethylene) into a high-temperature furnace containing a metallic catalyst substrate. The gas decomposes, and carbon atoms deposit and grow into nanotubes on the catalyst particles.
This process is highly controllable and can be run continuously, making it ideal for large-scale production. By carefully managing the process parameters, manufacturers can influence the diameter, length, and structure of the CNTs.
Arc Discharge: The High-Purity Pioneer
This method involves creating a high-temperature electric arc between two graphite electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere. The intense heat vaporizes the carbon from the anode, which then condenses to form CNTs.
Arc discharge is known for producing highly crystalline CNTs with few structural defects. However, the process is difficult to control, has a very low yield, and produces a mixture of soot and other carbon forms that require extensive purification.
Laser Ablation: The Precision Instrument
Similar to arc discharge, laser ablation uses a high-power laser to vaporize a graphite target in a furnace. The vaporized carbon is then carried by an inert gas to a cooler surface where it condenses into CNTs.
This method can produce CNTs of exceptionally high purity, particularly single-walled nanotubes. However, it is extremely expensive and has the lowest yield of the three, restricting its use to specialized research applications.
Key Factors Influencing Quality and Yield
The choice of method is only the first step. True quality control comes from mastering the critical operating parameters, a strength of the CVD process.
The Role of Temperature
Synthesis temperature directly impacts catalyst activity and the resulting crystalline structure of the nanotubes. An optimal temperature range ensures efficient growth while minimizing the formation of amorphous carbon and other defects.
Carbon Source and Concentration
The type of hydrocarbon gas and its concentration (or flow rate) are critical. These factors determine the carbon supply available for growth, influencing both the production rate and the potential for introducing impurities.
Catalyst Composition and Size
In the CVD method, the catalyst (typically nanoparticles of iron, nickel, or cobalt) is the seed for CNT growth. The size of the catalyst particle directly dictates the diameter of the nanotube, making catalyst engineering a crucial aspect of quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No production method is perfect. The choice always involves balancing competing priorities, which is why understanding the inherent trade-offs is crucial for making an informed decision.
Quality vs. Quantity
This is the central dilemma. Arc discharge and laser ablation prioritize crystalline perfection at the expense of yield. CVD prioritizes scalable quantity while providing sufficient quality for most commercial applications.
Cost vs. Purity
The high energy requirements and batch-process nature of arc discharge and laser ablation make them prohibitively expensive for mass production. CVD's ability to run continuously at lower temperatures gives it a significant cost advantage.
The Challenge of Post-Processing
A critical point is that CNTs produced via CVD are intimately mixed with their metal catalysts. They require a purification step (often an acid wash) to remove these impurities, a process which can introduce defects into the nanotubes' structure.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates which method is most appropriate. The "best" method is relative to the intended application.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial application (e.g., composites, electronics, coatings): Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the only viable choice due to its unmatched scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research requiring the highest possible purity: Arc discharge or laser ablation are superior, as they produce CNTs with fewer structural defects, despite their low yield and high cost.
- If your primary focus is sustainable or novel synthesis routes: Explore emerging "green" methods like methane pyrolysis or CO2 electrolysis, but be prepared for challenges in achieving consistent quality and scale.
Ultimately, the optimal production method is defined not by a universal standard of "best," but by the specific requirements of your final application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Scalability | Typical Quality | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Large-scale industrial production | High | Good to High | Requires post-processing purification |
| Arc Discharge | High-purity research applications | Low | Very High | Low yield, high cost |
| Laser Ablation | High-purity single-walled CNTs | Very Low | Exceptional | Extremely high cost, low yield |
Ready to integrate high-quality carbon nanotubes into your research or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for efficient and reliable CNT synthesis. Our expertise supports laboratories in achieving optimal results with methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition.
Let us help you scale your innovations.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and PCD coating? Process vs. Material Explained
- What is the CVD coating technique? Grow High-Performance, Durable Thin Films
- What is the temperature of LPCVD? Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What gases are typically used in the High-Density Plasma CVD (HDP-CVD) process? Optimize Your Film Deposition
- What is sputter damage? A Guide to Protecting Sensitive Materials During Thin-Film Deposition
- Which is an example of chemical vapour deposition? The CVD Process for High-Performance Materials
- What are the methods for synthesis of carbon nanotubes review? From Arc Discharge to Scalable CVD
- What are the advantages of thin film resistors? Precision, Stability & Low Noise for Sensitive Circuits



















