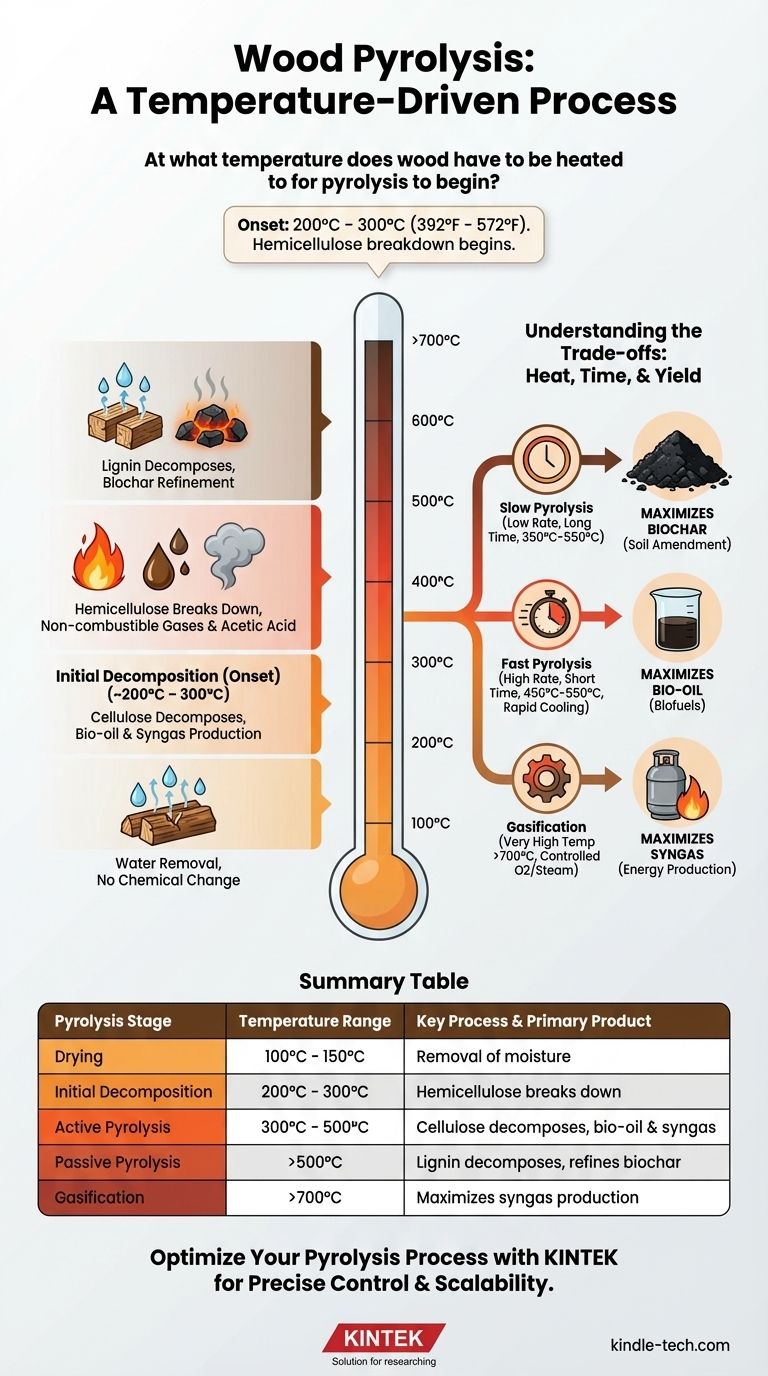
While significant thermal conversion occurs at higher temperatures, the initial stages of wood pyrolysis actually begin at a much lower threshold, typically between 200°C and 300°C (392°F - 572°F). At this point, in the absence of oxygen, the least stable chemical components of the wood start to irreversibly break down, marking the true onset of the process.
Pyrolysis is not an on/off switch flipped at a single temperature. It is a continuous process that unfolds across a wide temperature range, where controlling the heat and duration allows you to precisely determine whether the final output is dominated by solid char, liquid bio-oil, or flammable gas.
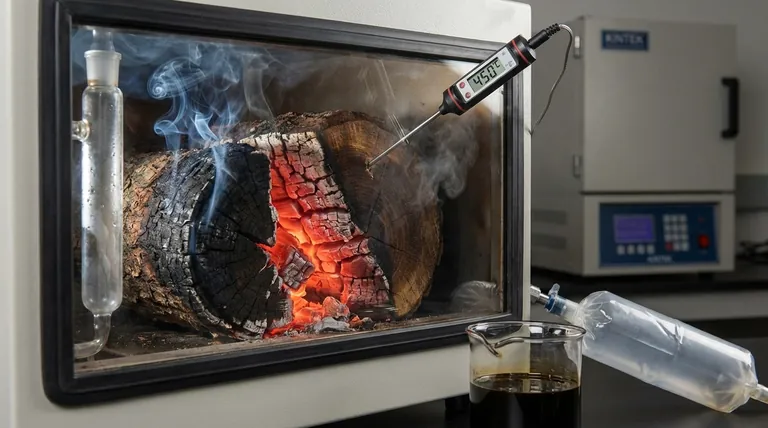

The Stages of Wood Pyrolysis: A Temperature-Driven Process
To truly understand wood pyrolysis, you must view it as a sequence of events, not a single reaction. Wood is a composite of three main polymers—hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin—each of which decomposes at a different temperature range.
Stage 1: Drying (~100°C – 150°C)
Before any chemical breakdown occurs, the free and bound water within the wood must be removed. This initial heating phase, just above the boiling point of water, consumes significant energy but does not yet constitute pyrolysis.
Effective drying is a critical prerequisite for an efficient and controllable pyrolysis process.
Stage 2: Initial Decomposition (Onset) (~200°C – 300°C)
This is the range where pyrolysis technically begins. The first component to break down is hemicellulose, the least stable polymer in wood.
This decomposition releases non-combustible gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, along with some acetic acid. This early stage is sometimes referred to as torrefaction, which makes the wood brittle and more energy-dense.
Stage 3: Active Pyrolysis (~300°C – 500°C)
This is the main event and the most vigorous phase of pyrolysis. Within this range, the primary structural component of wood, cellulose, rapidly decomposes.
This stage is characterized by the significant production of condensable vapors, which form bio-oil (tar), and flammable gases like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide, often called syngas. The remaining solid material is now becoming carbon-rich biochar.
Stage 4: Passive Pyrolysis (>500°C)
Once the hemicellulose and cellulose are mostly gone, the final and most resilient component, lignin, continues its slow decomposition. This process can extend to 900°C and beyond.
Heating within this higher range drives off any remaining volatile compounds from the biochar, increasing its carbon content, porosity, and stability. The final temperature directly dictates the final properties of the char.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Heat, Time, and Yield
The temperature at which you conduct pyrolysis is not just a threshold to be crossed; it is the primary control lever that determines the final products. The heating rate and residence time are equally critical.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
By heating the wood slowly (a low heating rate) over a long period to a relatively moderate peak temperature (e.g., 350°C - 550°C), you favor the production of biochar.
The slow process allows vapors to undergo secondary reactions, cracking and re-condensing on the surface of the solid, which increases the overall char yield.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-Oil
By heating the wood very rapidly (a high heating rate) to a moderate temperature (e.g., 450°C - 550°C) and then quickly cooling the vapors, you can maximize the yield of bio-oil.
The goal is to get the vapors out of the hot reaction zone in less than two seconds to prevent them from breaking down further into gas or re-forming into char.
Gasification: Maximizing Syngas
When pyrolysis is conducted at very high temperatures (>700°C), often with the introduction of a controlled amount of oxygen or steam, the process favors the breakdown of all components into syngas.
This shifts the goal from creating solid or liquid products to creating a combustible gas for generating heat or power.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "correct" temperature for pyrolysis is entirely dependent on your desired outcome. Use your target product as your guide.
- If your primary focus is high-quality biochar (for soil amendment or filtration): Use a slow pyrolysis process with a peak temperature between 450°C and 600°C to balance yield with high carbon content.
- If your primary focus is liquid bio-oil (for biofuels or chemicals): Use a fast pyrolysis process with a peak temperature between 450°C and 550°C and ensure rapid vapor quenching.
- If your primary focus is syngas (for energy production): Operate at very high temperatures, typically above 700°C, to maximize the conversion of all materials into non-condensable gases.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis means understanding that temperature is the tool you use to steer the chemical decomposition of wood toward your intended result.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Stage | Temperature Range | Key Process & Primary Product |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | 100°C - 150°C | Removal of moisture (no chemical change) |
| Initial Decomposition | 200°C - 300°C | Hemicellulose breaks down (onset of pyrolysis) |
| Active Pyrolysis | 300°C - 500°C | Cellulose decomposes; produces bio-oil & syngas |
| Passive Pyrolysis | >500°C | Lignin decomposes; refines biochar properties |
| Gasification | >700°C | Maximizes syngas production |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Whether your goal is to produce high-quality biochar, maximize bio-oil yield, or generate syngas for energy, precise temperature control is critical. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory furnaces and pyrolysis systems that deliver the exact heating profiles and thermal stability you need for reproducible results.
Our equipment helps researchers and engineers like you:
- Achieve precise temperature control from 200°C to 1200°C
- Optimize heating rates for slow or fast pyrolysis protocols
- Scale your process from lab research to pilot production
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's pyrolysis solutions can help you achieve your specific biomass conversion goals. Get in touch →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4



















