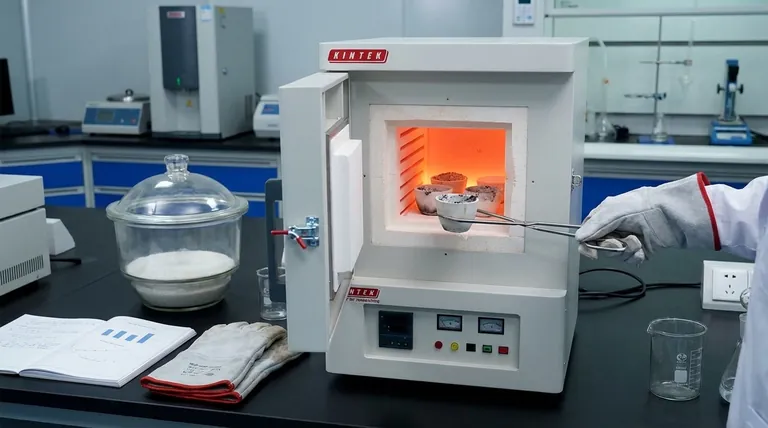
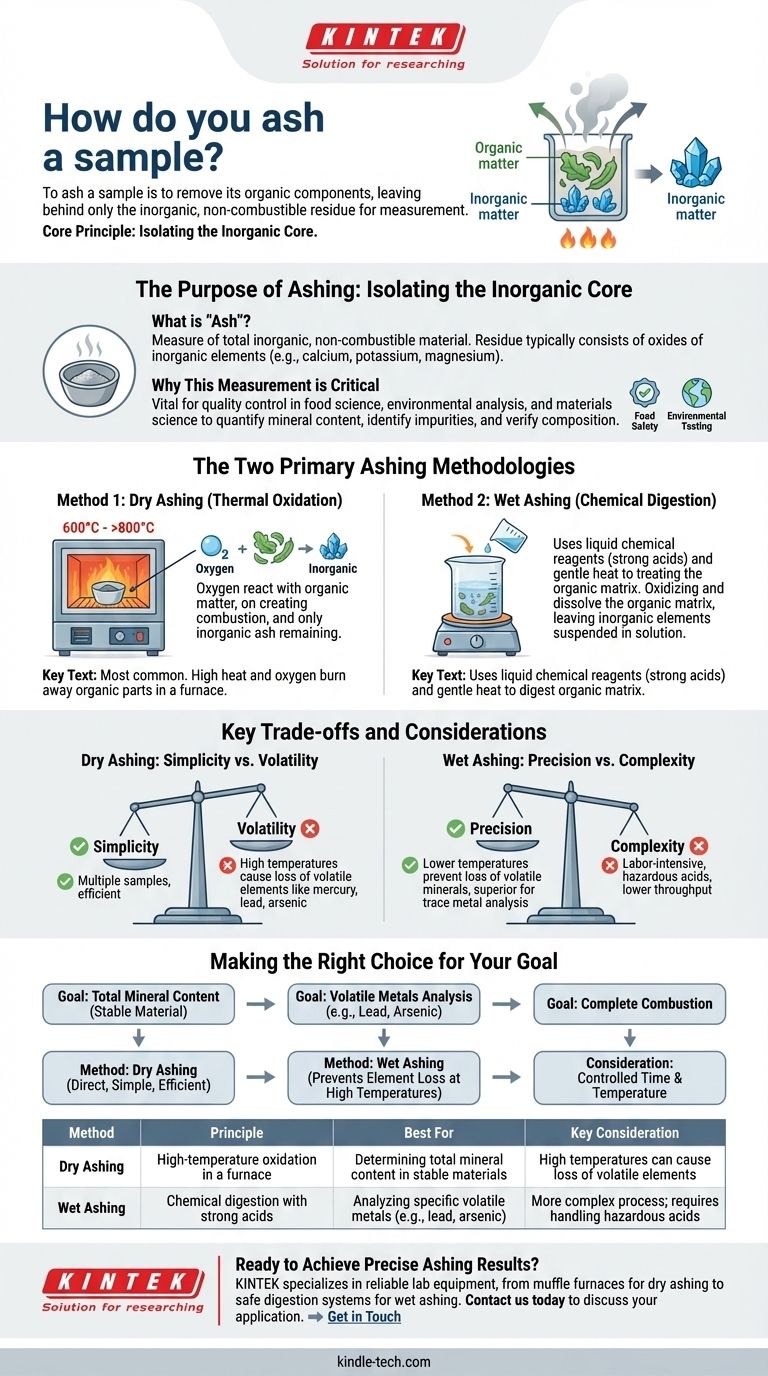
To ash a sample is to remove its organic components, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible residue for measurement. The most common method involves placing the sample in a high-temperature furnace and heating it in the presence of air until all the organic matter burns away through oxidation.
The core principle of ashing is the complete separation of organic and inorganic matter. Your choice of method—either high-temperature dry ashing or chemical wet ashing—is determined by the specific elements you need to measure and their stability.

The Purpose of Ashing: Isolating the Inorganic Core
Ashing is a fundamental analytical technique used to determine the mineral or inorganic content of a sample. The resulting ash provides a concentrated form of these components for further analysis.
What is "Ash"?
The ash content is a measure of the total amount of inorganic, non-combustible material within a sample. This residue typically consists of the oxides of the inorganic elements (like calcium, potassium, magnesium, etc.) that were present in the original material.
Why This Measurement is Critical
Determining ash content is vital for quality control in many industries, including food science, environmental analysis, and materials science. It helps quantify the mineral content, identify impurities, or verify the composition of a product.
The Two Primary Ashing Methodologies
While both methods achieve the same goal of removing organic material, they operate on entirely different principles.
Method 1: Dry Ashing (Thermal Oxidation)
Dry ashing is the most common approach. It leverages high heat and oxygen to burn away the organic parts of a sample.
The prepared sample is placed in a crucible, which is then heated in a muffle furnace. As the temperature rises, the organic compounds react with oxygen in the air and combust, leaving only the inorganic ash behind.
Method 2: Wet Ashing (Chemical Digestion)
Wet ashing, also known as acid digestion, uses liquid chemical reagents instead of high heat.
This process involves adding strong acids to the sample and heating it gently. The acids aggressively oxidize and dissolve the organic matrix, leaving the inorganic elements suspended in the resulting solution.
Key Trade-offs and Considerations
Choosing the wrong method can lead to inaccurate results. The decision hinges on the trade-off between simplicity and the potential for analyte loss.
Dry Ashing: Simplicity vs. Volatility
The primary advantage of dry ashing is its simplicity and ability to process multiple samples at once.
However, the high temperatures (often 600°C to over 800°C) can cause certain volatile inorganic elements, such as mercury, lead, or arsenic, to vaporize and be lost. This makes it unsuitable for analyzing those specific elements.
Wet Ashing: Precision vs. Complexity
Wet ashing operates at much lower temperatures, which prevents the loss of volatile minerals. This makes it the superior choice for trace metal analysis.
The downside is that it is a more complex, labor-intensive process. It requires careful handling of hazardous acids and has a much lower sample throughput compared to dry ashing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your analytical objective dictates the correct ashing procedure.
- If your primary focus is determining the total mineral content of a stable material: Dry ashing is the most direct, simple, and efficient method.
- If your primary focus is analyzing for specific volatile metals (like lead or arsenic): Wet ashing is essential to prevent the loss of these elements at high temperatures.
- If your goal is to ensure complete combustion: The ashing time and temperature must be carefully controlled to be long enough to remove all organics but not so long that it alters the inorganic residue.
Ultimately, selecting the correct ashing technique is a critical first step that depends entirely on the composition of your sample and the specific elements you intend to measure.
Summary Table:
| Method | Principle | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Ashing | High-temperature oxidation in a furnace | Determining total mineral content in stable materials | High temperatures can cause loss of volatile elements |
| Wet Ashing | Chemical digestion with strong acids | Analyzing specific volatile metals (e.g., lead, arsenic) | More complex process; requires handling hazardous acids |
Ready to Achieve Precise Ashing Results?
Choosing the correct ashing method is critical for accurate inorganic analysis. KINTEK specializes in providing the reliable lab equipment—from robust muffle furnaces for dry ashing to safe digestion systems for wet ashing—that your laboratory needs for consistent, high-quality results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and let our experts help you select the perfect solution. ➡️ Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now
- Why do we need to use properly some of the laboratory apparatus in the laboratory? The Foundation of Safe and Accurate Science
- What are the factors affecting the rate of melting process? Master Heat Transfer for Faster Results
- What is an example of quenching? Achieve Optimal Hardness with Precise Cooling



















