To properly maintain a vacuum furnace hot zone, you must implement a system of rigorous daily inspections and long-term strategic oversight. The core daily tasks involve visually checking heating elements and shields for physical damage like breaks, signs of discoloration which indicate a vacuum leak, and evidence of electrical arcing. This physical diligence must be supported by a disciplined process of logging operating hours, tracking component health, and proactively managing spare parts to prevent catastrophic failure.
The health of your hot zone is not merely a maintenance task; it is a direct predictor of your operational uptime, process quality, and financial performance. A reactive "fix it when it breaks" approach is a liability, while a proactive maintenance strategy is a competitive advantage.
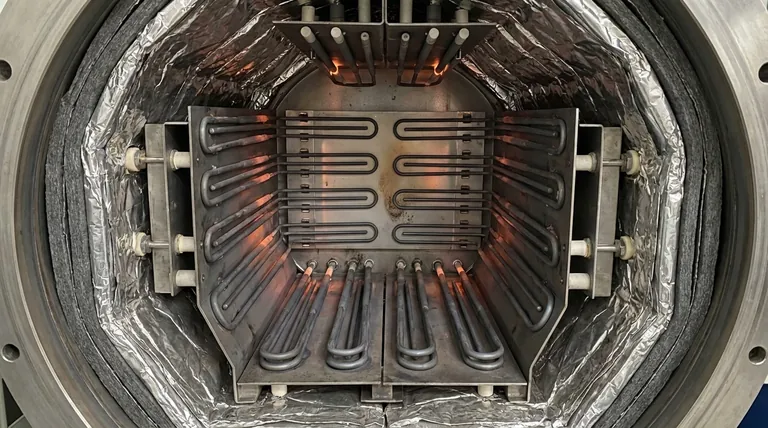
Why Meticulous Hot zone Maintenance is Critical
The hot zone is the functional core of the entire vacuum furnace system. Understanding its role clarifies why maintenance cannot be an afterthought.
The Heart of the Furnace
The hot zone is where the thermal processing occurs. It contains the heating elements, typically made of materials like molybdenum, which are resistively heated to extreme temperatures, often exceeding 1300°C (2372°F).
This entire assembly is designed to produce and contain immense heat uniformly within a high-quality vacuum, making its integrity essential for any successful process.
The High Cost of Failure
A hot zone failure is never a minor event. It directly leads to significant production downtime, costly emergency repairs, and potentially scrapped product batches.
Degradation of elements or insulation compromises temperature uniformity, jeopardizing the metallurgical properties of the parts being treated. Letting a small issue fester can cause a cascading failure that destroys the entire hot zone.
A Two-Part Maintenance Strategy
Effective maintenance is a combination of daily diligence on the floor and strategic management in the office. One cannot succeed without the other.
Part 1: Daily Visual Inspections
These routine checks are your first line of defense and can catch over 90% of developing problems.
Check for Broken or Damaged Elements
Visually inspect the heating elements. Look for any cracks, breaks, or significant sagging, which can lead to electrical shorts or uneven heating.
Check for Discoloration
Elements and heat shields should maintain their clean, metallic appearance. Any discoloration (often blueing or browning) is a critical warning sign.
It signifies a loss of vacuum integrity during a cycle, meaning oxygen has entered the chamber at high temperatures and caused oxidation. This accelerates component degradation.
Look for Signs of Arcing
Inspect the elements, insulators, and support hardware for any pitting, melting, or small, fused spots. Arcing indicates an electrical discharge and can quickly destroy an element or damage the insulation.
Part 2: Systemic Oversight and Record-Keeping
This is the strategic framework that turns maintenance from a chore into a management tool.
Establish Strict Operating Rules
Document and enforce standard operating procedures for every stage of the furnace process, from loading to cooling. Consistency reduces errors and premature wear.
Maintain Meticulous Records
Keep a detailed log for the furnace that includes operating hours, cycle parameters, repair history, and all observations from daily inspections. This data is invaluable for troubleshooting and predictive maintenance.
Anticipate Failures
Use your operating logs to track the service life of critical components like heating elements. Knowing a set of elements has 5,000 hours of service allows you to plan for their replacement, rather than react to a failure.
Prepare Spare Parts
Based on workload and component life data, maintain an inventory of essential spare parts. Having elements, insulators, or thermocouples on hand can reduce downtime from days to hours.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Trade-offs
A proactive maintenance culture requires buy-in, as it involves perceived upfront costs. However, these "costs" are investments that prevent much larger financial losses.
The Fallacy of "Running to Failure"
A reactive maintenance approach seems to save money by deferring service costs. This is a false economy.
The cost of unplanned downtime, emergency shipping for parts, overtime for technicians, and scrapped product will almost always exceed the cost of a planned, preventative maintenance program.
Misinterpreting the Signs
Ignoring discoloration is one of the most common and costly mistakes. It is not a cosmetic issue; it is a diagnostic indicator of a critical vacuum leak.
Failing to find and fix the source of the leak means you will be replacing oxidized hot zone components again and again, without ever solving the root cause.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance strategy can be tuned to your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: Prioritize tracking operating hours and proactively replacing components before they reach their expected end-of-life.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process quality: Make daily discoloration checks your most critical task, as this directly indicates contamination that can ruin product.
- If your primary focus is budget control: Use meticulous record-keeping to justify maintenance spending and demonstrate how preventative actions extend the life of expensive assets and avoid catastrophic, unbudgeted failures.
By treating hot zone maintenance as a core operational function, you take direct control over your furnace's reliability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Task | Key Action | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Visual Inspection | Check for breaks, discoloration, arcing | Catches 90% of problems early, prevents catastrophic failure |
| Systemic Record-Keeping | Log operating hours, repairs, observations | Enables predictive maintenance and data-driven decisions |
| Proactive Spare Parts | Maintain inventory of elements, insulators | Drastically reduces unplanned downtime from days to hours |
Protect your investment and ensure flawless thermal processing. A well-maintained vacuum furnace is the backbone of reliable production. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing the support, spare parts, and guidance you need to implement a proactive maintenance strategy. Don't wait for a failure to disrupt your operations—contact our team today to discuss your specific furnace and consumable needs.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.



















