At its core, heat treatment fundamentally alters a material's mechanical properties by changing its internal microscopic structure. This process allows engineers to precisely tailor characteristics like hardness, strength, and ductility by carefully controlling heating and cooling cycles.
Heat treatment is not about changing a material's chemical composition, but about rearranging its existing internal crystal structure to achieve a specific, desired balance of properties for a given application.

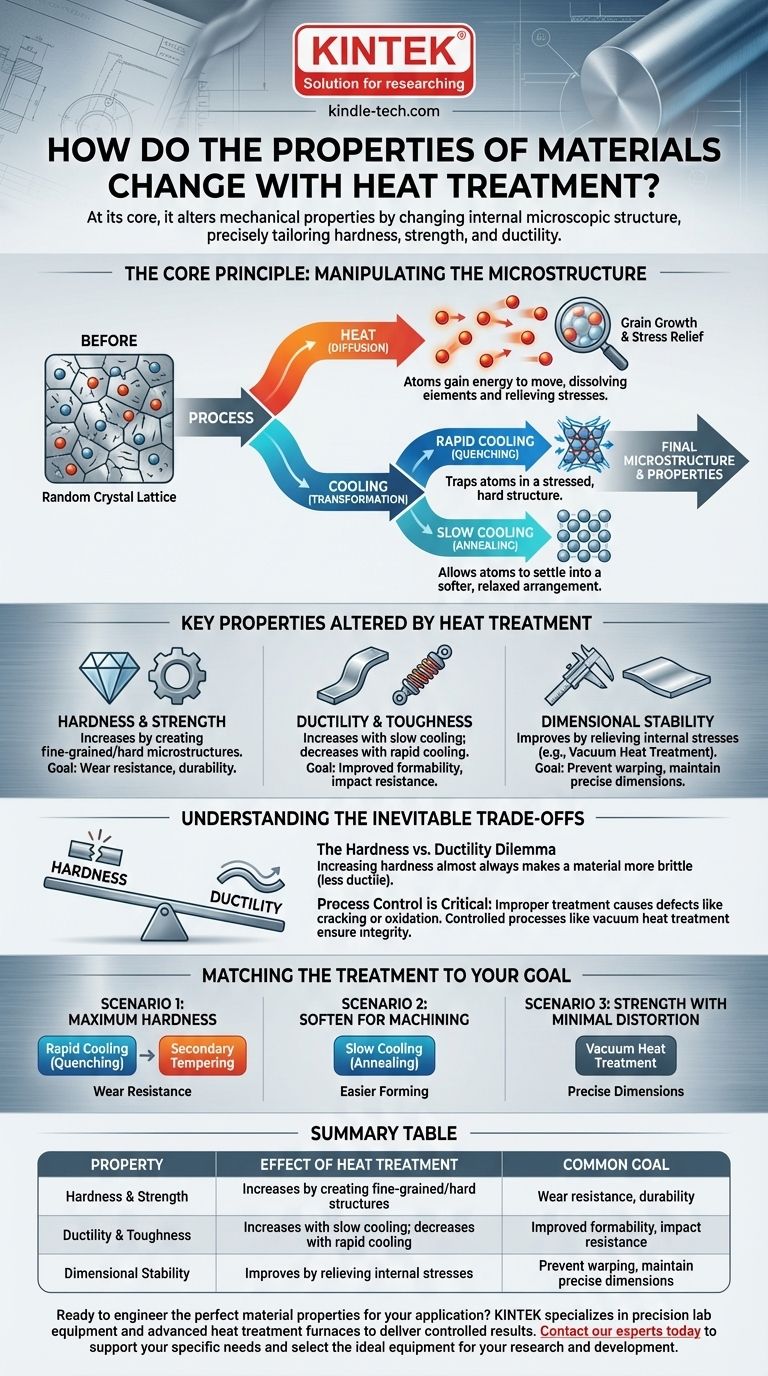
The Core Principle: Manipulating the Microstructure
Heat treatment works by giving atoms within a metal's crystal lattice the energy to move and then locking them into a new, more desirable arrangement upon cooling.
What is a Microstructure?
Metals are not uniform solids but are composed of countless tiny, individual crystals called grains. The size, shape, and arrangement of these grains—along with other phases within the metal—constitute its microstructure.
The specific nature of this microstructure is the primary determinant of the material's mechanical behavior.
The Role of Heat (Diffusion)
Heating a metal gives its atoms thermal energy, allowing them to move and rearrange within the crystal lattice. This process, known as diffusion, can dissolve elements, grow or shrink grains, and relieve internal stresses locked in from previous manufacturing steps.
The Role of Cooling (Transformation)
The rate of cooling is the most critical control parameter. It determines what final microstructure is "frozen" in place at room temperature.
Rapid cooling (quenching) traps the atoms in a highly stressed, hard structure, while slow cooling allows them to settle into a softer, more relaxed arrangement.
Key Properties Altered by Heat Treatment
The goal of manipulating the microstructure is to enhance specific properties required for the material's final use.
Hardness and Strength
Heat treatment is most commonly used to increase a material's hardness (resistance to scratching and indentation) and strength (resistance to deformation). This is achieved by creating fine-grained structures or specific hard phases that prevent the internal crystal planes from slipping past one another.
Ductility and Toughness
Ductility is the ability to bend or stretch without breaking, while toughness is the ability to absorb energy before fracturing. Often, treatments that increase hardness will decrease ductility and toughness, but other processes like annealing are designed specifically to make a material softer and more ductile.
Dimensional Stability
Relieving internal stresses is a crucial outcome of many heat treatment processes. This prevents parts from warping or distorting over time or during subsequent machining.
Specialized methods like vacuum heat treatment excel here, as they prevent surface reactions like oxidation and ensure uniform heating and cooling, minimizing the risk of distortion.
Understanding the Inevitable Trade-offs
You cannot maximize all properties simultaneously. Engineering is about choosing the right balance for the intended function.
The Hardness vs. Ductility Dilemma
This is the classic trade-off. Increasing a metal's hardness almost always makes it more brittle (less ductile). A file is extremely hard but will snap if you try to bend it. A paperclip is very ductile but not hard at all.
Process Control is Critical
Improper heat treatment can introduce defects. If cooling is too fast or non-uniform, a part can crack. If the atmosphere is not controlled, the surface can oxidize (scale), ruining the finish and dimensions of the component.
This is why controlled processes like vacuum heat treatment are used for high-performance applications where both surface integrity and dimensional stability are paramount.
Matching the Treatment to Your Goal
The right heat treatment process is dictated entirely by the desired outcome for the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: A process involving rapid cooling (quenching), often followed by a secondary tempering step to reduce brittleness, is the correct path.
- If your primary focus is to soften the material for easier machining or forming: A process like annealing, which uses very slow cooling, will create the desired soft and ductile microstructure.
- If your primary focus is strength with minimal distortion: A carefully controlled process, such as vacuum heat treatment, is essential to enhance mechanical properties while preserving the part's precise dimensions.
Ultimately, heat treatment is the essential step that transforms a generic metal alloy into a high-performance component engineered for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Property | Effect of Heat Treatment | Common Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Strength | Increases by creating fine-grained or hard microstructures. | Wear resistance, durability. |
| Ductility & Toughness | Increases with slow cooling (annealing); decreases with rapid cooling (quenching). | Improved formability, impact resistance. |
| Dimensional Stability | Improves by relieving internal stresses, especially with uniform processes like vacuum heat treatment. | Prevent warping, maintain precise dimensions. |
Ready to engineer the perfect material properties for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment, including advanced heat treatment furnaces. Whether you need to achieve maximum hardness, improve ductility, or ensure dimensional stability for your laboratory components, our solutions deliver controlled and reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you select the ideal heat treatment equipment for your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between oven and muffle furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heating Equipment
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play during the re-austenitization of 17-4 PH? Transform SLM Performance
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace influence NASICON-type LAGP pellets? Optimize Your Solid Electrolyte
- What are muffle furnaces used for? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace necessary for APTES-modified TiO2? Optimize Your Material Phase Transformation
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace contribute to the research of microstructure evolution in rare earth steel?
- Why is a high-temperature box furnace used for Ti/Cu annealing? Optimize Bimetallic Material Performance
- What is a muffle furnace? The Definitive Tool for Contaminant-Free, Precise Heating



















