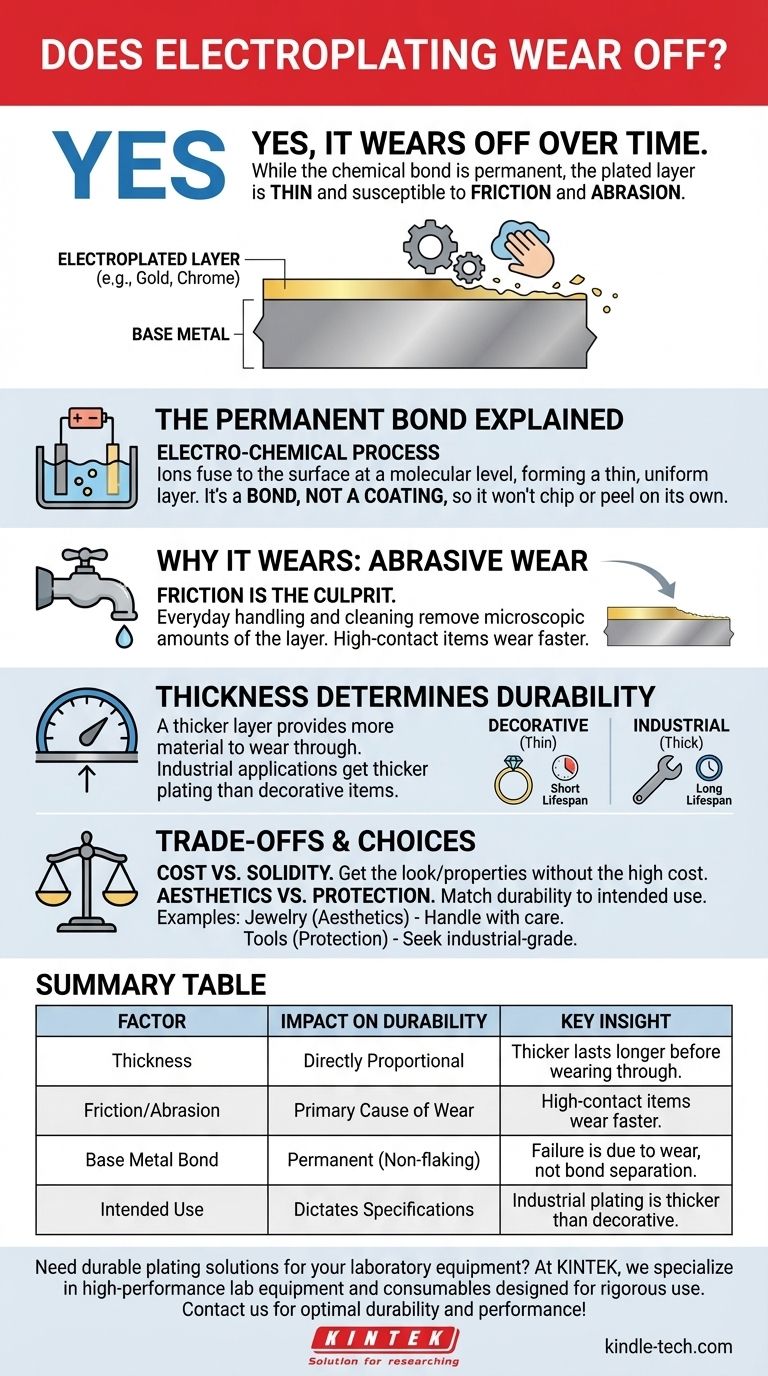
Yes, electroplating does wear off. While the process creates a permanent chemical bond that will not flake or peel on its own, the plated layer is exceptionally thin. Over time, this layer can be worn away through friction, abrasion, and exposure, revealing the base metal underneath.
The core principle to understand is that electroplating forms a permanent bond, not an invincible shield. Its lifespan is a direct function of its thickness and the amount of physical wear it endures, not a failure of the chemical bond itself.

How Electroplating Creates a Permanent Bond
Electroplating is a fascinating process that fuses a new metal layer onto an existing object at a molecular level.
The Electro-Chemical Process
An object is submerged in a chemical bath containing dissolved ions of the desired coating metal (like gold, chromium, or nickel). An electric current is passed through this bath, causing the metal ions to permanently deposit onto the surface of the object, forming a thin, uniform metallic layer.
A Bond, Not a Coating
Unlike paint, this new layer is not simply sitting on top of the surface. The electric current creates a genuine electro-chemical bond between the plating metal and the base metal. This is why properly applied electroplating does not spontaneously chip, flake, or separate.
The Real Cause of Plating Failure: Abrasive Wear
If the bond is permanent, why does plating disappear? The answer is simple mechanical wear.
Friction Is the Primary Culprit
Every time a plated object is handled, rubbed, or cleaned, a microscopic amount of the plated layer is removed. While the coating is typically only around 0.0002 inches thick, consistent friction over months or years will eventually wear through it. High-contact items like jewelry, faucet handles, or tools will always wear faster than purely decorative objects.
Thickness Determines Durability
The single most important factor in the longevity of electroplating is its thickness. A thicker layer of plating simply provides more material that has to be worn away before the base metal is exposed. Industrial applications, like chrome bumpers or tools, often receive a much thicker and more durable plating than decorative items.
The Purpose of the Plating
The intended use dictates the plating's properties. Plating can be used for several reasons:
- Aesthetics: To give a shiny, attractive finish (e.g., gold-plated jewelry).
- Corrosion Protection: To shield a reactive metal like steel from rust (e.g., chrome plating).
- Reflectivity: To create a mirror-like surface.
The durability is often matched to the purpose. A necklace doesn't need the same wear resistance as a wrench.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Electroplating is fundamentally a compromise between cost, appearance, and durability.
Cost vs. Solidity
The primary advantage of electroplating is achieving the look and surface properties of a precious or durable metal without the high cost of making the entire object from it. You get the appearance of a solid gold ring or the corrosion resistance of chromium on a less expensive base metal.
The Illusion of Invincibility
A gleaming chrome bumper or a polished silver tray can look incredibly solid and durable. However, it's crucial to remember you are dealing with a very thin surface layer. Harsh abrasive cleaners or impacts that would not harm a solid object can easily damage or wear through a plated finish.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your expectations for an electroplated item should align with its intended purpose and quality.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics (e.g., fashion jewelry): Understand that the plating is thin and will wear with frequent use, so handle it with care to preserve its finish.
- If your primary focus is protection (e.g., tools, fixtures): Look for items with thicker, industrial-grade plating designed to withstand abrasion and environmental exposure.
- If you are restoring a worn item: Remember that most plated objects can be professionally stripped and replated, fully restoring their original finish.
By understanding that electroplating offers a permanent surface bond of finite thickness, you can accurately judge the value and lifespan of any plated item.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Durability | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Directly proportional | Thicker plating lasts longer before wearing through |
| Friction/Abrasion | Primary cause of wear | High-contact items wear faster than decorative pieces |
| Base Metal Bond | Permanent and non-flaking | Failure is due to wear, not bond separation |
| Intended Use | Dictates plating specifications | Industrial plating is thicker than decorative plating |
Need durable plating solutions for your laboratory equipment? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables designed to withstand rigorous use. Whether you require corrosion-resistant surfaces or long-lasting finishes for your tools and instruments, our expertise ensures optimal durability and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency with reliable plating solutions tailored to your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
People Also Ask
- How should an RVC sheet be handled and set up during an experiment? Ensure Precision and Data Integrity
- What are the advantages of an electrolytic polishing device for EK-181 steel TEM samples? Ensure Peak Sample Integrity
- What is the general procedure and what precautions should be taken during the polishing process? Achieve a Flawless Electrode Finish
- What is a hot mounting press machine? Precision Control for Metallurgy & Electronics Assembly
- What is the difference between hot mounting and cold mounting? Choose the Right Method for Your Sample



















