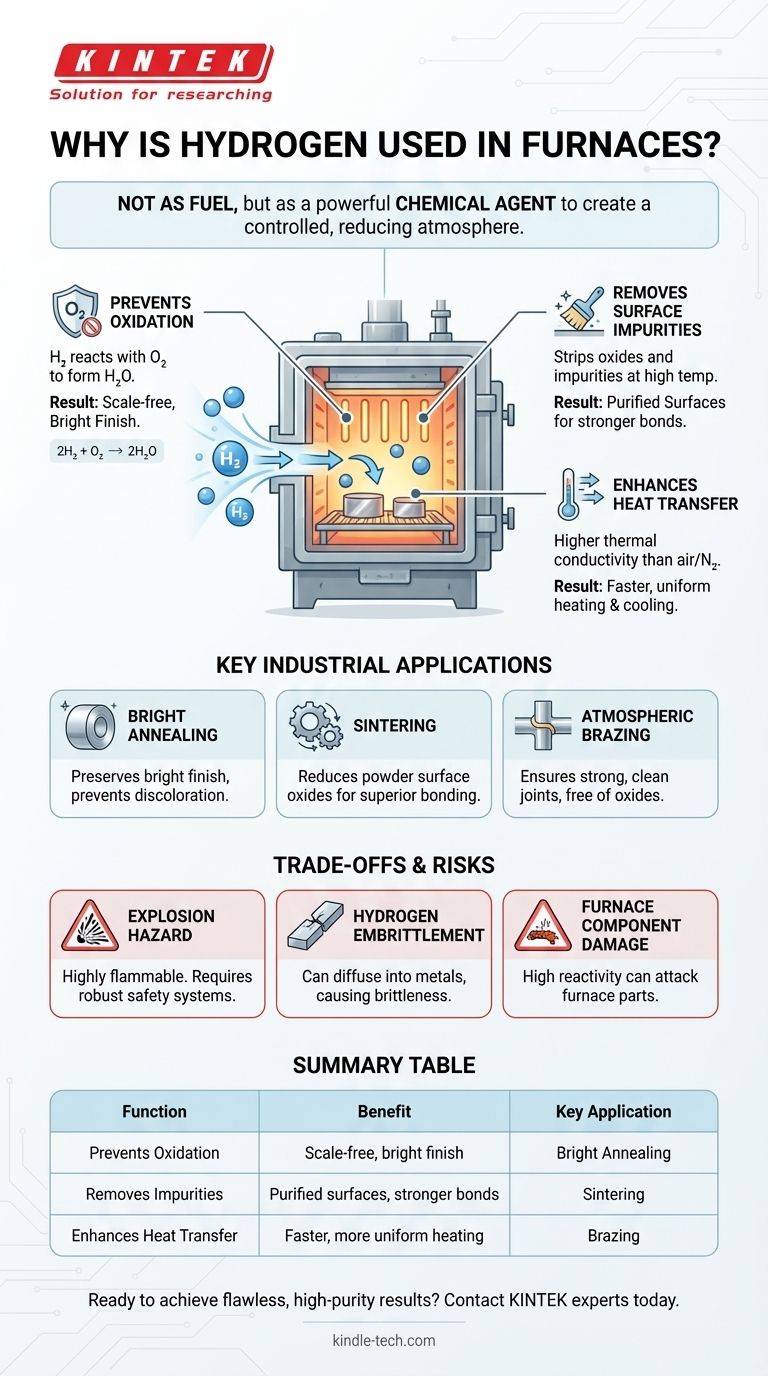
In short, hydrogen is used in industrial furnaces to create a highly reactive, controlled atmosphere that actively protects and refines materials during high-temperature processing. Its primary functions are to prevent oxidation by removing oxygen and to improve the speed and uniformity of heating and cooling due to its high thermal conductivity.
The core takeaway is that hydrogen is not used as a fuel in this context. Instead, it serves as a powerful chemical agent inside the furnace, creating a "reducing atmosphere" that purifies metal surfaces and prevents corrosion, enabling processes like bright annealing and high-purity sintering.
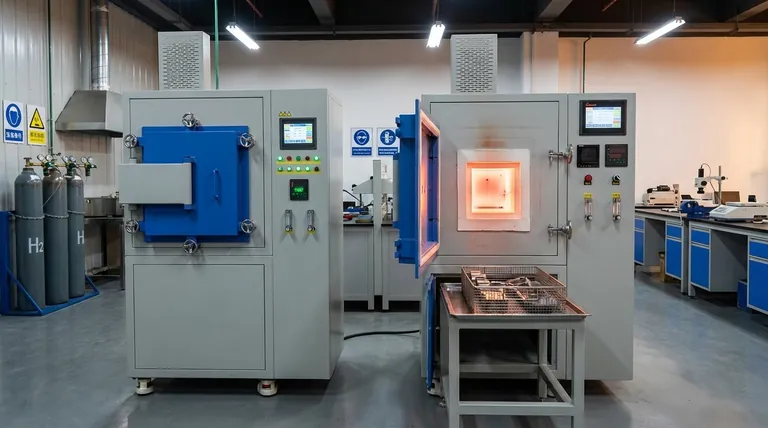

Why a Hydrogen Atmosphere is Critical
In many high-temperature applications, simply heating a metal in ambient air is destructive. The oxygen in the air rapidly reacts with the hot metal surface, forming oxides (scale or rust). A controlled atmosphere replaces the air with a specific gas mixture to dictate the chemical reactions that occur.
Preventing Oxidation
The most fundamental purpose of a hydrogen atmosphere is to eliminate oxygen. Hydrogen is an excellent deoxidizer.
It actively seeks out and reacts with any trace oxygen inside the furnace, forming water vapor (2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O) that can be safely vented. This prevents the metal parts from oxidizing, resulting in a clean, scale-free, and often shiny surface known as a bright finish.
Removing Surface Impurities
Beyond preventing new oxides from forming, hydrogen can reverse existing oxidation.
At high temperatures, it reacts with and strips away surface oxides and other impurities, such as silica, from the material. This purification step is critical in processes like sintering, where clean particle surfaces are necessary for strong metallurgical bonds.
Enhancing Heat Transfer
Hydrogen has a much higher thermal conductivity than air or nitrogen.
This physical property allows it to transfer heat to and from the parts much more quickly and evenly. The result is faster heating and cooling cycles, which can improve throughput and provide more precise control over the material's final properties.
Key Industrial Applications
Certain manufacturing processes are impossible or inefficient without a hydrogen atmosphere.
Bright Annealing
Annealing is a process of heating and slow cooling to soften metals and relieve internal stresses. When performed in a hydrogen atmosphere, it prevents any surface discoloration or scaling, preserving the metal's bright, clean finish.
Sintering
Sintering involves heating compacted metal powders to just below their melting point to fuse them into a solid part. A hydrogen atmosphere is crucial for reducing oxides on the surfaces of the powder particles, allowing for better bonding and resulting in parts with superior mechanical qualities.
Atmospheric Brazing
Brazing joins two metal parts using a filler metal. Using a continuous belt furnace with a hydrogen atmosphere allows for a high-volume, cost-effective process that ensures the joints are strong, clean, and free of oxides.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, using hydrogen is not without significant challenges that require careful engineering and control.
The Explosion Hazard
Hydrogen is highly flammable and can be explosive when mixed with air. Furnaces using hydrogen must be equipped with robust, explosion-proof safety provisions, leak detection systems, and strict operational protocols to ensure safety.
Material Degradation (Hydrogen Embrittlement)
Hydrogen can diffuse into the structure of certain metals, particularly high-carbon steels, and cause them to become brittle and fail under stress. This phenomenon, known as hydrogen embrittlement, must be carefully considered when selecting materials for processing.
Furnace Component Damage
The high reactivity of hydrogen at elevated temperatures can damage the furnace itself. Common heating elements like silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) can be chemically attacked. To prevent this, furnaces often use a protective inner chamber, or retort, to contain the hydrogen atmosphere and isolate it from the heating elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding whether to use a hydrogen atmosphere depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is a flawless, bright surface finish and maximum purity: A pure, dry hydrogen atmosphere is essential for applications like bright annealing stainless steel or sintering advanced metal components.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment without strict surface requirements: Other controlled atmospheres, such as inert nitrogen or a less-concentrated hydrogen/nitrogen mix ("forming gas"), may be safer and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is processing high-carbon steels or sensitive alloys: You must account for hydrogen embrittlement and may need a specialized furnace design with a retort to prevent damage.
Ultimately, hydrogen is a precision tool used to achieve metallurgical results that are impossible in a standard atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Creates a scale-free, bright finish | Bright Annealing |
| Removes Impurities | Purifies surfaces for stronger bonds | Sintering |
| Enhances Heat Transfer | Faster, more uniform heating/cooling | Brazing |
Ready to achieve flawless, high-purity results in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in furnaces and lab equipment designed for controlled atmosphere processing. Whether your application requires bright annealing, high-purity sintering, or atmospheric brazing, our solutions ensure safety, precision, and superior outcomes.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a hydrogen atmosphere furnace can transform your material processing and meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- Why is a hydrogen atmosphere furnace necessary for W-Cu composite? Unlock Superior Infiltration and Density
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- What are hydrogen furnaces used for? Achieve Purity and Speed in High-Temperature Processing
- Why must a hydrogen-reducing atmosphere be maintained for tungsten annealing? Ensure Purity in High-Temp Processing



















