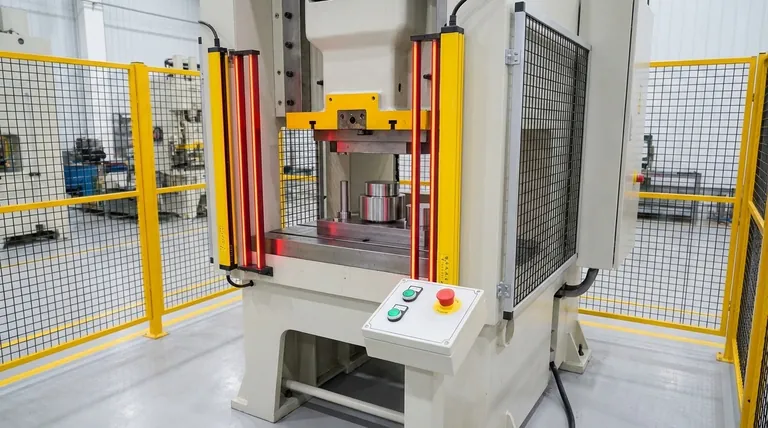
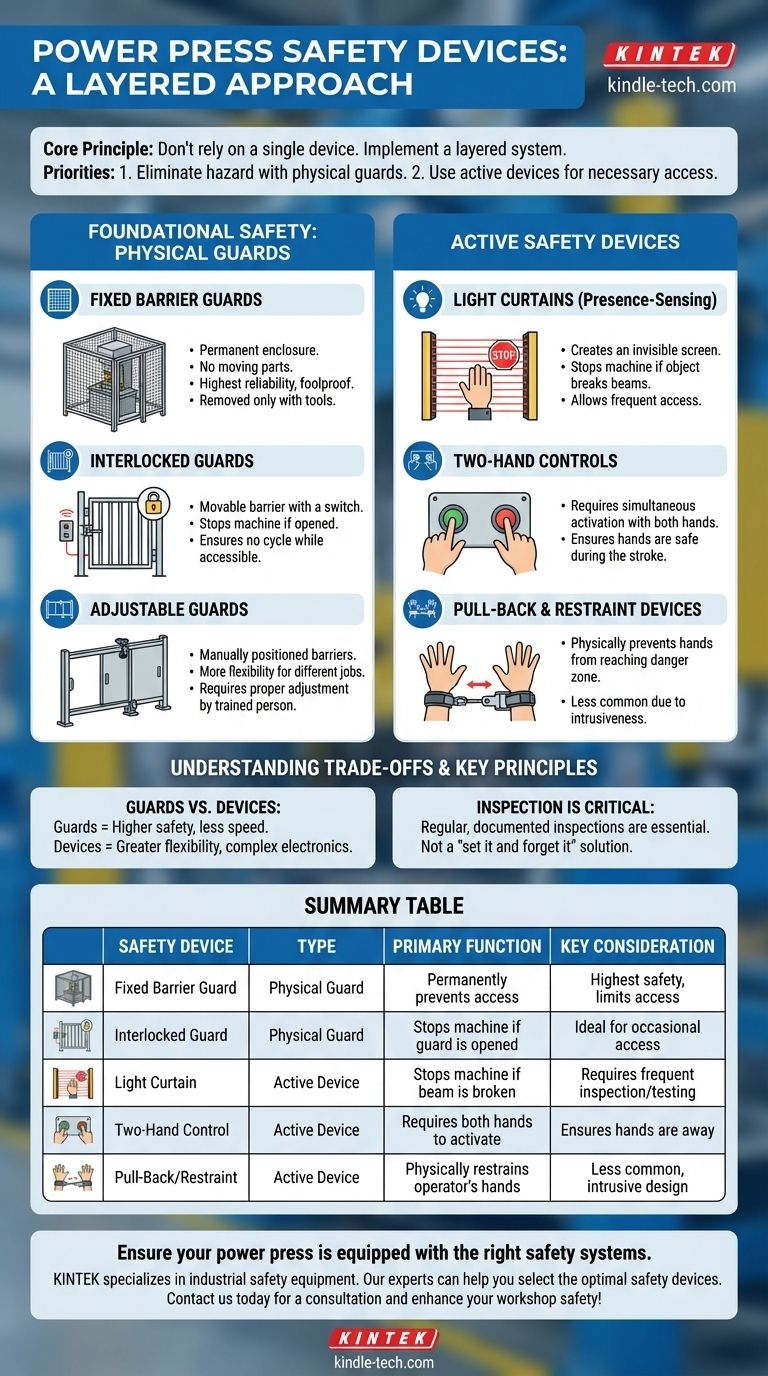
A power press machine uses a combination of physical guards and active safety devices to protect the operator. The most common systems include fixed barrier guards that physically prevent access, light curtains that stop the machine if an object crosses their path, and two-hand controls that require the operator's hands to be on the controls and away from the danger zone during the stroke.
The core principle of power press safety is not to rely on a single device, but to implement a layered system. The primary goal is always to physically eliminate the hazard with guarding; active devices are used when frequent access is essential for production.

Foundational Safety: Physical Guards
The most reliable form of safety is a physical barrier that makes it impossible to reach the point of operation—the area where the press performs its work. This is the first line of defense.
Fixed Barrier Guards
A fixed barrier guard is a permanent part of the machine enclosure. It has no moving parts and is designed to be removed only with tools, typically for maintenance. This is considered the most effective and foolproof method of guarding.
Interlocked Guards
An interlocked guard is a movable barrier, like a gate or door, equipped with a switch that is integrated into the machine's control circuit. If the guard is opened, the machine immediately stops or is prevented from starting, ensuring the press cannot cycle while the danger zone is accessible.
Adjustable Guards
Adjustable guards are physical barriers that can be manually positioned to suit different die sizes or production jobs. While offering more flexibility than fixed guards, they must be properly adjusted by a trained person for each new setup to be effective.
Active Safety Devices
When guards are not practical due to the need for frequent part loading and unloading, active safety devices are used. These systems sense the presence of the operator and stop the machine before an injury can occur.
Light Curtains (Presence-Sensing Devices)
A light curtain creates a screen of infrared beams in front of the danger zone. If any object, such as a hand or arm, breaks any of these beams while the press is in a dangerous part of its cycle, the machine's control system receives an immediate stop signal.
Two-Hand Controls
This device requires the operator to use both hands simultaneously to press two separate buttons to activate the press stroke. The buttons are spaced far enough apart that they cannot be pressed with one hand, ensuring both of the operator's hands are occupied and safely away from the point of operation during the hazardous motion.
Pull-Back and Restraint Devices
Restraint devices use straps attached to the operator's wrists and a fixed anchor point to physically prevent their hands from ever reaching the danger zone. Pull-back devices are similar but are mechanically linked to the machine's ram, actively pulling the operator's hands away as the stroke begins. These are less common today due to their intrusive nature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right safety system involves balancing absolute security with operational efficiency. A misunderstanding of these trade-offs can lead to compromised safety.
Guards vs. Devices
Fixed guards offer the highest level of safety because they are simple and difficult to bypass. However, they can slow down production if operators need constant access. Light curtains and other devices offer greater flexibility and speed but depend on complex electronics and regular inspection to function correctly.
The Danger of a Single System
Relying on only one safety method is a common pitfall. A robust safety plan uses a layered approach. For example, a machine might have fixed guards on the sides and back, with a light curtain at the front for part loading. This combines the reliability of guarding with the flexibility of a presence-sensing device.
Critical Need for Inspection and Maintenance
Safety devices are not "set it and forget it" solutions. They are subject to wear, damage, and misalignment. Regular, documented inspections (often required by safety regulations like OSHA) are absolutely essential to ensure the system, including the press's own braking mechanism, is working as designed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection should be based on a thorough risk assessment of the specific task being performed on the press.
- If your primary focus is maximum, foolproof protection on a dedicated, automated process: Use fixed barrier guarding to completely enclose the point of operation.
- If your primary focus is high-speed production requiring frequent manual loading: A light curtain is often the most effective solution for protecting the operator while maintaining efficiency.
- If your primary focus is operator-intensive work with smaller parts: Two-hand controls provide an excellent way to ensure the operator's hands are clear during the stroke.
- For all applications: Always supplement primary systems with clearly marked emergency stop buttons (E-stops) and ensure the machine's control and braking systems are safety-rated and properly maintained.
A well-designed safety system is the foundation for both protecting your team and enabling safe, efficient production.
Summary Table:
| Safety Device | Type | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Barrier Guard | Physical Guard | Permanently prevents access to danger zone | Highest safety, but limits access |
| Interlocked Guard | Physical Guard | Stops machine if guard is opened | Ideal for areas needing occasional access |
| Light Curtain | Active Device | Stops machine if beam is broken | Requires frequent inspection and testing |
| Two-Hand Control | Active Device | Requires both hands to activate press stroke | Ensures hands are away from danger zone |
| Pull-Back/Restraint | Active Device | Physically restrains operator's hands | Less common due to intrusive design |
Ensure your power press is equipped with the right safety systems. KINTEK specializes in industrial safety equipment and consumables, serving laboratory and manufacturing needs. Our experts can help you select and implement the optimal safety devices for your specific application, ensuring compliance and protecting your team. Contact us today for a consultation and enhance your workshop safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- Why is precise temperature and pressure control necessary for combustible cartridge cases? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- Why is hot press molding preferred over traditional solution casting? Expert Comparison for Polymer Electrolytes
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during hot pressing? Optimize Boron Carbide Sintering at 1850°C














