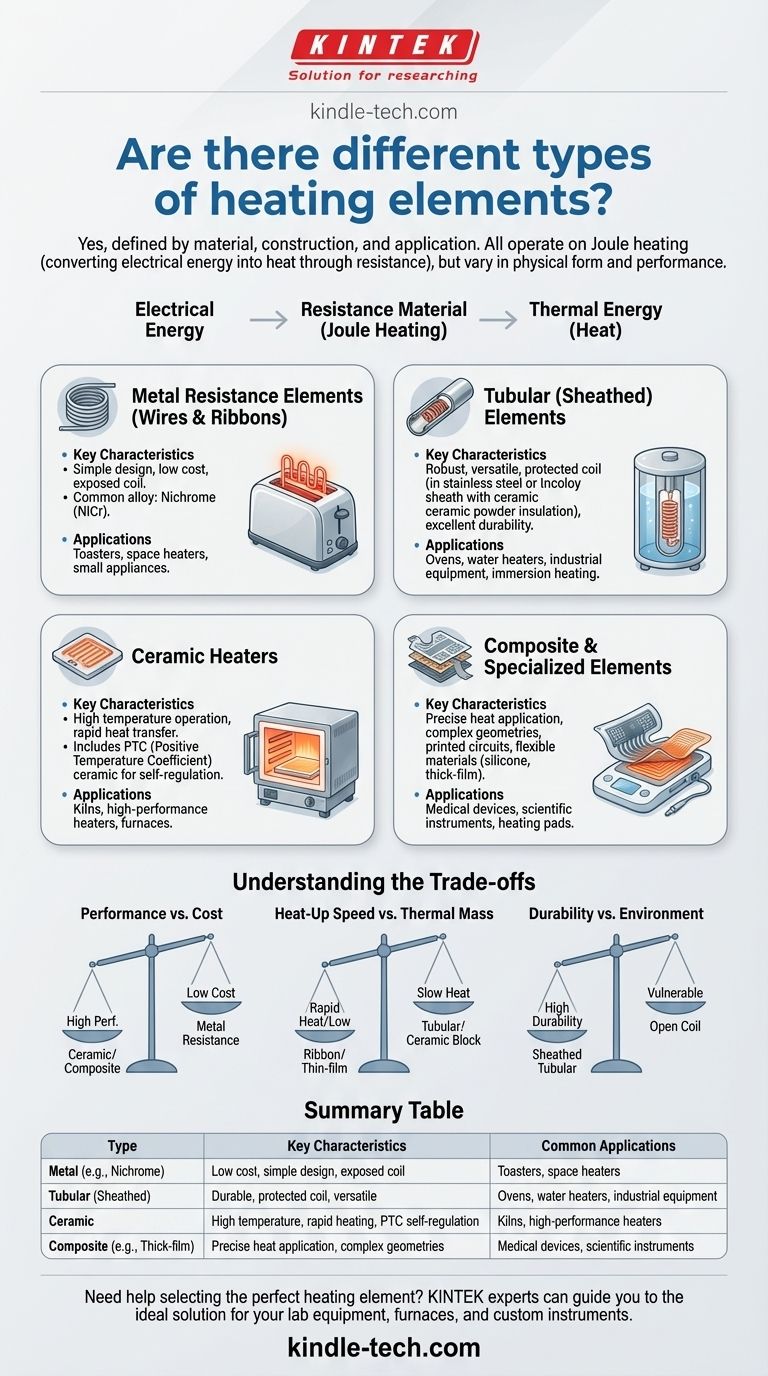
Yes, there are several distinct types of electric heating elements, each defined by its material, construction, and intended application. While they all operate on the principle of converting electrical energy into heat through resistance, their physical forms and performance characteristics vary significantly to suit different tasks, from heating air and liquids to reaching extremely high industrial temperatures.
The core principle for all electric heating elements is the same: resistance. The crucial difference between types lies in how they are constructed, the materials used, and their physical shape, which dictate their ideal use case, temperature range, and durability.

The Foundation: How Resistance Heating Works
All common electric heating elements function based on a principle known as Joule heating.
The Flow of Energy
When an electric current passes through a material with electrical resistance, some of that electrical energy is converted into thermal energy, or heat.
The key is selecting materials that have high enough resistance to generate significant heat without melting or degrading quickly. This fundamental concept is the basis for all the element types discussed below.
Key Categories of Heating Elements
Heating elements are best categorized by their core material and physical construction. Each design offers a unique profile of heat-up time, temperature capability, and ruggedness.
Metal Resistance Elements (Wires and Ribbons)
This is the most traditional and widespread form of heating element. It consists of a simple wire, coil, or ribbon made from a high-resistance metal alloy.
The most common alloy is Nichrome (nickel-chromium), prized for its high resistance and its ability to form a protective oxide layer at high temperatures, preventing further corrosion. They are often exposed directly to the air in applications like toasters and space heaters.
Tubular (Sheathed) Elements
Tubular elements, often known by the brand name Calrod, are a more robust and versatile design. They are the workhorses found in ovens, water heaters, and industrial equipment.
A metal resistance coil (like Nichrome) is encased inside a protective metal tube or sheath, typically made of stainless steel or Incoloy. The coil is electrically insulated from the sheath by a compacted ceramic powder, like magnesium oxide, which is an excellent electrical insulator but a good thermal conductor.
Ceramic Heaters
Ceramic heaters are valued for their ability to operate safely at very high temperatures and for their rapid heat transfer.
They generally come in two forms: a resistance coil embedded within a ceramic plate, or a solid block of a specialized Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) ceramic. PTC materials are unique because their resistance increases sharply at a specific temperature, causing them to become self-regulating and inherently safer against overheating.
Composite and Specialized Elements
Modern applications often demand more specialized solutions that integrate the heater directly into a component.
Thick-film heaters are created by printing a resistance paste onto a substrate like ceramic or metal. This allows for very precise heat application and complex geometries, ideal for medical devices and scientific instruments. Other composites embed graphite or carbon fibers into flexible materials like silicone to create heating pads and blankets.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element is always a matter of balancing competing factors. No single type is universally superior; the "best" choice depends entirely on the requirements of the job.
Performance vs. Cost
Simple Nichrome wire is extremely inexpensive but offers little protection and can have a shorter lifespan. Sheathed tubular elements cost more but provide excellent durability and safety. Advanced ceramic and composite heaters carry the highest cost but deliver unique benefits like self-regulation or precise heat mapping.
Heat-Up Speed vs. Thermal Mass
Elements with low mass, like an open ribbon or a thin-film heater, heat up and cool down very quickly. Heavier elements, like a large tubular heater or a ceramic block, have higher thermal mass. They take longer to heat up but will retain and radiate heat more evenly over time.
Durability vs. Environment
An open coil element is vulnerable to moisture, physical shock, and corrosion. A sheathed tubular element is specifically designed to protect the internal coil from harsh environments, making it suitable for immersion in liquids or use in corrosive atmospheres.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct element, start by defining your most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is low cost for a simple application (like air heating): A basic metal resistance element like a Nichrome coil is the most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is ruggedness and protection (for liquid heating or industrial ovens): A sheathed tubular element provides the necessary durability and safety.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and high temperatures (for kilns or high-performance space heaters): A conventional ceramic heater is the ideal solution.
- If your primary focus is inherent safety and self-regulation: A PTC ceramic heater is unmatched, as it naturally limits its own maximum temperature.
Ultimately, the goal is to match the element's properties to the demands of your specific heating task.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metal (e.g., Nichrome) | Low cost, simple design, exposed coil | Toasters, space heaters |
| Tubular (Sheathed) | Durable, protected coil, versatile | Ovens, water heaters, industrial equipment |
| Ceramic | High temperature, rapid heating, PTC self-regulation | Kilns, high-performance heaters |
| Composite (e.g., Thick-film) | Precise heat application, complex geometries | Medical devices, scientific instruments |
Need help selecting the perfect heating element for your lab equipment? The right choice is critical for performance, safety, and cost-efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, and our experts can guide you to the ideal heating solution for your specific application—whether it's for a furnace, oven, or custom instrument.
Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and ensure optimal performance for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C



















