Yes, absolutely. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are being extensively investigated as highly promising carriers for both drugs and antigens. Their unique physical and chemical properties, such as a massive surface area and needle-like shape, allow them to be loaded with therapeutic molecules and efficiently penetrate cell membranes, offering capabilities that traditional delivery systems cannot match.
The core challenge and opportunity with carbon nanotubes is a story of two faces. While their innate structure offers unparalleled potential for targeted therapy and diagnostics, their clinical viability is entirely dependent on sophisticated surface engineering—known as functionalization—to overcome their inherent toxicity and ensure safe passage through the body.
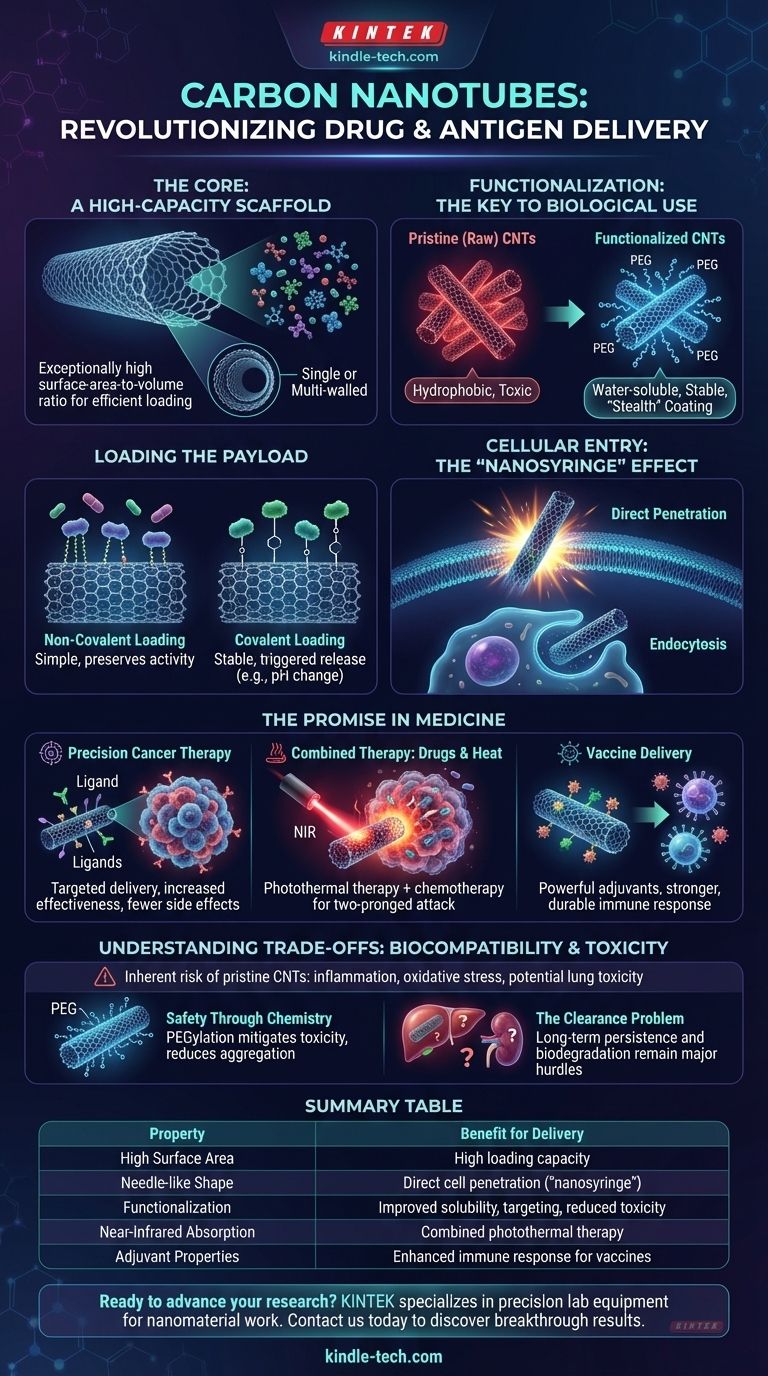
How Carbon nanotubes Function as Delivery Vehicles
The Core Structure: A High-Capacity Scaffold
Carbon nanotubes are hollow cylinders made of a single rolled-up sheet of graphite (single-walled, or SWCNTs) or multiple concentric sheets (multi-walled, or MWCNTs).
This structure gives them an exceptionally high surface-area-to-volume ratio. This means a tiny amount of CNT material can carry a very large number of drug or antigen molecules, making them highly efficient carriers.
Functionalization: The Key to Biological Use
In their raw, pristine state, CNTs are hydrophobic (water-repelling) and tend to clump together in biological fluids, which can be toxic.
To solve this, their surfaces are chemically modified in a process called functionalization. This involves attaching specific molecules, like polymers (e.g., PEG), to make the CNTs water-soluble, stable, and less visible to the immune system.
Loading the Payload: Attaching Drugs and Antigens
Once functionalized, therapeutic molecules can be attached. This is done in two primary ways:
- Non-covalent loading: Drugs, especially those with aromatic rings, can be attached to the CNT surface through weak physical interactions (pi-pi stacking). This method is simple and often preserves the drug's activity.
- Covalent loading: Drugs are attached via strong chemical bonds using a linker molecule. This provides a more stable attachment, and the drug release can be triggered by specific conditions in the target environment, like a change in pH inside a cancer cell.
Cellular Entry: The "Nanosyringe" Effect
The needle-like shape of CNTs allows some of them to directly penetrate cell membranes, acting like a "nanosyringe" to inject their payload directly into the cell's cytoplasm.
Alternatively, functionalized CNTs can be taken up by cells through natural processes like endocytosis, where the cell membrane engulfs the nanotube.
The Promise of CNTs in Medicine
Precision Targeting for Cancer Therapy
By attaching targeting ligands (such as antibodies or folic acid) to their surface, CNTs can be guided specifically to cancer cells.
This concentrates the chemotherapy drug at the tumor site, drastically increasing its effectiveness while minimizing the debilitating side effects on healthy tissues.
Combined Therapy: Drugs and Heat
CNTs have a unique property of strongly absorbing near-infrared (NIR) light, which can pass harmlessly through skin and tissue.
When a laser is shone on a tumor containing CNTs, the nanotubes heat up rapidly, killing the cancer cells through hyperthermia. This can be combined with a heat-triggered release of a chemotherapy drug for a powerful, two-pronged attack.
Immunomodulation and Vaccine Delivery
When used to carry antigens (fragments of a pathogen or tumor), CNTs can act as powerful adjuvants.
They help stimulate the immune system and facilitate the antigen's delivery to key immune cells, resulting in a much stronger and more durable immune response than the antigen alone. This makes them a promising platform for next-generation vaccines.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs: Biocompatibility and Toxicity
The Inherent Risk of Pristine CNTs
It is critical to understand that unmodified CNTs are generally not safe for clinical use. Their insolubility and tendency to aggregate can cause inflammation and oxidative stress.
Furthermore, long, rigid CNTs can have physical properties similar to asbestos fibers, raising serious concerns about long-term lung toxicity if inhaled.
The Role of Surface Chemistry in Safety
Functionalization, especially with biocompatible polymers like polyethylene glycol (PEG), is the primary strategy to mitigate toxicity.
PEGylation creates a "stealth" coating that shields the CNT from the immune system, improves its solubility, and prevents aggregation, dramatically improving its safety profile.
The Biodegradation and Clearance Problem
A major unresolved hurdle for the clinical use of CNTs is understanding how the body gets rid of them.
While some studies show that certain enzymes in immune cells can slowly break down functionalized CNTs, their long-term persistence in organs like the liver and spleen is a significant safety concern. The inability to guarantee full clearance from the body remains a key barrier to FDA approval.
Applying This to Your Goal
Before proceeding with CNTs, you must be clear on your primary objective, as the design strategy will differ significantly.
- If your primary focus is novel cancer therapy: Prioritize systems that combine targeted delivery with a secondary mechanism like photothermal therapy, but ensure rigorous testing of your specific formulation's long-term toxicity and clearance.
- If your primary focus is vaccine development: Leverage the inherent adjuvant properties of CNTs, focusing on how different surface modifications can shape the resulting immune response to be more effective.
- If your primary focus is fundamental biocompatibility: Investigate the in-vivo fate and degradation pathways of various CNT lengths and functionalizations, as solving the clearance challenge is the most critical step for the entire field.
Successfully harnessing the power of carbon nanotubes requires a dual mastery of their potent therapeutic capabilities and the intricate surface science needed to ensure their safety.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Drug/Antigen Delivery |
|---|---|
| High Surface Area | Enables high loading capacity for therapeutic molecules |
| Needle-like Shape | Facilitates direct cell penetration (nanosyringe effect) |
| Functionalization | Improves solubility, reduces toxicity, and allows targeting |
| Near-Infrared Absorption | Enables combined drug delivery and photothermal therapy |
| Adjuvant Properties | Enhances immune response for vaccine development |
Ready to advance your research with cutting-edge laboratory solutions? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables to support your work with nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes. Whether you're developing targeted cancer therapies or next-generation vaccines, our products ensure accuracy and reliability. Contact us today to discover how we can help you achieve breakthrough results in drug delivery and immunology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is a sputtering target? The Blueprint for High-Performance Thin-Film Coatings
- Why does carbon nanotubes conduct electricity? The key role of chirality and graphene structure
- Can a carbon nanotube conduct electricity? The Answer Lies in Its Atomic Structure
- What is sputtering of thin films? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is a thin film semiconductor? Unlock Flexible, Large-Area Electronics
- What does the deposition rate depend on? Key Factors for Thin-Film Process Control
- What is thin film deposition in semiconductor? The Atomic-Level Architecture of Modern Chips
- What is the chemical makeup of carbon nanotubes? Unlocking the Power of Pure Carbon






