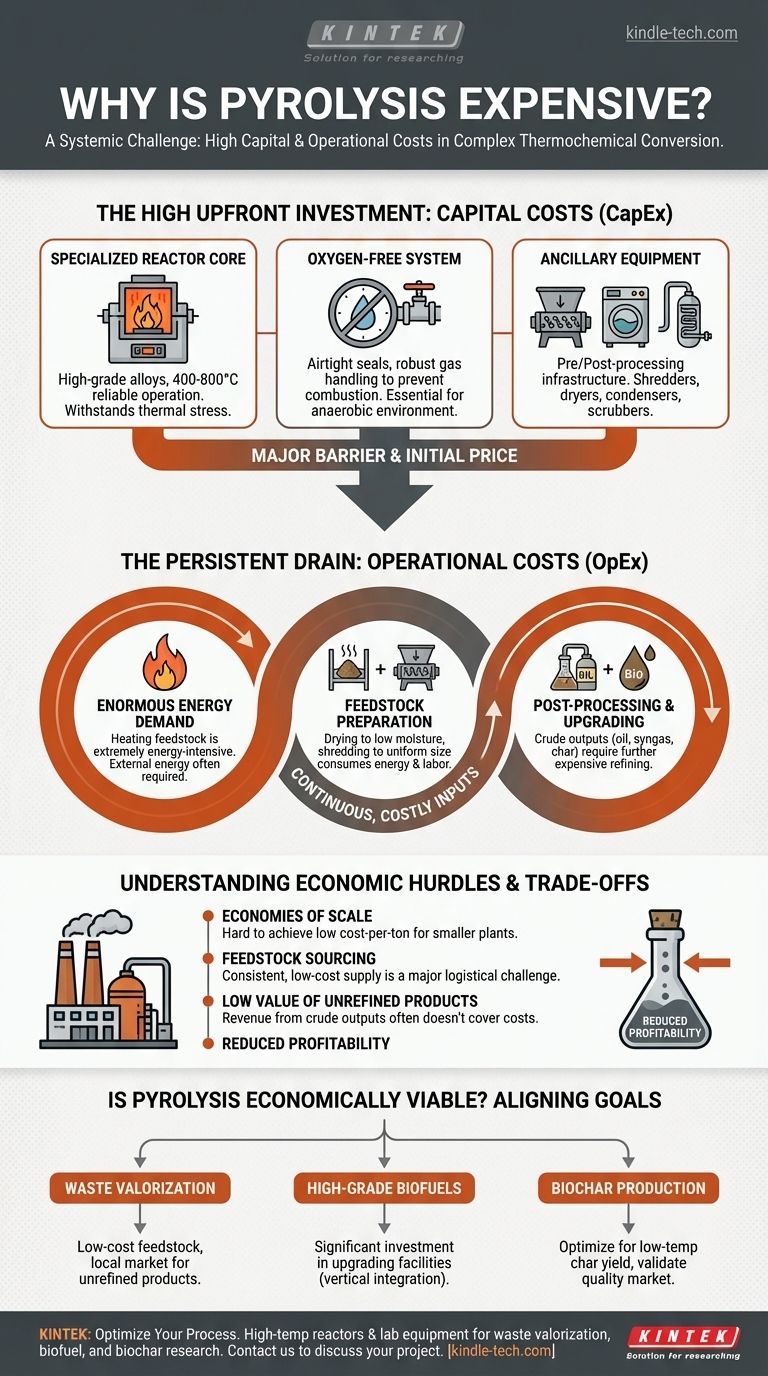
Pyrolysis is expensive because it combines the high capital costs of a specialized, high-temperature chemical reactor with the significant operational costs of continuous energy input and multi-stage material processing. It is not a simple "burn" but a precise, energy-intensive thermochemical conversion that requires substantial investment before, during, and after the core reaction.
The high cost of pyrolysis is a systemic challenge rooted in the fundamental physics of heating material in an oxygen-free environment and the chemical complexity of preparing the feedstock and refining the crude outputs into valuable products.

The High Upfront Investment: Deconstructing Capital Costs (CapEx)
The initial price of a pyrolysis plant is a major barrier, driven by the specialized nature of the equipment required to control a high-temperature, anaerobic reaction.
The Specialized Reactor Core
The heart of the plant is the reactor, which must operate reliably at temperatures between 400°C and 800°C (750°F to 1470°F).
This requires construction from expensive, high-grade alloys (like stainless steel or Inconel) that can withstand thermal stress and potential corrosion without failing.
The Necessity of an Oxygen-Free System
Pyrolysis is, by definition, thermal decomposition without oxygen. If oxygen enters the reactor, the feedstock will simply combust, ruining the process and creating hazardous conditions.
Achieving and maintaining this anaerobic environment requires sophisticated and costly engineering, including airtight seals, specialized feeding mechanisms, and robust gas handling systems.
Ancillary Equipment for a Full Workflow
A functional plant is far more than just the reactor. Significant capital is required for the surrounding infrastructure.
This includes pre-processing equipment like industrial shredders and dryers, and post-processing equipment such as condensers to capture pyrolysis oil, scrubbers to clean syngas, and systems for handling and storing biochar.
The Persistent Drain: Understanding Operational Costs (OpEx)
Once built, a pyrolysis plant requires continuous, costly inputs to run effectively. These recurring expenses are a primary factor in its overall economic profile.
The Enormous Energy Demand for Heating
Heating tons of feedstock to the required reaction temperature and keeping it there is an extremely energy-intensive process.
While the non-condensable syngas produced during pyrolysis can be looped back to provide some of this heat, it is often not enough to make the process self-sustaining. This reliance on external energy, especially during startup and for certain feedstocks, is a major operational cost.
The "Hidden" Cost of Feedstock Preparation
Raw materials like biomass, plastic, or tires are rarely ready for pyrolysis. They must be prepared to a specific standard, which consumes both energy and labor.
Feedstock typically needs to be dried to a low moisture content (an energy-intensive step) and shredded to a uniform particle size to ensure efficient heat transfer within the reactor.
The Demands of Post-Processing and Upgrading
The direct outputs of pyrolysis—pyrolysis oil (bio-oil), syngas, and char—are crude products with limited immediate value.
Pyrolysis oil, for example, is often acidic, unstable, and contains high levels of water and oxygen. Upgrading it into a stable, usable biofuel requires further expensive processing, such as hydrotreating, which is a complex chemical refining process in its own right.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Economic Hurdles
The high direct costs are compounded by broader economic and logistical challenges that can impact the profitability of a pyrolysis venture.
The Challenge of Achieving Economies of Scale
Like many industrial processes, pyrolysis benefits from economies of scale. However, the high initial investment and feedstock sourcing challenges mean many plants are built at a smaller, less economically efficient scale.
These smaller operations struggle to reduce their cost-per-ton of processed material, making it difficult to compete with larger, established industries.
Feedstock Sourcing and Consistency
The ideal feedstock for pyrolysis is consistent, dry, and available at a very low or even negative cost (i.e., a tipping fee is paid to take it).
In reality, securing a stable, long-term supply of suitable feedstock is a major logistical challenge. Variability in the material's composition or moisture content can disrupt the process, reduce yield, and lower product quality.
The Low Value of Unrefined Products
Without significant investment in upgrading and refining, the revenue generated from raw pyrolysis products may not be sufficient to cover the high capital and operational costs. The business model is highly sensitive to the market prices for crude pyrolysis oil and char.
Is Pyrolysis Economically Viable for Your Goal?
To determine if pyrolysis is the right choice, you must align the technology's economic realities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is waste valorization (e.g., end-of-life tires or plastics): Your economic model must hinge on securing a consistent, low-cost (or negative-cost) feedstock and identifying a local market for the unrefined products to minimize transport and upgrading costs.
- If your primary focus is producing high-grade biofuels: Be prepared for a vertically integrated project with significant capital investment in both the core pyrolysis unit and the downstream upgrading facilities required to create a finished fuel.
- If your primary focus is biochar production: Your process should be optimized for lower temperatures to maximize char yield, and you must validate a market for your specific quality of char, whether in agriculture or specialty applications.
Understanding these inherent cost drivers is the first step toward engineering a pyrolysis project that is not just technically sound, but economically viable.
Summary Table:
| Cost Driver | Key Factors | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs (CapEx) | Specialized reactor (high-grade alloys), oxygen-free system, ancillary equipment | High upfront investment |
| Operational Costs (OpEx) | Energy for heating, feedstock drying/shredding, post-processing (oil upgrading) | Continuous financial drain |
| Economic Hurdles | Scale limitations, feedstock variability, low-value crude products | Reduced profitability |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process or explore cost-effective lab solutions? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature reactors and lab equipment for waste valorization, biofuel production, and biochar research. Our expertise helps you navigate capital and operational challenges—contact us today to discuss your project needs and how we can support your goals. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















