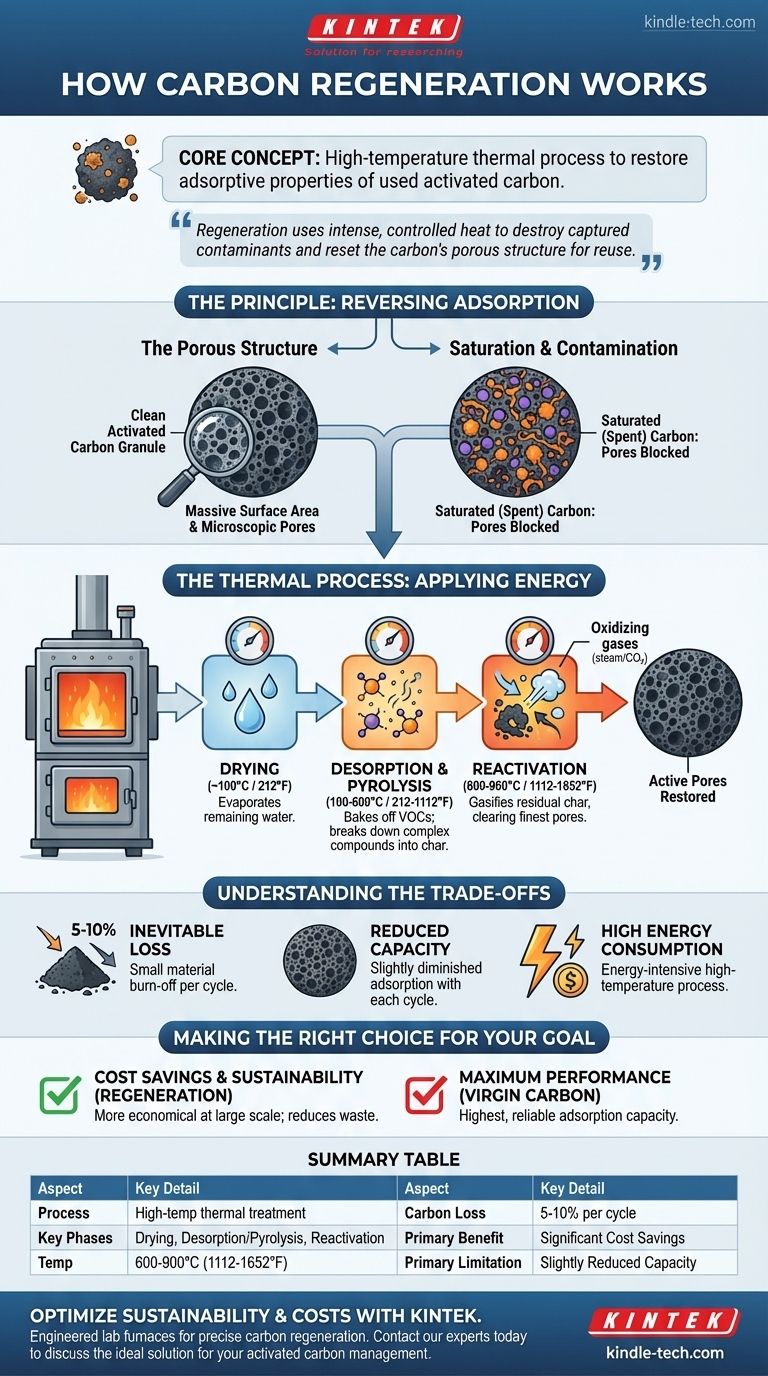
At its core, carbon regeneration is a high-temperature thermal process designed to restore the adsorptive properties of used activated carbon. By applying intense, controlled heat, the organic compounds that have been captured and are clogging the carbon's pores are destroyed or vaporized. This effectively "cleans" the carbon, allowing it to be reused for filtration and purification.
The central challenge with activated carbon is that it eventually becomes saturated with contaminants. Regeneration solves this by using a thermal process, often called reactivation, to violently strip away and destroy these adsorbed components, resetting the carbon's porous structure so it can be used again.

The Principle: Reversing Adsorption
To understand regeneration, you must first understand how activated carbon works. It is not a simple filter but a material with an incredibly vast internal surface area filled with microscopic pores.
The Role of the Porous Structure
Think of a single granule of activated carbon as a massive sponge at a microscopic level. This network of pores creates an immense surface area where contaminants, through a process called adsorption, stick to the surface.
Saturation: When the "Sponge" is Full
Over time, these surfaces become completely coated with the adsorbed components. The carbon is now "spent" or saturated, and can no longer effectively remove contaminants from a liquid or gas stream.
Applying Thermal Energy
Regeneration works by applying the energy needed to break the bonds holding the contaminants to the carbon's surface. The process typically occurs in a low-oxygen environment within a specialized furnace.
This thermal process happens in distinct phases:
- Drying (~100°C / 212°F): Any remaining water is evaporated from the carbon.
- Desorption & Pyrolysis (100-600°C / 212-1112°F): As the temperature rises, volatile organic compounds are baked off (desorbed). More complex, heavier compounds are broken down into smaller molecules and elemental char through pyrolysis.
- Reactivation (600-900°C / 1112-1652°F): At very high temperatures, oxidizing gases like steam or carbon dioxide are introduced. This final, critical step gasifies and removes the residual pyrolyzed char, clearing out the finest pores and restoring the carbon's adsorptive capacity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, regeneration is not a perfect process. It is a harsh thermal treatment that comes with inherent limitations.
Inevitable Carbon Loss
Each regeneration cycle burns off a small amount of the activated carbon itself. Typically, there is a 5-10% loss of material by weight with each reactivation. This "burn-off" means there is a finite number of times a batch of carbon can be regenerated before it is depleted.
Reduced Adsorption Capacity
The regenerated carbon is almost never as effective as virgin (new) carbon. The extreme heat can cause minor damage to the pore structure. As a result, the total surface area and adsorption capacity are slightly diminished with each cycle.
High Energy Consumption
Heating materials to over 800°C is an energy-intensive and costly process. While often more economical than purchasing new carbon for large-scale operations, the energy footprint is a significant factor to consider.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding between using regenerated carbon and purchasing new material depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost savings at a large scale: Regeneration is almost always the more economical choice, as the cost to reactivate is significantly lower than the cost of virgin carbon.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Regeneration is the superior option, as it dramatically reduces landfill waste and the carbon footprint associated with producing and transporting new material.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance for a critical application: Virgin activated carbon will always provide the highest and most reliable adsorption capacity.
By understanding regeneration as a process of thermal restoration, you can make an informed decision that balances performance, cost, and environmental impact.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature thermal treatment in a low-oxygen furnace |
| Key Phases | Drying, Desorption/Pyrolysis, Reactivation |
| Typical Temperature | 600-900°C (1112-1652°F) |
| Carbon Loss Per Cycle | 5-10% by weight |
| Primary Benefit | Significant cost savings vs. new carbon |
| Primary Limitation | Slightly reduced adsorption capacity after each cycle |
Optimize your laboratory's sustainability and operational costs with KINTEK.
Our specialized lab furnaces are engineered for precise, efficient thermal processes like carbon regeneration. By choosing KINTEK, you gain a reliable partner for maintaining your critical filtration and purification systems, reducing both expenses and environmental impact.
Ready to explore how our equipment can support your specific laboratory needs? Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal solution for your activated carbon management.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- Why is a muffle furnace or oven used for thermal annealing after silver nanowire deposition? Unlock Peak Conductivity
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play during the re-austenitization of 17-4 PH? Transform SLM Performance
- What is ashing in chemistry? Enhance Analytical Accuracy with Ashing Techniques
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the sintering process of coating? Building Durable, Solid Layers from Powder














