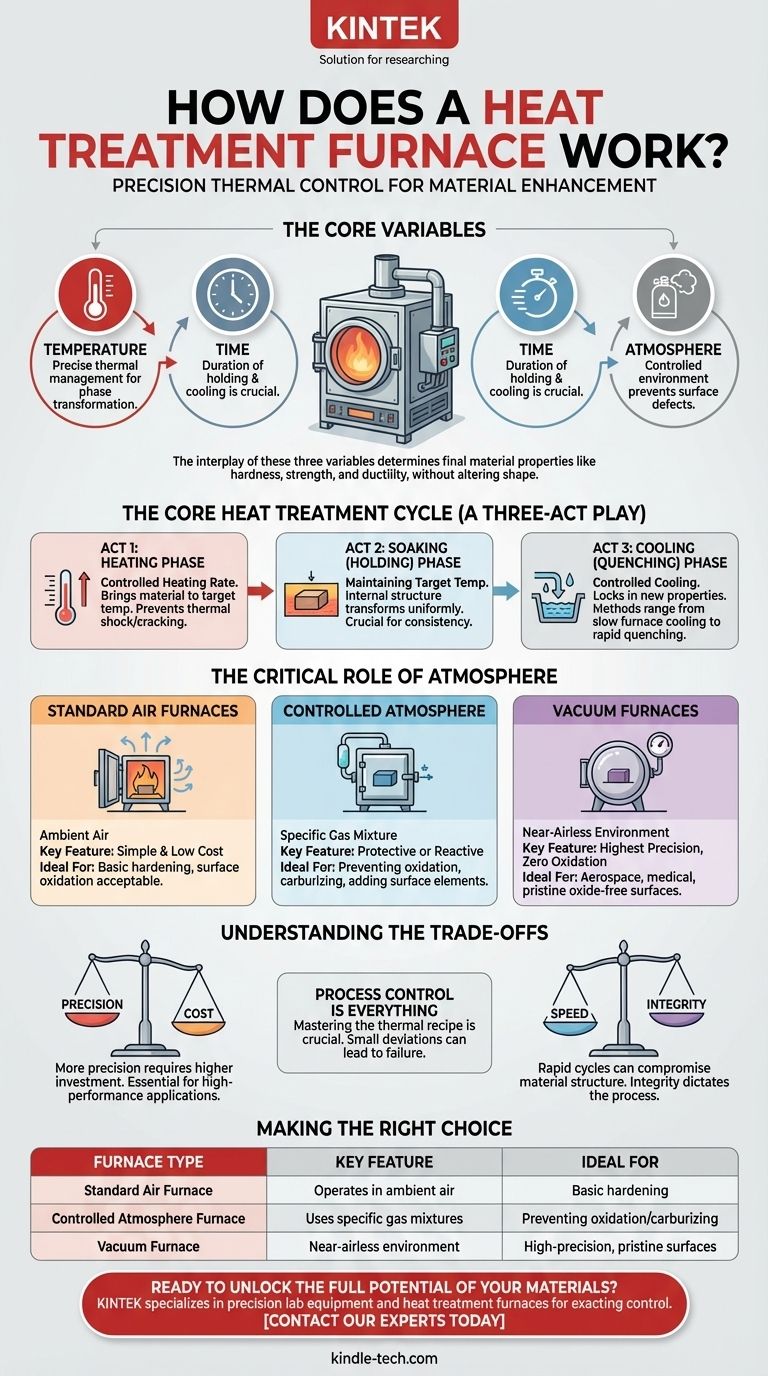
At its core, a heat treatment furnace is a precision instrument that uses a highly controlled thermal cycle—heating, holding (soaking), and cooling—to deliberately alter a material's internal structure. This process isn't about simply making something hot; it's a carefully executed recipe designed to enhance specific properties like hardness, strength, or ductility without changing the material's shape.
The fundamental principle of any heat treatment furnace is the precise management of three critical variables: temperature, time, and atmosphere. How these three are controlled determines the final properties of the material being treated.

The Core Heat Treatment Cycle
Think of the process as a three-act play, where each stage serves a distinct metallurgical purpose. The furnace's control system automates this entire sequence to ensure consistency and repeatability.
Act 1: The Heating Phase
The first step is to bring the material up to a target temperature at a controlled rate. The furnace applies a high amount of energy during this phase to overcome the material's thermal mass.
The rate of heating is critical. Heating too quickly can induce thermal shock and stress, potentially causing cracks or distortion in complex parts.
Act 2: The Soaking (Holding) Phase
Once the target temperature is reached, the furnace reduces its energy output to maintain that temperature precisely. This holding period is called "soaking."
During the soak, the material's internal crystalline structure transforms. The length of this phase is crucial for ensuring the entire part, from surface to core, achieves a uniform and stable new structure.
Act 3: The Cooling (Quenching) Phase
After soaking, the material is cooled in a controlled manner to "lock in" the new properties. The cooling rate is one of the most decisive factors in determining the final outcome.
Methods can range from slow cooling within the furnace itself to rapid cooling (quenching) in a medium like oil, water, or even a fast-cooling gas chamber.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace is just as important as the temperature cycle. At high temperatures, most metals will readily react with oxygen in the air, causing scaling and discoloration (oxidation) that can ruin the part's surface.
Standard Furnaces
The simplest furnaces operate in ambient air. These are suitable for processes where surface oxidation is not a concern or will be removed later.
Controlled Atmosphere Furnaces
These furnaces have a well-sealed body that allows the air to be replaced with a specific mixture of gases. This "atmosphere" can be protective (inert) to prevent reactions or even reactive to intentionally add elements to the material's surface (like in carburizing).
Vacuum Furnaces
For the highest level of control, a vacuum furnace is used. The process begins by pumping nearly all the air out of the sealed chamber, creating a low-pressure environment.
This vacuum eliminates the risk of oxidation and other surface reactions. Often, an inert gas like argon is backfilled into the chamber to assist with uniform heat transfer. The entire process is computer-controlled for extreme precision.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing and operating a heat treatment furnace involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these is key to achieving the desired result reliably.
Precision vs. Cost
A simple air furnace is far less expensive than a computer-controlled vacuum furnace. However, the vacuum furnace offers vastly superior control over the final surface finish and material properties, which is non-negotiable for high-performance applications like aerospace or medical components.
Process Control is Everything
The most advanced furnace is ineffective if the wrong thermal recipe is used. Mastering the correct operating process is crucial. A small deviation in temperature, soak time, or cooling rate can lead to a failed part, wasted energy, and reduced furnace lifespan.
Speed vs. Integrity
While faster cycle times seem efficient, they can be detrimental. Rapid heating or cooling rates that are not suited for the specific material or part geometry are a primary cause of internal stress, distortion, and cracking. The integrity of the final product dictates the cycle parameters, not the clock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of furnace and process you need depends entirely on the material and the properties you aim to achieve.
- If your primary focus is basic hardening of simple tool steels: A standard air furnace with an associated quench tank is often sufficient.
- If your primary focus is preventing discoloration and achieving a clean, bright finish: A controlled atmosphere or vacuum furnace is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive, high-performance alloys with maximum precision and repeatability: A computer-controlled vacuum furnace is the industry standard.
Ultimately, a heat treatment furnace is a tool that uses a meticulously controlled recipe of heat, time, and atmosphere to unlock a material's hidden potential.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Air Furnace | Operates in ambient air | Basic hardening where surface oxidation is acceptable |
| Controlled Atmosphere Furnace | Uses specific gas mixtures | Preventing oxidation or adding surface elements (e.g., carburizing) |
| Vacuum Furnace | Processes in a near-airless environment | High-precision applications requiring pristine, oxide-free surfaces |
Ready to unlock the full potential of your materials? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including heat treatment furnaces designed for reliability and exacting control. Whether you're hardening tool steels or processing sensitive alloys, our solutions ensure consistent, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















