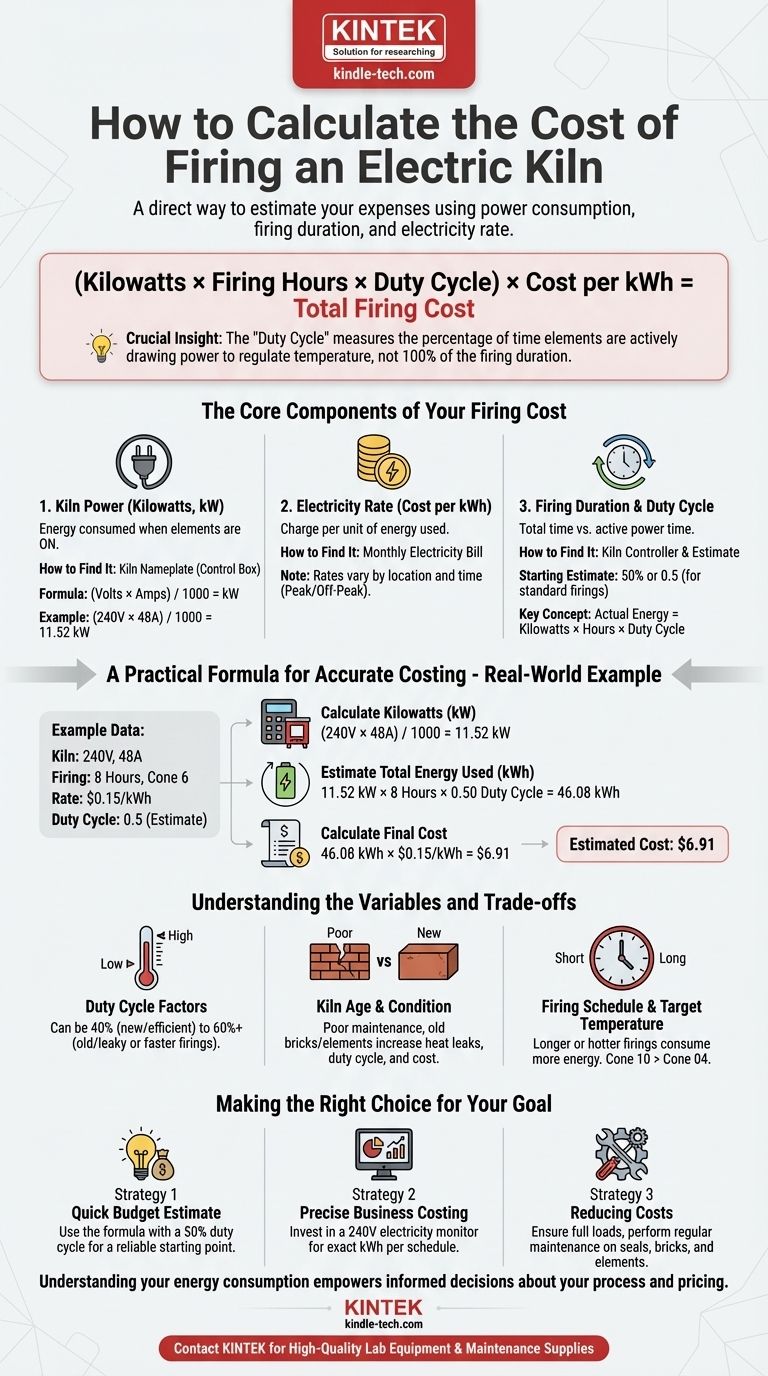
The most direct way to calculate your kiln firing cost is by combining your kiln's power consumption (in kilowatts), the total duration of the firing, and your electricity rate. A simple but effective formula is: (Kilowatts × Firing Hours × Duty Cycle) × Cost per kWh = Total Firing Cost. We will break down what each of those terms means.
The crucial insight is that your kiln is not drawing maximum power for the entire firing. It cycles on and off to regulate temperature. Understanding this "duty cycle" is the key to moving from a rough guess to an accurate, reliable cost calculation.
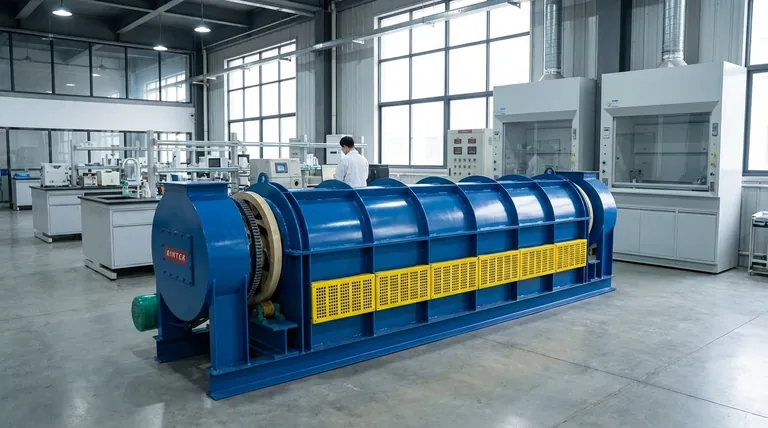

The Core Components of Your Firing Cost
To accurately project your expenses, you must first understand the three variables that determine the final cost on your utility bill.
1. Kiln Power (Kilowatts)
Your kiln's power rating is a measure of how much electricity it consumes when the elements are on. This is measured in kilowatts (kW).
You can calculate this using the information on your kiln's metal nameplate, which is usually located on the control box. You will need the Volts and Amps.
The formula is: (Volts × Amps) / 1000 = Kilowatts (kW)
For example, a common kiln might be rated for 240 volts and 48 amps. Its power would be (240 × 48) / 1000 = 11.52 kW.
2. Electricity Rate (Cost per kWh)
Your utility company charges you based on the amount of energy you use, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). One kWh is equivalent to running a 1,000-watt appliance for one full hour.
You can find your cost per kWh on your monthly electricity bill. This rate can vary significantly by location and time of day. Be aware of "peak" and "off-peak" rates if your plan has them.
3. Firing Duration & Duty Cycle
This is the most overlooked and critical variable. Your kiln's heating elements are not on 100% of the time. They cycle on and off to follow the programmed temperature ramp.
The Duty Cycle is the percentage of time the elements are actively drawing power. A safe and common starting estimate for a standard bisque or mid-range glaze firing is 50% (or 0.5).
Therefore, the actual energy used is not just Kilowatts × Hours. It's Kilowatts × Hours × Duty Cycle.
A Practical Formula for Accurate Costing
With these three components understood, you can calculate your cost in a few simple steps. Let's use a real-world example.
- Kiln: 240 Volts, 48 Amps
- Firing: 8-hour program to Cone 6
- Electricity Rate: $0.15 per kWh
Step 1: Calculate Kilowatts (kW)
Use the formula from the kiln's nameplate.
(240 Volts × 48 Amps) / 1000 = 11.52 kW
Step 2: Estimate Total Energy Used (kWh)
Multiply the kiln's power by the firing duration and the estimated duty cycle.
11.52 kW × 8 hours × 0.50 Duty Cycle = 46.08 kWh
This is the total kilowatt-hours your firing will consume.
Step 3: Calculate the Final Cost
Multiply the total energy used by your electricity rate.
46.08 kWh × $0.15/kWh = $6.91
The estimated cost for this specific 8-hour firing is $6.91.
Understanding the Variables and Trade-offs
Your actual cost can vary. The 50% duty cycle is an estimate, and several factors can push it higher or lower.
Why the Duty Cycle is the Biggest Factor
A new, efficient kiln firing on a cool day might have a duty cycle closer to 40%. An old, leaky kiln with worn elements firing on a hot day might have a duty cycle of 60% or more, significantly increasing the cost. Faster firing schedules also result in a higher duty cycle because the elements must stay on longer to keep up.
The Impact of Kiln Age and Condition
Proper maintenance is an investment. Old or damaged firebricks, worn-out elements, and poor lid seals create heat leaks. This forces the kiln to work harder, increasing the duty cycle and driving up your firing costs.
Firing Schedule and Target Temperature
Longer or hotter firings naturally consume more energy. A slow 12-hour bisque may use a similar amount of energy as a faster 8-hour glaze firing because the lower duty cycle of the bisque is offset by the longer duration. Firing to Cone 10 will always cost more than firing to Cone 04 in the same kiln.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use this knowledge to move from guessing to strategically managing your studio costs.
- If your primary focus is a quick budget estimate: Use the formula with a 50% duty cycle; it provides a reliable starting point for most standard firings.
- If your primary focus is precise business costing: Invest in a dedicated 240V electricity usage monitor to measure the exact kWh for each of your common firing schedules.
- If your primary focus is reducing costs: Ensure your kiln is fully loaded for every firing and perform regular maintenance on seals, bricks, and elements to maximize efficiency.
Understanding your energy consumption empowers you to make informed decisions about your process and pricing.
Summary Table:
| Variable | Description | How to Find It |
|---|---|---|
| Kilowatts (kW) | Power consumption when elements are on. | Kiln nameplate: (Volts × Amps) / 1000 |
| Firing Hours | Total duration of the firing program. | Your kiln controller. |
| Duty Cycle | % of time elements are actively on. | Estimate: ~50% for standard firings. |
| Cost per kWh | Your electricity rate. | Your utility bill. |
| Total Cost | Final firing expense. | Formula: (kW × Hours × Duty Cycle) × Cost per kWh |
Take Control of Your Lab's Efficiency and Budget
Now that you can accurately project your kiln's operating costs, ensure your equipment is running at peak performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable electric kilns and essential maintenance parts like heating elements and firebricks.
We help laboratories like yours:
- Reduce energy costs with efficient, well-maintained equipment.
- Achieve consistent, reliable results with precise temperature control.
- Minimize downtime with durable consumables and expert support.
Ready to optimize your firing process and reduce expenses? Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on the right kiln or maintenance supplies for your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















