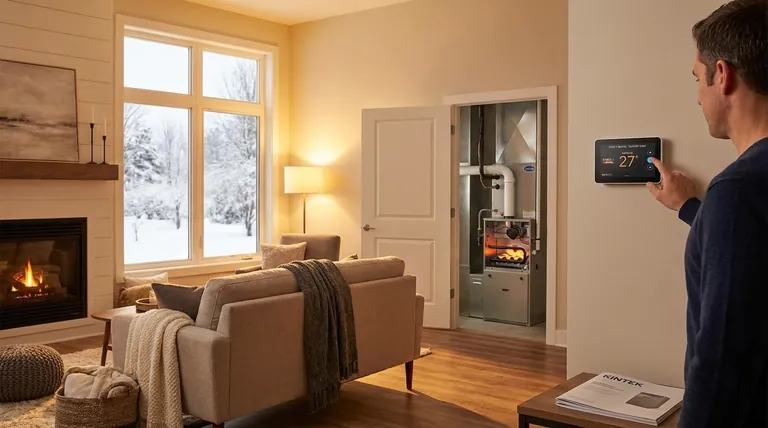
In short, a two-stage furnace does not run all the time, but it is designed to run for much longer periods than a traditional furnace. It accomplishes this by operating most of the time on a low-power, energy-saving first stage. The second, high-power stage only activates when necessary during periods of extreme cold, ensuring your home reaches its target temperature quickly.
The core misunderstanding is viewing long runtimes as a flaw. For a two-stage furnace, longer, lower-power cycles are its greatest strength, leading to superior energy efficiency and more consistent household comfort compared to the "all or nothing" blasts of a single-stage system.

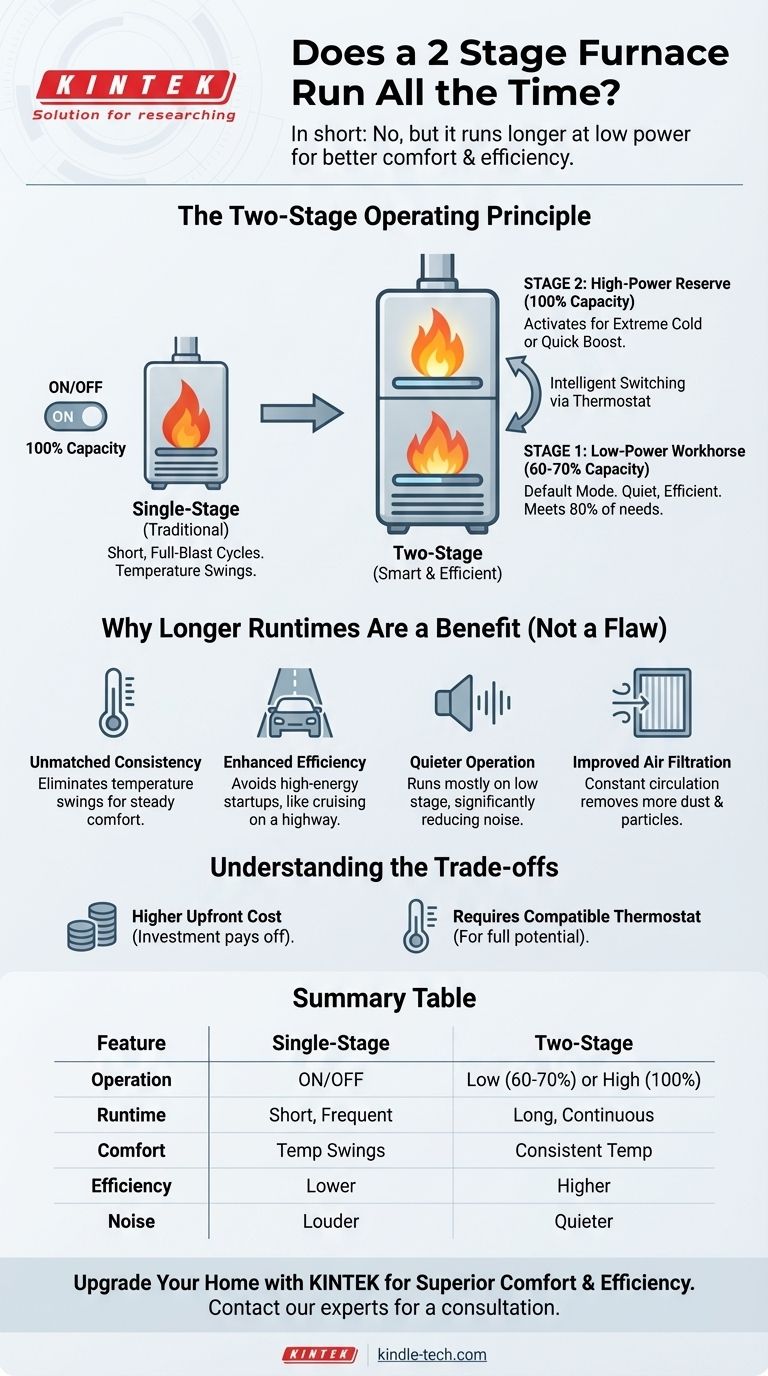
The Two-Stage Operating Principle
A traditional, single-stage furnace knows only two states: off and on at 100% capacity. A two-stage furnace introduces nuance by adding an intermediate, low-power setting.
Stage One: The Low-Power Workhorse
The first stage is the default mode of operation. It runs at approximately 60-70% of the furnace's total heating capacity.
This low-and-slow approach is sufficient to meet your home's heating needs about 80% of the time. Because it uses less fuel and a lower fan speed, this stage is significantly quieter and more energy-efficient.
Stage Two: The High-Power Reserve
The second stage is equivalent to a traditional furnace running at full blast. It delivers 100% of the furnace's heating capacity.
This stage is reserved for two primary situations: when you first turn the heat on after it's been off for a while, or during the coldest days of the year when the low stage can't maintain the thermostat's set temperature on its own.
How It Decides When to Switch
The furnace's control board, working with your thermostat, manages the stages. If the low stage runs for a set period (e.g., 10-15 minutes) and fails to raise the temperature, the system intelligently decides to activate the second stage to provide the necessary boost.
Why Longer Runtimes Are a Benefit, Not a Flaw
The longer, more consistent operation of a two-stage furnace directly translates into significant improvements in comfort and efficiency.
Unmatched Temperature Consistency
Single-stage furnaces create noticeable temperature swings. The room gets warm quickly, the furnace shuts off, and then it gets chilly before the system kicks back on. The long, gentle heating of a two-stage furnace's low setting nearly eliminates these uncomfortable peaks and valleys, keeping the temperature remarkably steady.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Think of it like driving a car. A single-stage furnace is like flooring the gas pedal and then slamming on the brakes in city traffic—it burns a lot of fuel. A two-stage furnace is like cruising at a steady speed on the highway. By avoiding the repeated, high-energy startups, it consumes less fuel over time.
Quieter Operation
The loud roar of a furnace kicking on is a common complaint. Because a two-stage furnace spends most of its time on the quiet low stage, it dramatically reduces operational noise, creating a more peaceful home environment.
Improved Air Filtration
Since the furnace fan is running for longer periods, it is constantly circulating air throughout your home. This means the air passes through your furnace filter more frequently, helping to remove more dust, dander, and other airborne particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, a two-stage furnace is not without its considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging them.
Higher Upfront Cost
The primary drawback is the initial investment. A two-stage furnace and its installation will cost more than a comparable single-stage model. This cost is eventually offset by long-term energy savings, but the initial price is higher.
Requires a Compatible Thermostat
To unlock the full potential of your furnace, you need a two-stage thermostat that can intelligently control both stages. If you use a basic, single-stage thermostat, the furnace itself will rely on an internal timer to switch stages, which is less efficient than thermostat-driven control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on your specific priorities for your home.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible purchase price: A reliable single-stage furnace is the more budget-friendly initial investment.
- If your primary focus is consistent comfort and lower energy bills: A two-stage furnace is the superior choice for eliminating temperature swings and achieving long-term efficiency.
- If your primary focus is quiet operation and better air quality: The longer, lower-power runtimes of a two-stage furnace make it the clear winner.
Ultimately, choosing a two-stage system is an investment in long-term comfort and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Single-Stage Furnace | Two-Stage Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | On (100%) or Off | Low (60-70%) or High (100%) |
| Runtime | Short, frequent cycles | Long, continuous cycles |
| Comfort | Noticeable temperature swings | Consistent, even temperatures |
| Efficiency | Lower (frequent startups) | Higher (steady operation) |
| Noise Level | Louder when starting | Quieter overall |
Upgrade Your Home's Comfort and Efficiency with KINTEK
Choosing the right furnace is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. If you're seeking the superior temperature control, quieter operation, and long-term energy savings of a two-stage system, KINTEK is here to help.
As specialists in precision heating solutions, we understand the unique needs of modern households. Our expertise ensures you get a system perfectly matched to your home's requirements, maximizing both comfort and cost savings.
Ready to experience the benefits of a two-stage furnace? Contact our heating experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can transform your home's heating performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the typical heating zone configurations and maximum temperature capabilities of tube furnaces? Find the Right Setup for Your Lab
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency
- What are the advantages of using a Multi-zone Tube Furnace? Enhanced Thermal Uniformity for Diffusion Research
- What is a multi-position furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Flexible HVAC Installation



















