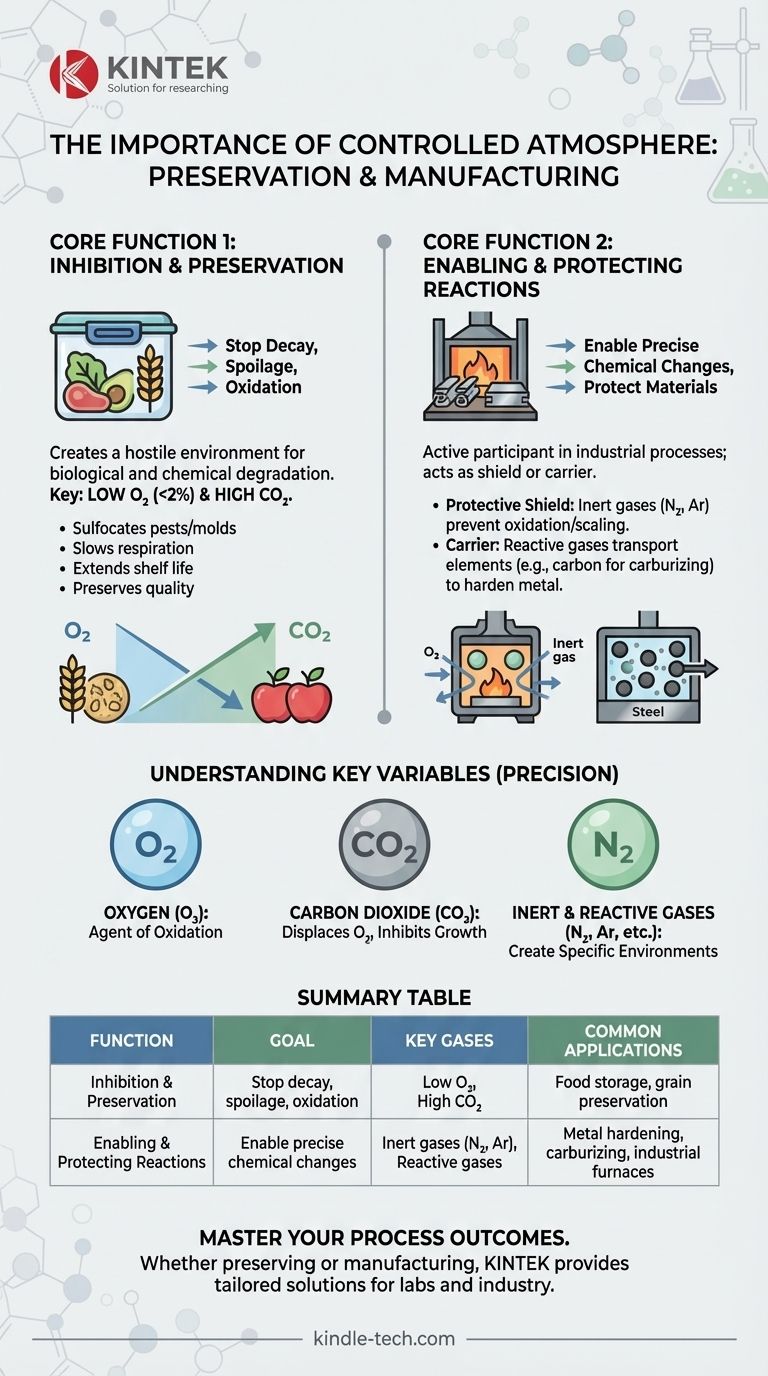
At its core, a controlled atmosphere is a powerful tool for preservation and manufacturing. It involves deliberately altering the normal atmospheric composition within a sealed environment to achieve a specific outcome, either by preventing unwanted decay or by enabling precise chemical reactions.
A controlled atmosphere is not about one specific gas mixture; it is the strategic manipulation of the air to either inhibit natural processes like spoilage and oxidation, or to promote specific chemical changes required for industrial processes like hardening metal.
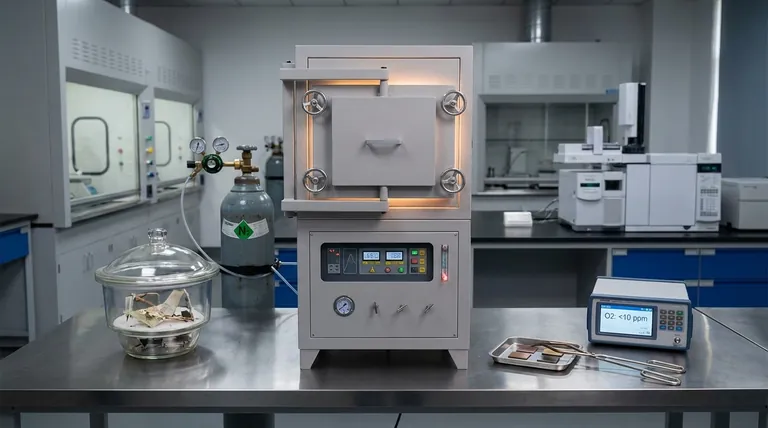

The Two Core Functions of Atmosphere Control
The importance of a controlled atmosphere stems from its two primary, and nearly opposite, applications: preventing change and causing change.
Function 1: Inhibition and Preservation
In many contexts, the goal is to stop or drastically slow down natural processes. This is accomplished by creating an environment hostile to biological or chemical degradation.
A primary example is in food and grain storage. By sealing a storage facility and increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide while reducing oxygen, you effectively suffocate the processes that cause spoilage.
Most insects and molds cannot survive when oxygen levels fall below 2%. Furthermore, the grain's own respiration process, which leads to decay, is significantly slowed, extending its life and preserving its quality.
Function 2: Enabling and Protecting Reactions
In industrial settings, the atmosphere is often an active participant in the process. It can be used to protect a material or to fundamentally change its properties.
In industrial furnaces, a controlled atmosphere can act as a protective shield. Flooding the chamber with an inert gas prevents oxygen from reacting with hot metal, which would otherwise cause scaling or oxidation (rust).
Conversely, the atmosphere can be a carrier for elements that need to be introduced into a material. Processes like carburizing or hardening rely on a specific gas mixture to transport carbon into the surface of steel, creating a harder, more durable final product.
Understanding the Key Variables
Controlling an atmosphere is a game of precision. The balance of a few key gases determines the outcome.
The Role of Oxygen (O₂)
Oxygen is the agent of oxidation and is essential for most biological life. Removing oxygen is the most common goal in preservation, as it prevents rust, stops mold growth, and kills pests.
The Role of Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
In preservation, increasing carbon dioxide helps displace oxygen and creates an acidic environment that inhibits the growth of many microorganisms.
The Role of Inert and Reactive Gases
In manufacturing, gases like nitrogen or argon are used to create an inert, non-reactive environment. Other gases are used specifically for their ability to react with the material to achieve desired properties.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The right atmospheric strategy depends entirely on whether you are trying to stop a process or create one.
- If your primary focus is preservation: Your goal is to create an inert or hostile environment, which almost always involves minimizing or eliminating oxygen.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing or material treatment: Your goal is to use the atmosphere as a precise tool, either to protect the material from reactions or to cause a very specific one.
Ultimately, mastering the atmosphere is about mastering the outcome of your process.
Summary Table:
| Function | Goal | Key Gases | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition & Preservation | Stop decay, spoilage, oxidation | Low O₂, High CO₂ | Food storage, grain preservation |
| Enabling & Protecting Reactions | Enable precise chemical changes | Inert gases (N₂, Ar), Reactive gases | Metal hardening, carburizing, industrial furnaces |
Ready to master your process outcomes with precision atmosphere control? Whether you need to preserve materials or enable advanced manufacturing reactions, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help. We provide tailored solutions for laboratories and industrial settings to ensure your controlled atmosphere processes are efficient and effective. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- What is an inert condition? A Guide to Preventing Fires and Explosions
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained



















