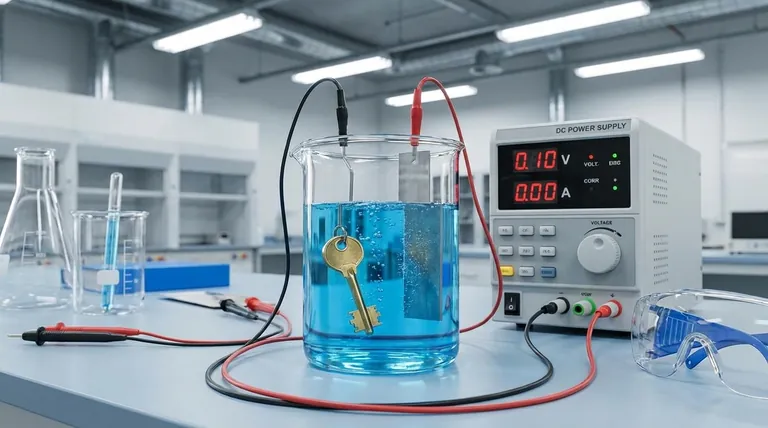
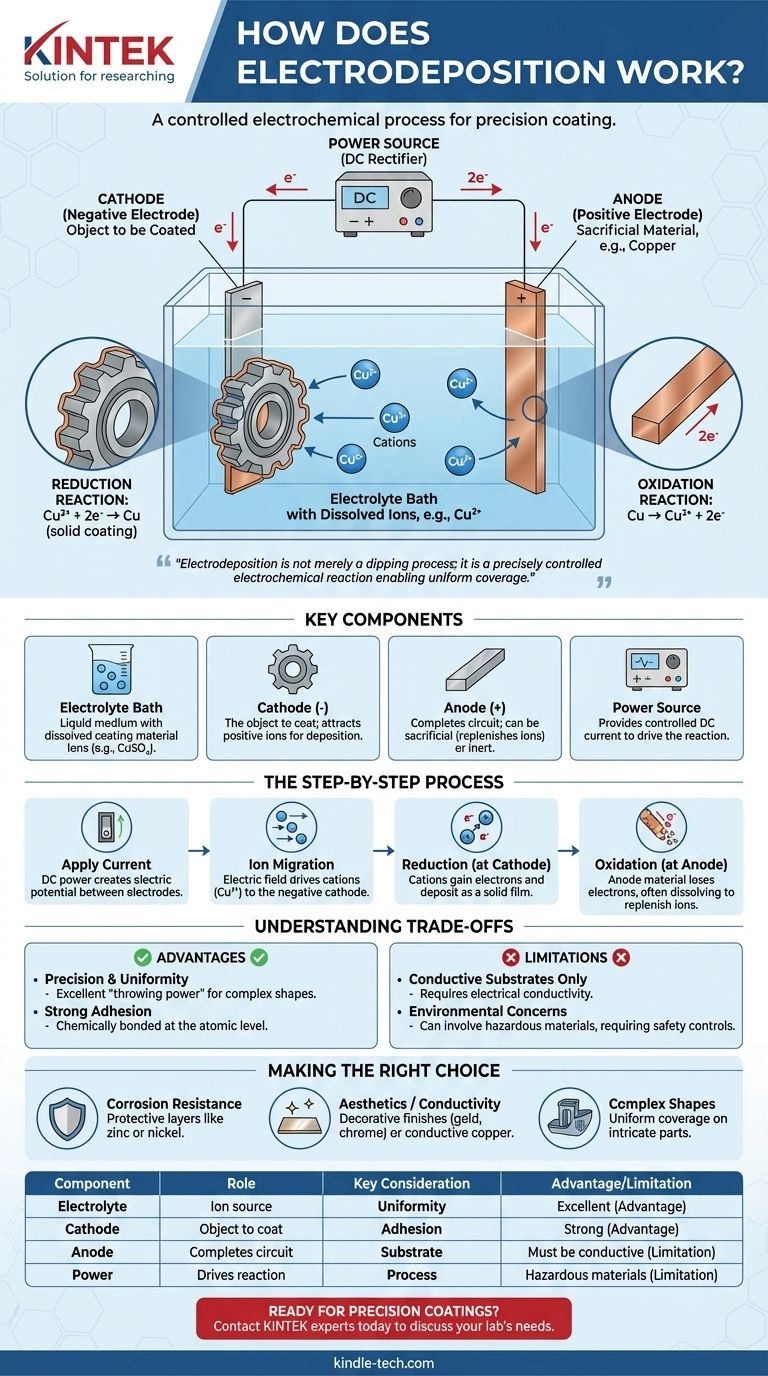
At its core, electrodeposition is a process that uses an electric current to coat a conductive object with a thin layer of material. This is achieved by immersing the object (the cathode) and a second electrode (the anode) into a chemical solution, or electrolyte bath, containing dissolved ions of the coating material. When a direct current is applied, these ions are drawn to the object's surface, where they are "deposited" as a solid, creating a uniform and adherent metallic or organic film.
The crucial insight is that electrodeposition is not merely a dipping process; it is a precisely controlled electrochemical reaction. The electric field dictates where and how the coating forms, enabling the uniform coverage of even the most complex shapes with a layer whose thickness is directly proportional to the applied current and time.

The Key Components of the Electrodeposition Cell
To understand the process, you must first understand its fundamental components. Every electrodeposition setup, from a lab beaker to an industrial tank, consists of four essential parts working in concert.
The Electrolyte Bath
The electrolyte is the liquid medium that facilitates the entire process. It's a solution, typically water-based, containing dissolved salts of the material to be deposited. For example, in copper plating, the bath would contain a salt like copper sulfate (CuSO₄), which provides the copper ions (Cu²⁺).
The Cathode (Negative Electrode)
This is the object you intend to coat. It is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply. The negative charge on its surface is what attracts the positively charged metal ions from the electrolyte bath.
The Anode (Positive Electrode)
Connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, the anode completes the electrical circuit. Anodes can be either "sacrificial," made of the same material as the coating, dissolving to replenish ions in the bath, or "inert," made of a non-reactive material like platinum or carbon.
The Power Source
A direct current (DC) power supply, such as a rectifier, provides the electrical energy needed to drive the reaction. The voltage and current are carefully controlled to manage the rate and quality of the deposition.
The Step-by-Step Electrochemical Process
With the components in place, the process unfolds as a controlled sequence of electrochemical events.
Applying the Current
The moment the DC power is switched on, an electric potential is established between the anode and the cathode. This creates an electric field throughout the electrolyte bath.
Ion Migration
Driven by this electric field, charged particles (ions) in the solution begin to move. Positively charged ions, known as cations (e.g., Cu²⁺), are attracted to the negatively charged cathode (the workpiece).
The Reduction Reaction at the Cathode
This is the heart of the coating process. When the cations reach the surface of the cathode, they gain electrons. This chemical process is called reduction. Gaining electrons neutralizes their charge, causing them to deposit onto the surface as a solid metal film.
For copper, the reaction is: Cu²⁺ (in solution) + 2e⁻ → Cu (solid coating)
The Oxidation Reaction at the Anode
Simultaneously, a corresponding reaction called oxidation occurs at the anode, where a substance loses electrons. If a sacrificial anode is used, it slowly dissolves into the bath, replenishing the metal ions that were deposited on the cathode and ensuring a stable process.
The sacrificial copper anode reaction is: Cu (solid anode) → Cu²⁺ (in solution) + 2e⁻
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, electrodeposition is not a universal solution. Understanding its advantages and limitations is critical for its proper application.
Advantage: Precision and Uniformity
The primary strength of electrodeposition is its ability to create highly uniform coatings, even on objects with complex geometries, holes, and internal surfaces. This "throwing power" is difficult to achieve with line-of-sight methods like spray painting.
Advantage: Strong Adhesion
Because the coating is formed through an electrochemical bond at the atomic level, the adhesion between the substrate and the deposited layer is exceptionally strong and durable.
Limitation: Conductive Substrates Only
The process fundamentally relies on the workpiece being able to conduct electricity. Non-conductive materials like plastics or ceramics cannot be directly coated without first being treated with a conductive layer.
Limitation: Environmental and Safety Concerns
Many industrial electrolyte baths contain hazardous materials, such as strong acids, heavy metals, or cyanides. This necessitates strict process controls, specialized waste treatment, and robust safety protocols to protect workers and the environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use electrodeposition hinges on your specific technical objective.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: Electrodeposition is an excellent choice for applying protective layers like zinc (galvanizing) or nickel, which create a dense, non-porous barrier against the elements.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics or conductivity: The process is ideal for decorative finishes like chrome, gold, and silver, or for applying highly conductive layers of copper in electronics manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, intricate shapes: Electrodeposition's ability to uniformly cover all wetted surfaces makes it superior to almost any other method for parts with complex internal or external features.
By mastering the interplay of chemistry and electricity, electrodeposition offers unparalleled control for engineering a surface to meet a specific need.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Electrodeposition |
|---|---|
| Electrolyte Bath | Solution containing dissolved ions of the coating material. |
| Cathode | The object to be coated; attracts positive ions. |
| Anode | Completes the circuit; can be sacrificial or inert. |
| Power Source | Provides the direct current (DC) to drive the reaction. |
| Key Consideration | Advantage / Limitation |
|---|---|
| Coating Uniformity | Excellent for complex shapes (Advantage) |
| Adhesion | Strong, atomic-level bond (Advantage) |
| Substrate | Requires a conductive surface (Limitation) |
| Process | Involves hazardous materials (Limitation) |
Ready to achieve precision coatings in your lab?
The controlled process of electrodeposition is essential for applications requiring uniform metal layers, from corrosion protection to electronic conductivity. KINTEK specializes in providing the reliable lab equipment and consumables you need to perfect your electrodeposition processes safely and efficiently.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and help you meet your specific coating goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis



















