In short, sieve analysis is important because it determines a soil's grain size distribution, a fundamental property that directly influences its strength, permeability, and overall engineering behavior. This simple test provides the foundational data needed to classify soil and predict how it will perform under various construction and environmental conditions.
Understanding a soil's composition is not an academic exercise; it's the basis for predicting its real-world performance. Sieve analysis is the primary tool for coarse-grained soils, translating a simple sample into critical predictions about water flow, stability, and load-bearing capacity.

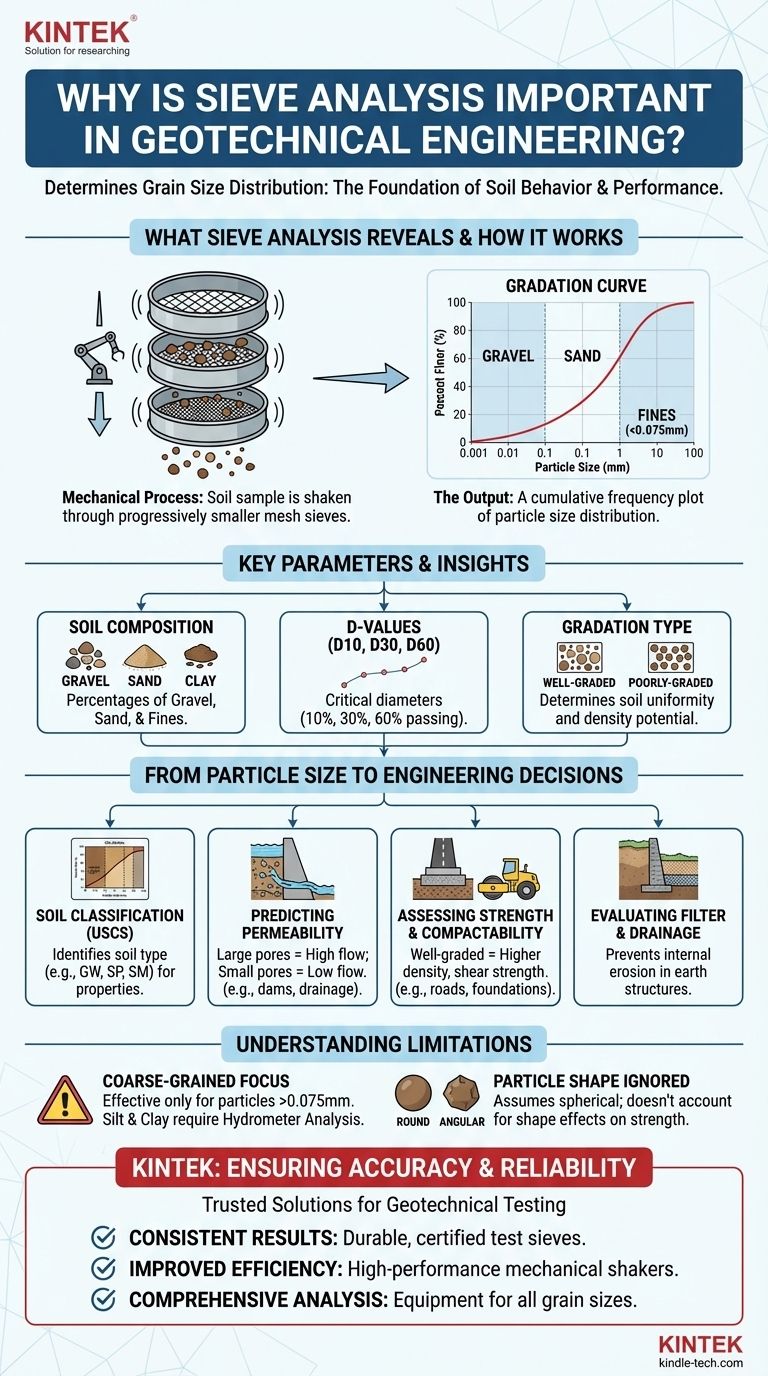
What Sieve Analysis Reveals: The Gradation Curve
Sieve analysis is a mechanical procedure used to assess the particle size distribution of a granular material. Its simplicity and reliability make it a cornerstone of geotechnical testing.
The Mechanics of the Test
A dried soil sample with a known weight is placed on top of a stack of wire-mesh sieves. Each sieve has progressively smaller openings, from top to bottom.
The stack is mechanically shaken, causing particles to fall through until they are retained on a sieve with openings smaller than their diameter. The material retained on each sieve is weighed, and the results are used to plot a grain size distribution curve.
The Output: The Gradation Curve
The result is not a single number, but a gradation curve. This graph plots the percentage of the soil that is finer than a given particle size. The shape of this curve tells a detailed story about the soil's composition.
Key Classification Parameters
From this curve, we determine percentages of gravel, sand, and fines (silt and clay). Fines are defined as particles that pass through the No. 200 sieve (0.075 mm). This initial breakdown is the first step in any soil classification.
We also identify key diameters like D10, D30, and D60, which represent the particle sizes at which 10%, 30%, and 60% of the soil (by weight) is finer. These values are not just abstract points; they are essential inputs for further analysis.
From Particle Size to Engineering Decisions
The true importance of sieve analysis lies in how its results are used to make critical engineering and design decisions. The gradation curve is the key that unlocks predictions about soil behavior.
Soil Classification
The primary use of sieve analysis is to classify coarse-grained soils (sands and gravels) using systems like the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS). Classification tells an engineer whether they are dealing with a well-graded gravel (GW), a poorly-graded sand (SP), or silty sand (SM), each with vastly different engineering properties.
Predicting Hydraulic Conductivity (Permeability)
The size of soil particles directly controls the size of the void spaces between them. Water flows through these voids.
Soils dominated by large particles (like clean gravels) have large voids and thus high permeability. Soils with many fine particles have small, tortuous void spaces and low permeability. This is critical for designing dams, landfills, and drainage systems.
Assessing Strength and Compactability
A well-graded soil, which has a wide distribution of particle sizes, can typically be compacted to a higher density than a poorly-graded (or uniform) soil.
The smaller particles fill the voids between the larger ones, creating a dense, interlocked mass with higher shear strength. This information is vital for constructing stable foundations, road bases, and earthen embankments.
Evaluating Filter and Drainage Suitability
In earth dams and retaining walls, filter layers are needed to allow water to pass without washing away fine soil particles. Sieve analysis of both the base soil and the proposed filter material is used to ensure they meet specific criteria for filtration and drainage, preventing internal erosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While fundamental, sieve analysis is not a complete picture of soil behavior. Understanding its limits is key to using it properly.
The Coarse-Grained Focus
Sieve analysis is only effective for particles larger than 0.075 mm (those retained on the No. 200 sieve). It cannot distinguish between silt and clay, whose properties are governed by plasticity and mineralogy, not just size.
The Need for Hydrometer Analysis
For the fine-grained portion of a soil (silts and clays), a hydrometer test must be performed. This test uses the principle of sedimentation to determine the particle size distribution of materials too small for sieving. A complete analysis often involves both tests.
Particle Shape is Ignored
The test inherently assumes particles are roughly spherical. However, the shape of particles (e.g., rounded vs. angular) also significantly affects soil strength and packing. Angular particles tend to have higher shear strength than rounded ones, a factor not captured by sieve analysis alone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The gradation curve is a multi-purpose tool. How you interpret it depends entirely on your project's objective.
- If your primary focus is foundation stability: Use the classification and gradation to estimate the soil's shear strength and its potential for compaction, which dictates its bearing capacity.
- If your primary focus is drainage or seepage control: Use the D10 size and overall gradation to estimate the soil's hydraulic conductivity and design effective filters or drainage blankets.
- If your primary focus is earthworks and road construction: Use the gradation curve to assess the material's suitability for use as fill and to predict the maximum density you can achieve through compaction.
- If your primary focus is hazard assessment: Use the gradation curve to screen for soils that are highly susceptible to frost heave or liquefaction, such as uniform fine sands.
Ultimately, this simple and inexpensive test provides the essential framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of coarse-grained soils.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Analysis Parameter | What It Reveals | Key Engineering Application |
|---|---|---|
| Gradation Curve | Particle size distribution (Gravel, Sand, Fines) | Soil Classification (USCS) |
| D10, D30, D60 Sizes | Key diameters for gradation analysis | Estimating Hydraulic Conductivity (Permeability) |
| Well-Graded vs. Poorly-Graded | Distribution of particle sizes | Assessing Compactability & Shear Strength |
| Fines Content (Passing #200 Sieve) | Percentage of silt and clay | Identifying need for further testing (e.g., Hydrometer Analysis) |
Ready to ensure the accuracy and reliability of your geotechnical testing?
The right lab equipment is fundamental to obtaining precise sieve analysis results. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality sieves, shakers, and sample preparation tools trusted by geotechnical laboratories worldwide.
We help you:
- Achieve Consistent Results: With durable, certified test sieves that deliver reliable gradation data.
- Improve Workflow Efficiency: Our mechanical sieve shakers ensure thorough, repeatable sample processing.
- Support Comprehensive Analysis: From coarse sieves for gravel to the No. 200 sieve for fines, we have the equipment you need for a complete assessment.
Contact us today to discuss your specific soil testing requirements and let our experts help you build a safer, more reliable foundation for your projects.
#ContactForm to get a personalized quote or technical support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials



















