It is critical to distinguish between synthesis and characterization. The provided information details common synthesis (production) techniques for carbon nanotubes (CNTs), such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), laser ablation, and arc discharge. It does not, however, list any characterization techniques, which are methods used to analyze and measure the properties of the CNTs after they have been created.
The core misunderstanding to correct is the difference between making a material and measuring it. The listed techniques (CVD, arc discharge) are for synthesis—the process of creating CNTs. Characterization is the subsequent step of analyzing what you have made to understand its structure, quality, and properties.

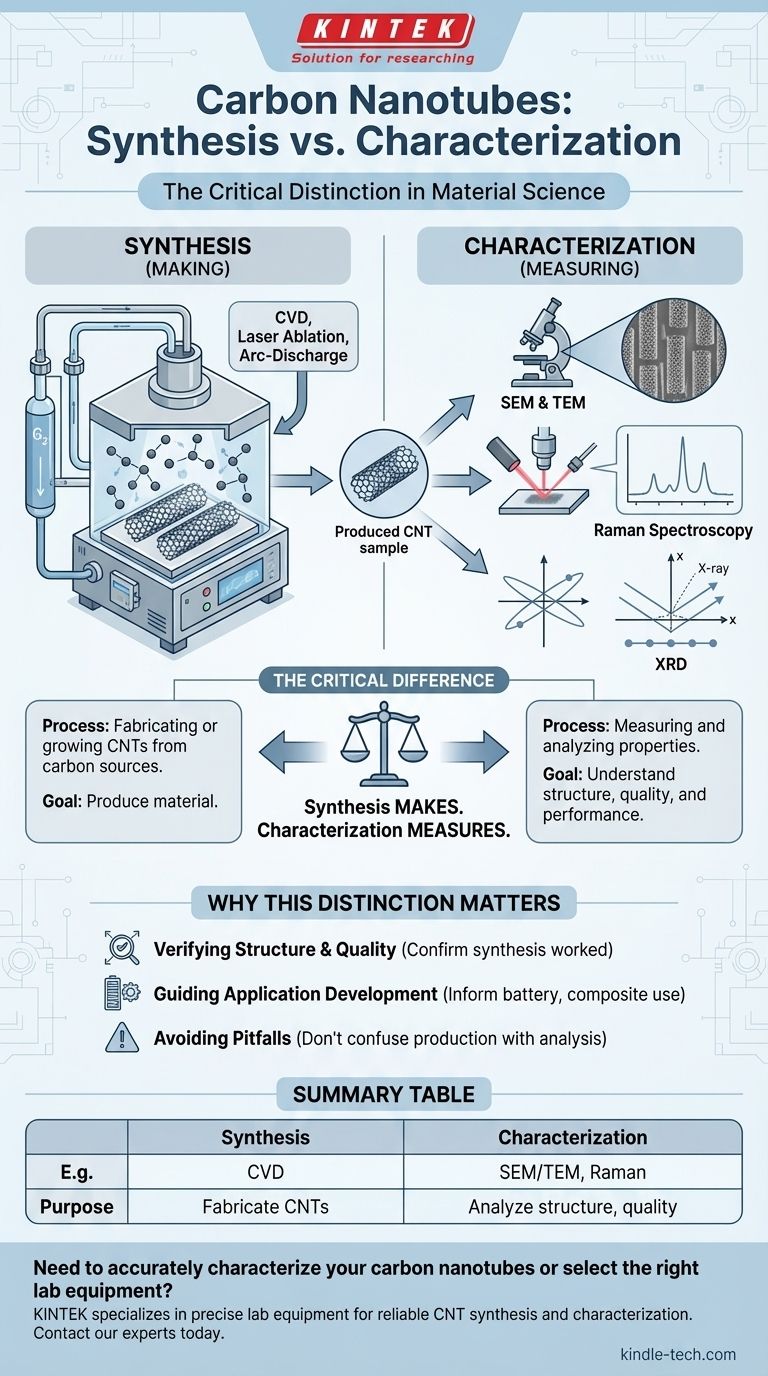
The Critical Difference: Synthesis vs. Characterization
To work with any advanced material, you must first create it and then verify what you have created. These are two distinct, essential stages of the process.
What is Synthesis?
Synthesis is the process of fabricating or growing a material. The goal is to produce CNTs from a carbon source.
The techniques mentioned in the references—laser ablation, arc-discharge, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD)—are all methods of synthesis. They describe how to make carbon nanotubes.
Key parameters in synthesis, such as temperature and carbon source, are controlled to influence the final product's quality and yield.
What is Characterization?
Characterization is the process of measuring and analyzing the properties of the material that has been synthesized. The goal is to understand its structure, dimensions, purity, and performance attributes.
Common characterization techniques for CNTs, which are not listed in the provided text, include:
- Electron Microscopy (SEM & TEM): Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) are used to visualize the nanotubes directly, revealing their length, diameter, morphology, and structural integrity.
- Raman Spectroscopy: This is one of the most powerful techniques for CNTs. It provides detailed information about their diameter, chirality (the angle of the atomic structure), and the presence of defects or impurities.
- X-ray Diffraction (XRD): XRD helps determine the crystalline structure of the CNTs and can be used to assess their alignment and purity within a sample.
Why This Distinction Matters
Failing to separate these two concepts can lead to significant problems in both research and commercial applications. The synthesis method determines the raw output, but only characterization can confirm if that output is suitable for its intended purpose.
Verifying Structure and Quality
You use characterization to confirm that your synthesis process worked correctly. For example, after producing CNTs via CVD, you would use TEM to ensure they have the desired diameter and Raman spectroscopy to check for a low level of defects.
Guiding Application Development
The properties revealed by characterization directly inform how CNTs can be used. For an application in a lithium-ion battery, you need to confirm high conductivity and purity. For a composite material, you might need to verify a high aspect ratio (length vs. diameter) to ensure mechanical strength.
Characterization provides the data needed to integrate CNTs effectively into products like conductive polymers, transparent films, and advanced sensors.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the workflow of material science helps prevent common but costly errors in judgment and resource allocation.
Confusing Production with Analysis
The most frequent error is assuming a synthesis method's name describes an analytical process. Remember: CVD makes the material; microscopy and spectroscopy measure it.
Assuming a Single "Best" Technique
There is no single "best" characterization technique. They are complementary. An electron microscope shows you what the CNT looks like, while a Raman spectrometer tells you about its vibrational and electronic structure. A comprehensive analysis requires multiple methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The technique you focus on depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is to produce CNTs: You will concentrate on optimizing a synthesis method like CVD by controlling parameters such as temperature and feedstock.
- If your primary focus is to verify the quality of existing CNTs: You will use characterization tools like electron microscopy (SEM/TEM) and Raman spectroscopy to analyze their structure and purity.
- If your primary focus is to develop a new product using CNTs: You will need both—a reliable synthesis process and rigorous characterization to ensure the material meets the precise performance specifications for your application.
Understanding the fundamental difference between making and measuring is the first step toward successfully innovating with any advanced material.
Summary Table:
| Technique Type | Common Examples | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Synthesis | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Arc-Discharge, Laser Ablation | To fabricate or grow carbon nanotubes from a carbon source. |
| Characterization | Electron Microscopy (SEM/TEM), Raman Spectroscopy, X-ray Diffraction (XRD) | To measure and analyze the structure, quality, and properties of the synthesized CNTs. |
Need to accurately characterize your carbon nanotubes or select the right lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for reliable CNT synthesis and characterization, from CVD systems to Raman spectrometers. Ensure your material's quality and performance—contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production



















