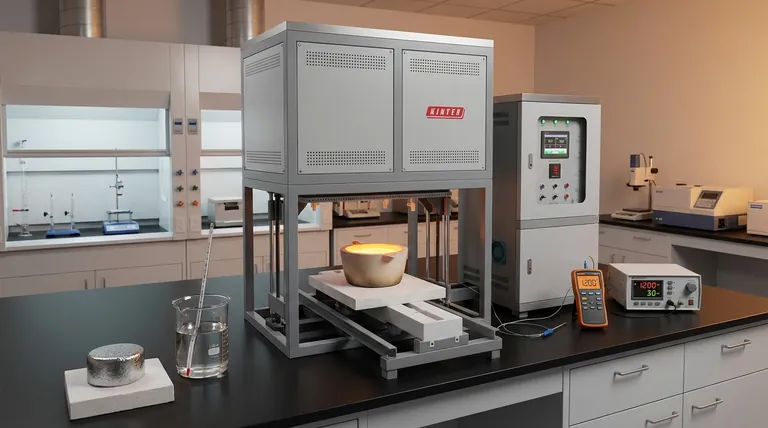
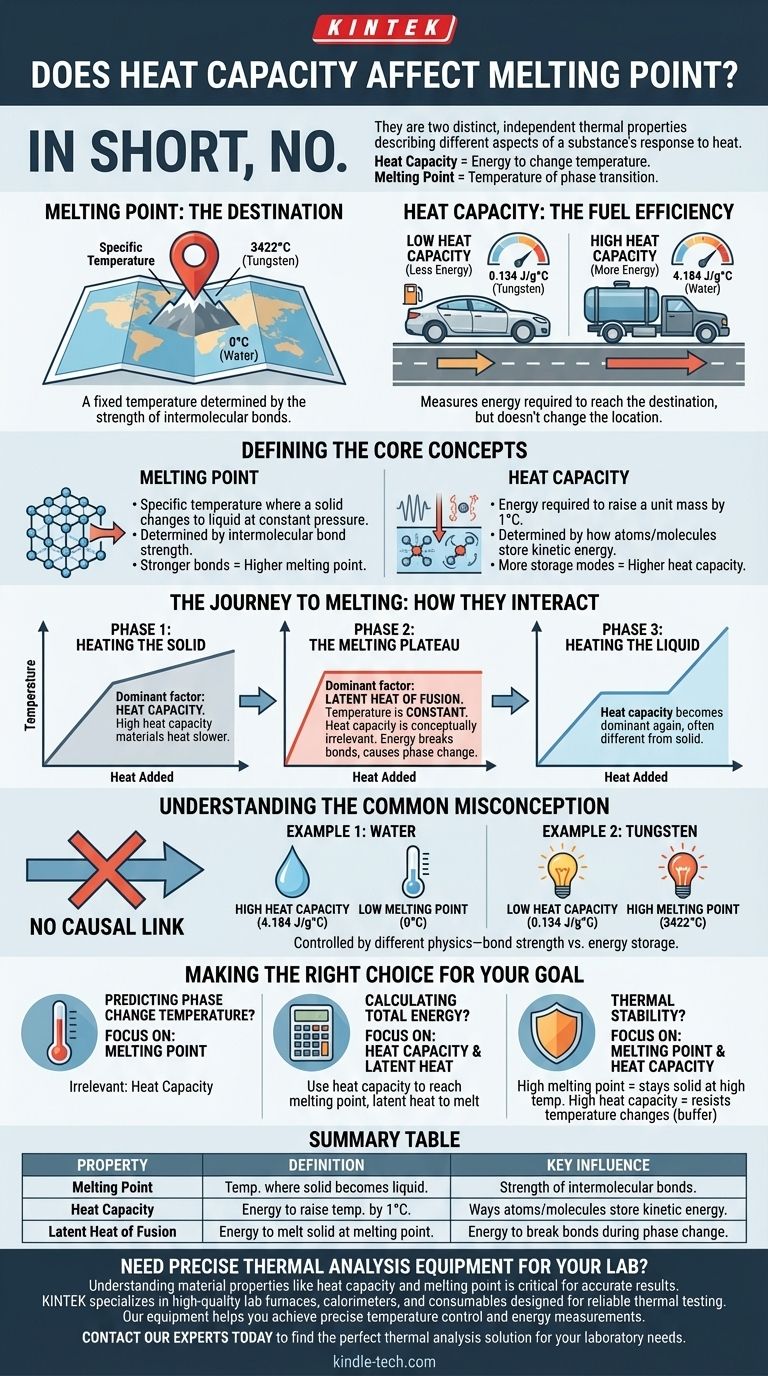
In short, no. Heat capacity does not directly affect or determine a material's melting point. They are two distinct, independent thermal properties that describe different aspects of a substance's response to heat. Heat capacity measures the energy required to change a material's temperature, while the melting point is the specific temperature at which it transitions from a solid to a liquid.
Think of a material's melting point as a fixed destination on a map (a specific temperature). Heat capacity, in contrast, is like the fuel efficiency of the car you're using to get there. A car with poor fuel efficiency (high heat capacity) requires more fuel (energy) to reach the destination, but the location of the destination itself does not change.

Defining the Core Concepts
To understand why these properties are separate, we must first define them clearly. They describe different physical phenomena at the molecular level.
What is Melting Point?
The melting point is the specific temperature at which a pure crystalline solid, at a constant pressure, changes into a liquid.
This temperature is determined by the strength of the intermolecular bonds holding the atoms or molecules together in a fixed crystal lattice.
To melt a substance, you must provide enough energy to overcome these forces. Therefore, materials with stronger bonds require more energy and have a higher melting point.
What is Heat Capacity?
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree (e.g., one Kelvin or one Celsius).
This property is determined by how many ways a material's atoms and molecules can store kinetic energy. This includes vibrations, rotations, and translations.
A substance with a high heat capacity can absorb a large amount of heat energy with only a small increase in its temperature.
The Journey to Melting: How They Interact
While they are independent properties, heat capacity and melting point both play sequential roles in the process of melting a substance. The process occurs in distinct phases.
Phase 1: Heating the Solid
This is the phase where heat capacity is the dominant factor. As you add heat energy to a solid, its temperature rises.
A material with a high heat capacity will heat up slower than one with a low heat capacity, assuming the same rate of energy input. It "soaks up" more energy for every degree of temperature increase.
Phase 2: The Melting Plateau
Once the material reaches its melting point, something crucial happens: its temperature stops rising, even as you continue to add heat.
All the energy being added is now used exclusively to break the bonds of the solid structure, a process governed by another property called the latent heat of fusion.
During this phase change, heat capacity is conceptually irrelevant because the temperature is static. The energy is causing a change of state, not a change of temperature.
Phase 3: Heating the Liquid
After all the solid has transformed into a liquid, the temperature of the substance will begin to rise again as more heat is added.
The liquid phase of the substance has its own distinct heat capacity, which is often different from the heat capacity of its solid form.
Understanding the Common Misconception
The confusion between these two properties often arises because they are both fundamental to a material's thermal behavior. However, mistaking their correlation for causation is a critical error.
The Correlation vs. Causation Trap
There is no reliable causal link between heat capacity and melting point. A high heat capacity does not imply a high melting point, and vice versa.
Consider these examples:
- Water has a very high specific heat capacity (4.184 J/g°C) but a low melting point of 0°C.
- Tungsten has a much lower specific heat capacity (0.134 J/g°C) but one of the highest melting points of any element, at 3,422°C.
This demonstrates that one property cannot be used to predict the other. They are controlled by different underlying physics—bond strength for melting point and modes of energy storage for heat capacity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When analyzing a material's thermal properties, focus on the property that directly answers your question.
- If your primary focus is predicting the temperature of a phase change: Look only at the melting point. Heat capacity is irrelevant to at what temperature it will melt.
- If your primary focus is calculating total energy requirements: You must use the heat capacity to find the energy needed to reach the melting point, and then the latent heat of fusion to find the energy needed to complete the melt.
- If your primary focus is thermal stability: A high melting point means a material remains solid at high temperatures. A high heat capacity means the material resists temperature changes, making it a good thermal buffer.
Understanding the distinct roles of heat capacity and melting point is the key to accurately predicting and engineering how materials behave under thermal stress.
Summary Table:
| Property | Definition | Key Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | The specific temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. | Strength of intermolecular bonds. |
| Heat Capacity | The energy needed to raise a material's temperature by 1°C. | Ways atoms/molecules store kinetic energy. |
| Latent Heat of Fusion | The energy required to melt a solid at its melting point. | Energy to break bonds during phase change. |
Need precise thermal analysis equipment for your lab? Understanding material properties like heat capacity and melting point is critical for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces, calorimeters, and consumables designed for reliable thermal testing. Our equipment helps you achieve precise temperature control and energy measurements, ensuring your research and quality control are built on solid data. Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal analysis solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is magnetron sputtering done? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the sputtering process for deposition? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Coating
- What are the impurities in pyrolysis oil? Unlocking the Complex Chemistry of Bio-Crude
- How does temperature affect the mechanical properties of materials? Avoid Brittle Fracture & Creep Failure
- Why is potassium bromide used in FTIR? The Key to Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is sputtering target material? The Blueprint for High-Quality Thin Film Coatings
- What are the three types of graphite? A Guide to Natural and Synthetic Graphite for Industrial Use
- What is the use of sinter in blast furnace? Optimize Iron Production with Engineered Feedstock



















