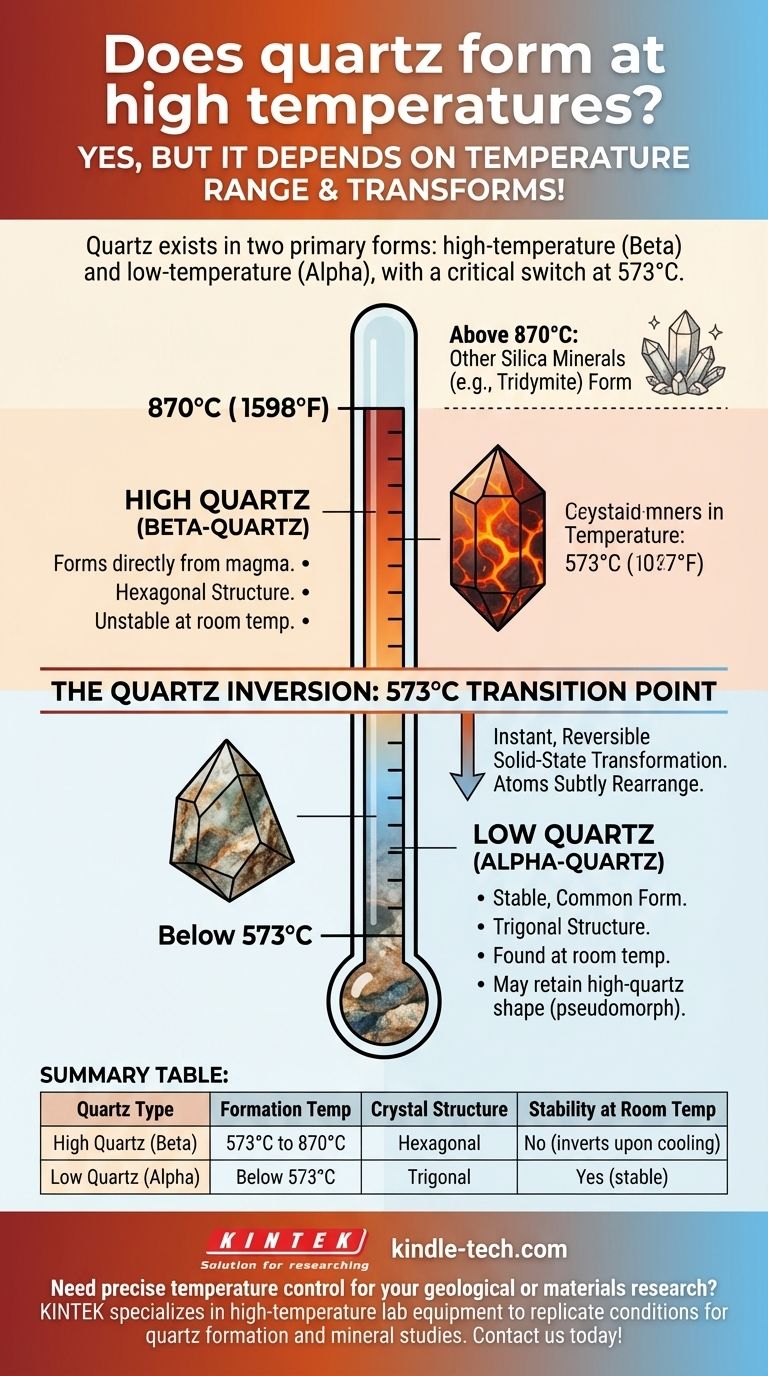
Yes, quartz absolutely forms at high temperatures, but the specific type of quartz depends on the exact temperature range. While it can crystallize at temperatures up to 870°C, the common quartz we find at room temperature is technically a transformed version of its original high-temperature form.
The critical concept to understand is that quartz exists in two primary forms: a high-temperature version (beta-quartz) and a low-temperature version (alpha-quartz). The switch between them happens at 573°C, which means nearly all quartz found on Earth's surface originally formed as high-temperature quartz and inverted as it cooled.

The Two Forms of Quartz
Quartz is a polymorph, meaning it can exist in different crystal structures despite having the same chemical formula (SiO₂). The structure it takes depends entirely on the temperature and pressure during its formation.
Low Quartz (Alpha-Quartz)
This is the stable, common form of quartz that we see and handle in our daily lives.
It forms at temperatures below 573°C (1063°F) at atmospheric pressure. Its crystal structure is trigonal.
High Quartz (Beta-Quartz)
This is the version of quartz that crystallizes directly from magma or in high-temperature hydrothermal veins.
It forms in the temperature range of 573°C to 870°C (1063°F to 1598°F). High quartz has a hexagonal crystal structure, which is slightly more symmetrical.
The Critical Transition: The Quartz Inversion
The temperature of 573°C is not just a dividing line; it is a fundamental transition point known as the quartz inversion.
What Happens at 573°C?
When high quartz cools below 573°C, its internal atomic structure instantly rearranges itself into the low-quartz configuration.
This is not a chemical change. It is a physical, solid-state transformation where the silicon and oxygen atoms subtly shift their positions and bonds.
Why This Inversion is Crucial
This inversion is so important because it happens instantly and is reversible.
Because of this, high quartz cannot exist at room temperature. Any quartz crystal that originally formed above 573°C will have inverted to low quartz by the time it has cooled enough for us to find it.
Common Pitfalls and Nuances
Understanding this process helps avoid common misconceptions about mineral formation.
The Upper Temperature Limit
Quartz has a ceiling on its formation temperature. Above 870°C at atmospheric pressure, other silica minerals like tridymite will form instead of quartz.
The Footprint of High Quartz
Even though we only ever find low quartz, it often retains the hexagonal crystal shape of its high-temperature past. Geologists can identify this original shape (a "pseudomorph") to understand the temperature conditions under which a rock originally formed.
The Overlooked Role of Pressure
The 573°C inversion point is true for atmospheric pressure. Deep within the Earth's crust, immense pressure can shift this transition temperature, a critical factor for geologists modeling mineral formation.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your interpretation of quartz's formation depends on your objective.
- If your primary focus is mineral identification: You will always be handling low quartz (alpha-quartz), as the high-temperature form is unstable at surface conditions.
- If your primary focus is geology or petrology: Recognizing the original crystal shape of high quartz in a low-quartz specimen provides a powerful clue, indicating the rock must have cooled from a temperature above 573°C.
Ultimately, temperature dictates the fundamental crystal structure of this ubiquitous and essential mineral.
Summary Table:
| Quartz Type | Formation Temperature | Crystal Structure | Stability at Room Temp |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Quartz (Beta) | 573°C to 870°C | Hexagonal | No (inverts upon cooling) |
| Low Quartz (Alpha) | Below 573°C | Trigonal | Yes (stable) |
Need precise temperature control for your geological or materials research? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment, including furnaces that can accurately replicate the conditions needed to study quartz formation and other mineral transformations. Our solutions help geologists, petrologists, and materials scientists achieve reliable results. Contact us today to learn how our equipment can support your research goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the lab safety rules for heating substances? Essential Protocols to Prevent Accidents
- How do you check the temperature of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Monitoring
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food lab? Essential for Accurate Ash Content Analysis
- What are the 3 official methods in determining ash and water content? A Guide to Proximate Analysis
- What is the temperature range of a laboratory muffle furnace? Find the Right Model for Your Application



















