No, metals are fundamentally not easy to compress. They are, in fact, exceptionally resistant to any force attempting to reduce their volume. This high resistance to compression is a defining characteristic that originates from their unique atomic structure and the powerful electrostatic forces that govern it.
While we often see metals being bent, stretched, or reshaped, these actions primarily involve changing the material's shape, not significantly reducing its volume. True volumetric compression requires overcoming the immense repulsive forces between atomic nuclei, making metals one of the most incompressible classes of materials available.
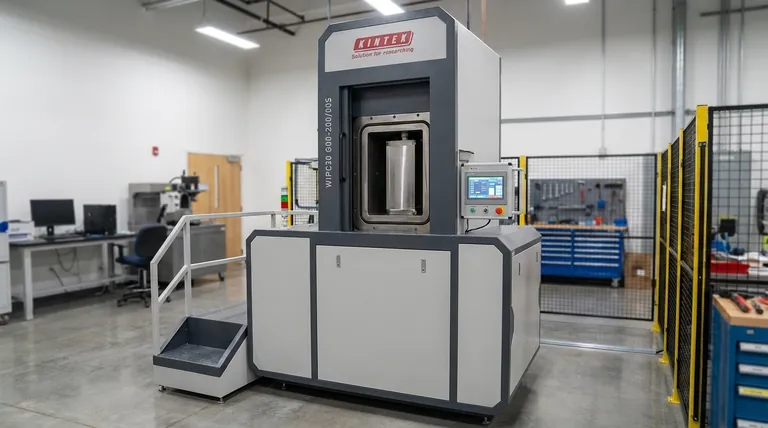

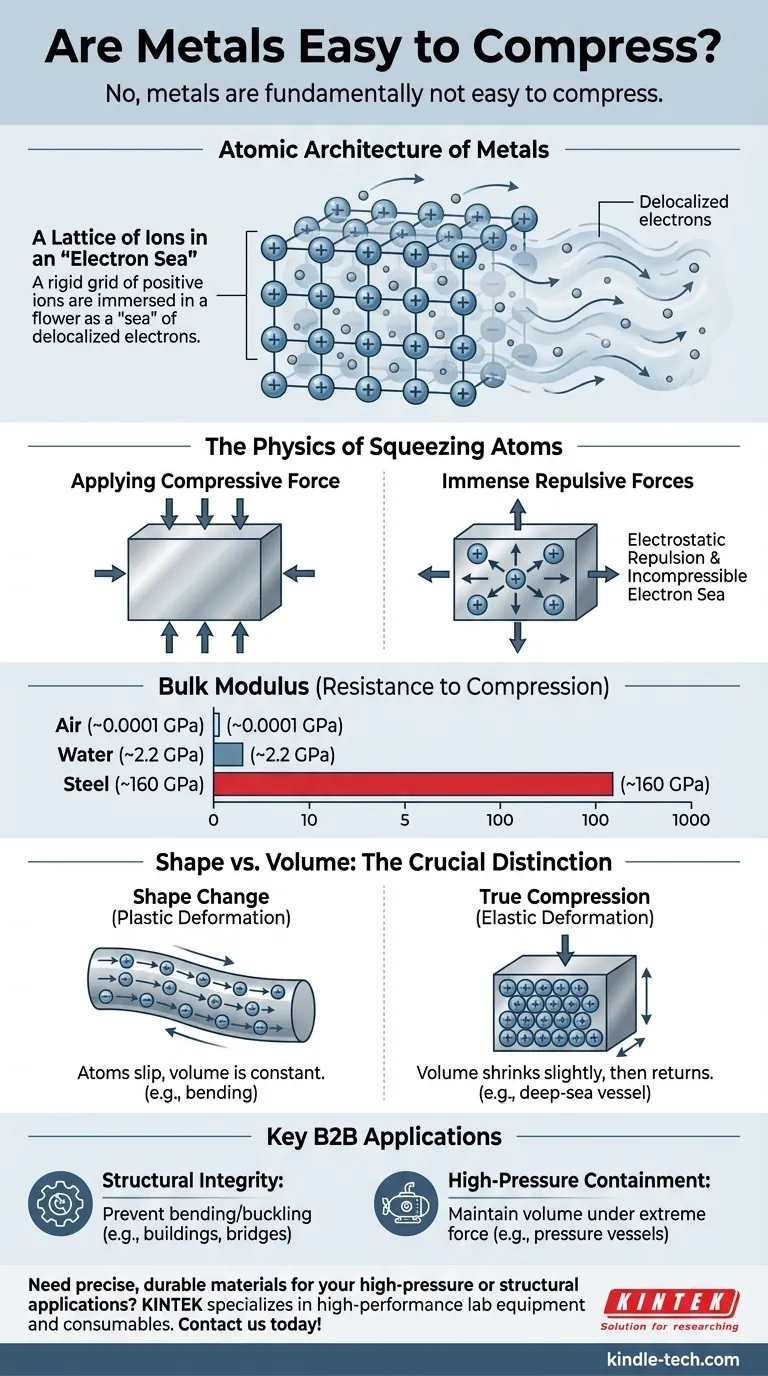
The Atomic Architecture of Metals
To understand why metals resist compression, we must first look at their internal structure. It is unlike that of many other materials.
A Lattice of Ions in an "Electron Sea"
Metals are not composed of discrete, neutral atoms. Instead, they form a highly ordered crystalline structure, or lattice, made of positively charged ions.
The outermost electrons from each atom detach and become delocalized. They are no longer associated with any single atom and are free to move throughout the entire structure.
This creates the classic model of a metal: a rigid lattice of positive ions immersed in a mobile "sea" of shared electrons.
The Flexible "Glue"
This sea of electrons acts as a powerful, yet flexible, electrostatic glue. It holds the positive ions together, which is why metals are strong.
The mobility of these electrons is also what allows metal atoms to slide past one another without breaking the bonds. This explains why metals are ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (can be hammered into sheets).
The Physics of Squeezing Atoms
When you apply a compressive force to a metal, you are attempting to force this stable atomic arrangement into a smaller space.
Pushing Nuclei Together
The primary action of compression is trying to push the positively charged atomic nuclei closer to one another.
As the distance between these nuclei decreases, the electrostatic repulsion between them—the force pushing them apart—increases exponentially. This force becomes incredibly powerful at very small distances.
An Incompressible Fluid
Simultaneously, the "sea" of electrons itself resists being compressed. Just as it is incredibly difficult to compress a liquid like water, this dense cloud of negatively charged electrons strongly resists being packed into a smaller volume.
The combination of these two effects creates an immense internal pressure that counteracts any external compressive force.
Quantifying Incompressibility: The Bulk Modulus
This resistance to compression is not just a qualitative concept; it is a measurable physical property.
What is Bulk Modulus?
The bulk modulus is the precise measure of a substance's resistance to uniform compression. It is defined as the ratio of the increase in pressure to the resulting fractional decrease in volume.
A higher bulk modulus means a material is more difficult to compress.
Metals Have Extremely High Bulk Moduli
Metals like steel, titanium, and tungsten have some of the highest bulk moduli of all common materials. This is a direct result of the strong repulsive forces within their atomic lattice.
To provide context, the bulk modulus of steel is about 160 gigapascals (GPa). In contrast, water's is about 2.2 GPa, and the air you're breathing is about 0.0001 GPa. You would need immense pressure to achieve even a tiny reduction in a metal's volume.
Understanding the Nuances: Shape vs. Volume
A common point of confusion is mistaking a change in shape for a change in volume.
Elastic vs. Plastic Deformation
When you press on a metal rod and make it shorter, this is typically plastic deformation (yielding). The atoms are slipping past each other, changing the object's dimensions. However, the total volume of the material remains almost exactly the same.
True compression, measured by the bulk modulus, is an elastic deformation, where the volume shrinks slightly under pressure and returns to its original state when the pressure is released. For metals, this volume change is minuscule.
Behavior in Tension vs. Compression
While metals strongly resist changes in volume, their behavior in tension (pulling) and compression (pushing) can have different failure modes.
A metal rod pulled in tension will eventually "neck down" and fracture. The same rod pushed in compression is more likely to buckle (if it's slender) or barrel out (if it's short) long before its volume is significantly reduced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this property is critical for nearly any engineering or design application.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Choose metals with high compressive yield strength, like structural steel or aluminum alloys, to prevent permanent bending, buckling, or shortening under load.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure containment: Select materials with a very high bulk modulus, such as steel alloys, nickel alloys, or tungsten, for applications like pressure vessels or deep-sea submersibles where maintaining volume under extreme external force is paramount.
Ultimately, a metal's profound resistance to compression is a direct and powerful consequence of the fundamental forces governing its atomic structure.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Modulus | Measures resistance to uniform compression. | High values (e.g., steel: 160 GPa) mean extreme incompressibility. |
| Atomic Structure | Lattice of positive ions in a "sea" of delocalized electrons. | Creates strong electrostatic repulsion when compressed. |
| Deformation Type | Volume change (elastic) vs. shape change (plastic). | True compression is minimal; shape changes are more common. |
| Key Applications | Structural integrity, high-pressure containment. | Guides material choice for engineering and design. |
Need precise, durable materials for your high-pressure or structural applications? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving industries that rely on material integrity under stress. Let our experts help you select the right solutions for your laboratory's unique challenges. Contact us today to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process
- What are the components of a hot isostatic pressing system? A Guide to Core HIP Equipment
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance



















