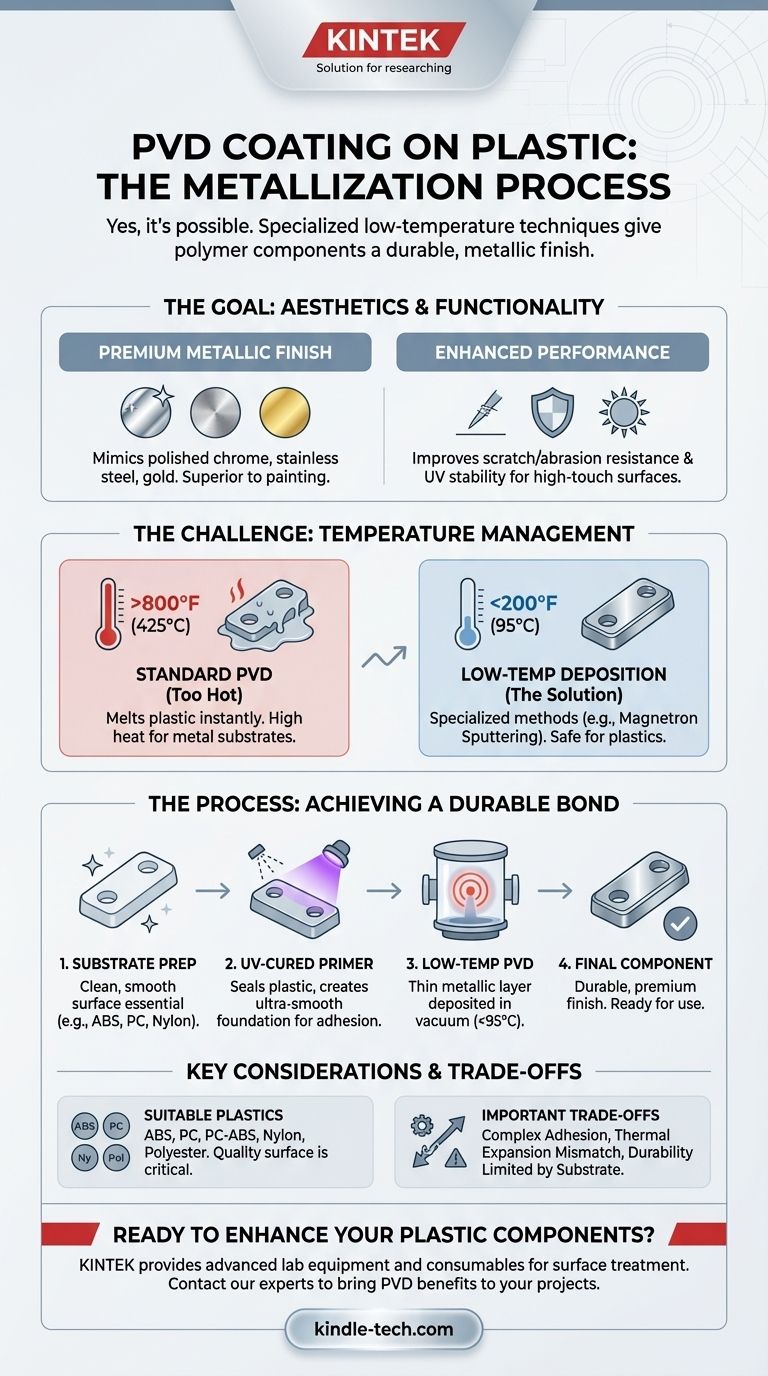
Yes, you can apply PVD coatings to plastic. This process, often called plastic metallization, is widely used to give polymer components a durable, high-quality metallic finish. It is a specialized technique that differs from the high-temperature PVD processes used for metals, but it is highly effective for both decorative and functional purposes.
The ability to PVD coat plastic is not a question of if, but how. Success depends entirely on using specialized low-temperature PVD processes, as traditional methods operate at temperatures that would melt or deform the polymer substrate.

Why PVD Coat Plastic? The Goal of Metallization
Applying a thin film of metal onto a plastic part leverages the benefits of both materials: the light weight and design flexibility of plastic, and the surface properties of metal.
Achieving a Premium Metallic Finish
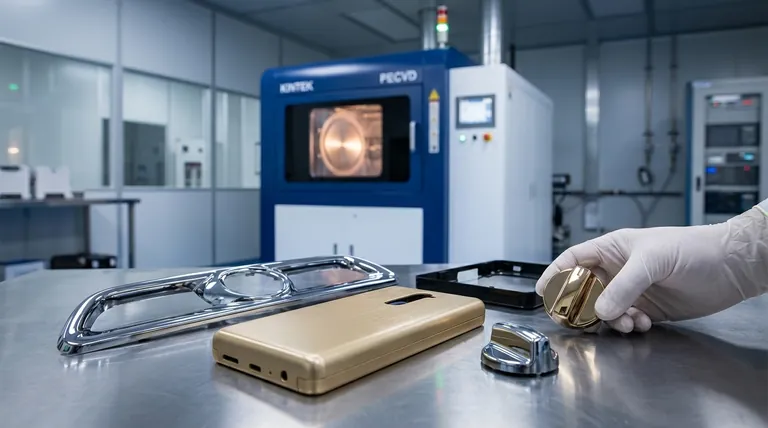
The most common driver for PVD on plastics is aesthetics. The process deposits a thin, dense, and highly adherent metallic layer that provides a premium look and feel. This is a significant upgrade over traditional methods like painting, offering finishes that mimic polished chrome, brushed stainless steel, gold, and other alloys.
Enhancing Functional Properties
Beyond looks, PVD coatings add tangible performance benefits. The hard ceramic or metallic layer can significantly improve a plastic part's scratch resistance, abrasion resistance, and UV stability. This makes it ideal for high-touch surfaces in automotive interiors, electronics, and consumer goods.
The Critical Factor: Managing Temperature
The primary challenge in coating plastics is their low tolerance for heat. Understanding how the PVD process is adapted to overcome this is key.
The Problem with Standard PVD
Traditional PVD processes, particularly those for coating tool steels and medical implants, can operate at temperatures up to 800°F (425°C). This high heat is necessary to ensure strong adhesion and coating density on metal substrates. Applying this process directly to a polymer like ABS or polycarbonate would cause it to melt instantly.
The Solution: Low-Temperature Deposition
To coat plastics, specialized PVD techniques such as magnetron sputtering are used. These methods are engineered to operate in a much lower temperature range, typically well below 200°F (95°C), which most common plastics can safely withstand within the vacuum chamber.
The Importance of Surface Preparation
PVD coatings require an exceptionally clean and smooth surface for proper adhesion. Unlike metal, plastic surfaces can be porous and may release gases in a vacuum. To solve this, parts are often pre-treated with a UV-cured primer or basecoat. This seals the plastic and creates an ideal, ultra-smooth foundation for the PVD layer to bond to.
Suitable Plastics and Key Considerations
While many plastics can be coated, some are better suited for the process than others due to their stability and surface characteristics.
Common PVD-Compatible Plastics
The process works well on a wide variety of polymers. Some of the most frequently coated plastics include:
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- PC (Polycarbonate)
- PC-ABS (Polycarbonate / ABS Blends)
- Nylon
- Polyester
- Polypropylene
Factors for a Successful Coating
The quality of the final product depends heavily on the initial plastic part. Substrates must have a high-quality surface finish, be free of mold-release agents, and possess the thermal stability to withstand the low-heat vacuum process without deforming or outgassing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD on plastic is not without its limitations. A clear understanding of the trade-offs is essential for any project.
Adhesion is Complex
Achieving a permanent bond between a metal film and a polymer is more challenging than on a metal substrate. The success of the coating is critically dependent on meticulous cleaning, proper outgassing procedures, and the quality of the basecoat.
Thermal Expansion Mismatch
Metal and plastic expand and contract with temperature changes at very different rates. In applications with extreme temperature swings, this mismatch can create stress at the bond line between the coating and the substrate, potentially impacting long-term durability if not properly engineered.
Overall Durability is Substrate-Limited
A PVD coating adds impressive surface hardness, but it is only a few microns thick. It can protect a part from scratches, but it cannot prevent the underlying plastic from denting or breaking under a significant impact. The bulk properties of the part are still defined by the plastic itself.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice to use PVD should be guided by your primary goal for the plastic component.
- If your primary focus is premium aesthetics: PVD offers a far more durable and authentic metallic appearance than painting or chrome-look spray paint.
- If your primary focus is surface durability: PVD is an excellent choice for adding scratch and wear resistance to high-touch plastic parts, extending their cosmetic lifespan.
- If you are in the early design phase: Select a plastic known for its PVD compatibility and consult with a coating provider early to ensure your part design and surface finish are optimized for the process.
By using the correct low-temperature process, PVD effectively transforms plastic components, giving them the performance and appearance of solid metal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Process | Requires specialized low-temperature PVD (e.g., magnetron sputtering) |
| Temperature | Typically operates below 200°F (95°C) to prevent substrate damage |
| Key Benefit | Combines plastic's lightweight flexibility with metal's surface properties |
| Common Plastics | ABS, PC, PC-ABS, Nylon, Polyester |
| Critical Step | Surface preparation with a UV-cured primer/basecoat for adhesion |
| Limitation | Overall impact resistance is still limited by the plastic substrate |
Ready to enhance your plastic components with a premium PVD coating?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface treatment and coating processes. Whether you are developing a new product or improving an existing one, our expertise can help you achieve a durable, high-quality metallic finish on your polymer parts.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can bring the benefits of PVD coating to your plastic components, improving both aesthetics and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















