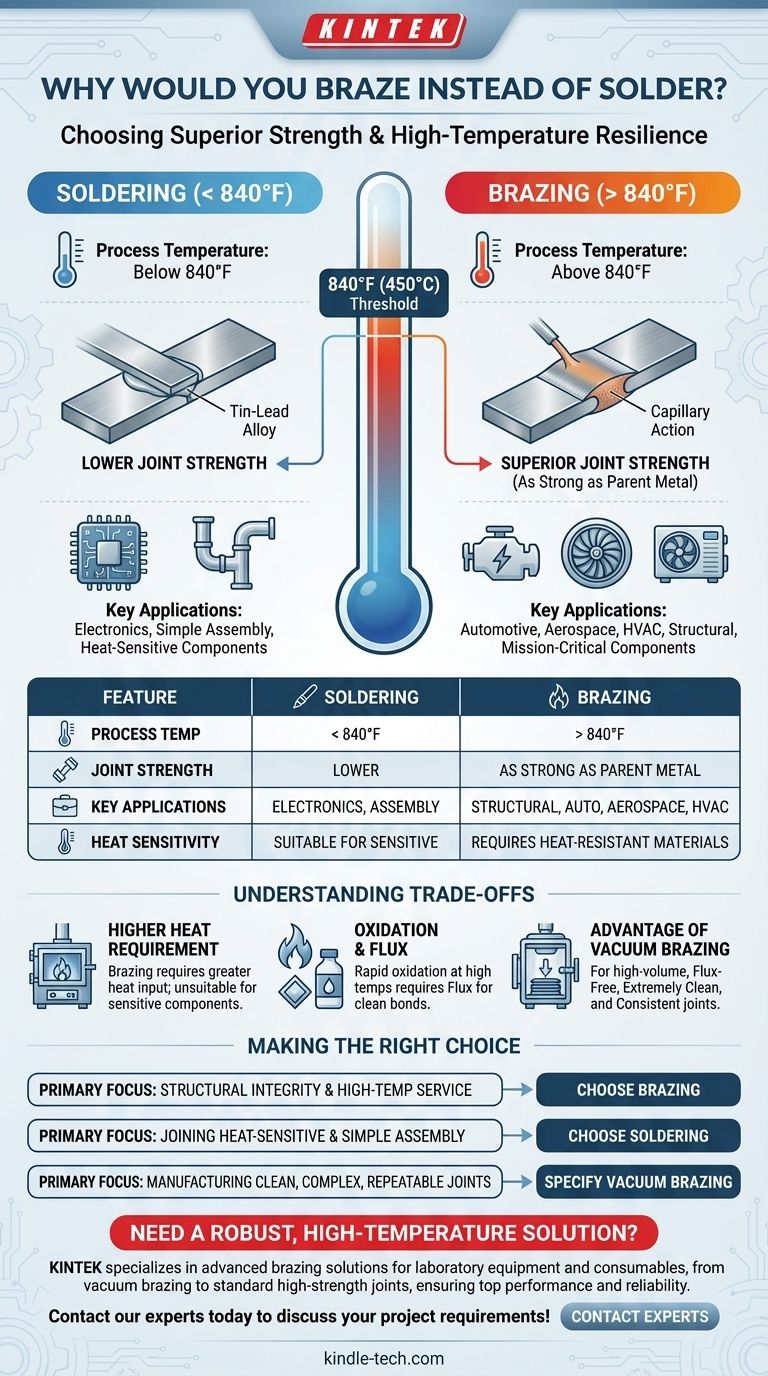
The primary reasons to choose brazing over soldering are for applications demanding superior joint strength and the ability to withstand high service temperatures. While both processes join metals without melting them, brazing uses higher-temperature filler alloys to create bonds that are often as strong as the parent materials themselves, making it ideal for structural and mission-critical components.
The decision between brazing and soldering is fundamentally a choice about performance requirements. You select brazing when the mechanical strength and thermal resilience of the final joint are non-negotiable.

The Fundamental Difference: Temperature
The core distinction between brazing and soldering is the temperature at which the process occurs. This single factor dictates the types of filler metals used, the resulting joint strength, and the applications for which each method is suitable.
Defining the 840°F (450°C) Threshold
By industry definition, soldering occurs at temperatures below 840°F (450°C).
In contrast, brazing is always performed at temperatures above 840°F (450°C), though still below the melting point of the base metals being joined.
How Temperature Dictates Filler Metal and Strength
This temperature difference is not arbitrary. It allows brazing to use filler alloys (like silver, copper, and nickel) that have significantly higher strength and better metallurgical properties than the lead- or tin-based alloys used in soldering.
Why Brazing Delivers Superior Performance
The higher process temperature of brazing enables a fundamentally different kind of bond, resulting in joints that are far more robust and reliable than soldered connections.
Achieving a Strong Metallurgical Bond
Brazing creates a strong metallurgical bond between the filler metal and the base materials. The filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting joint via capillary action, diffuses slightly into the base metals, and forms a solid, cohesive connection upon cooling.
Joints as Strong as the Parent Metal
A properly executed brazed joint is exceptionally strong. In many cases, the finished joint will be as strong or even stronger than the original base metals it connects.
Suitability for Critical Applications
This inherent strength is why brazing is the preferred method in demanding industries. It's used for critical components in automotive, aerospace, and HVAC systems where joint failure is not an option.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing brazing introduces a different set of process demands. The higher heat required presents both challenges and opportunities compared to the relative simplicity of soldering.
The Higher Heat Requirement
Brazing requires a much greater heat input, which means components must be able to withstand these temperatures without warping or suffering damage. This often rules it out for joining sensitive electronics.
Oxidation and the Need for Flux
At brazing temperatures, metals oxidize rapidly. To ensure a clean, strong bond, a flux is almost always required to remove and prevent oxides, or the process must be done in a controlled atmosphere.
The Advantage of Vacuum Brazing
For high-volume production, vacuum brazing offers a superior solution. By performing the process in a vacuum, the need for flux is eliminated, preventing oxidation and resulting in extremely clean parts with excellent consistency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your project. The trade-off is between the low-impact nature of soldering and the high-performance result of brazing.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and high-temperature service: Choose brazing for its unparalleled joint strength and thermal resilience.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive components or simple assembly: Choose soldering for its low-temperature process and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing clean, complex, and highly repeatable joints: Specify a controlled process like vacuum brazing.
Ultimately, selecting the correct joining method is about matching the process capabilities to your application's end-use requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Soldering | Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Below 840°F (450°C) | Above 840°F (450°C) |
| Joint Strength | Lower | As strong as parent metals |
| Key Applications | Electronics, simple assembly | Structural, automotive, aerospace, HVAC |
| Heat Sensitivity | Suitable for sensitive components | Requires heat-resistant materials |
Need a robust, high-temperature solution for your lab equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced brazing solutions for laboratory equipment and consumables. Whether you require the precision of vacuum brazing for complex assemblies or standard brazing for durable, high-strength joints, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Let us help you select the right joining process for your specific application. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are some applications of brazing? Join Dissimilar Metals with Strong, Leak-Proof Bonds
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds



















