In essence, freeze drying supports laboratory research by providing a gentle, low-temperature method to remove water from sensitive samples. This process, also known as lyophilization, is used to preserve the structure and biological activity of materials like cell cultures, enzymes, antibodies, and vaccines, enabling stable long-term storage and simplified transport without the need for refrigeration.
Freeze drying's true value in the lab isn't just preservation, but preservation with near-perfect fidelity. By removing water at ultra-low temperatures via sublimation, it maintains the original structure and biological function of sensitive materials, making them stable, easily transportable, and simple to reconstitute for future experiments.
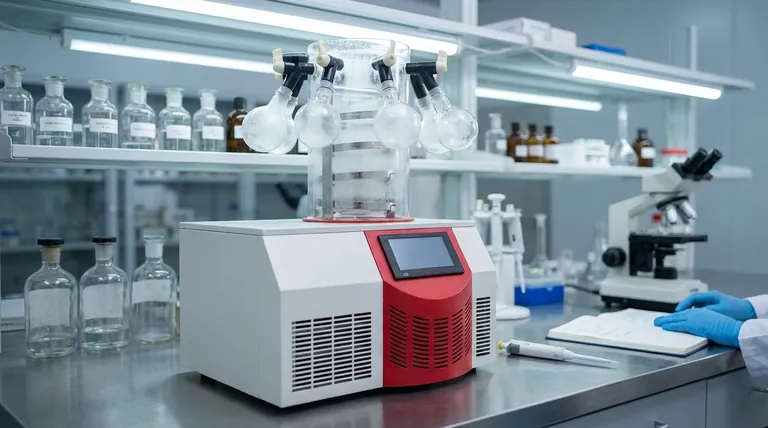

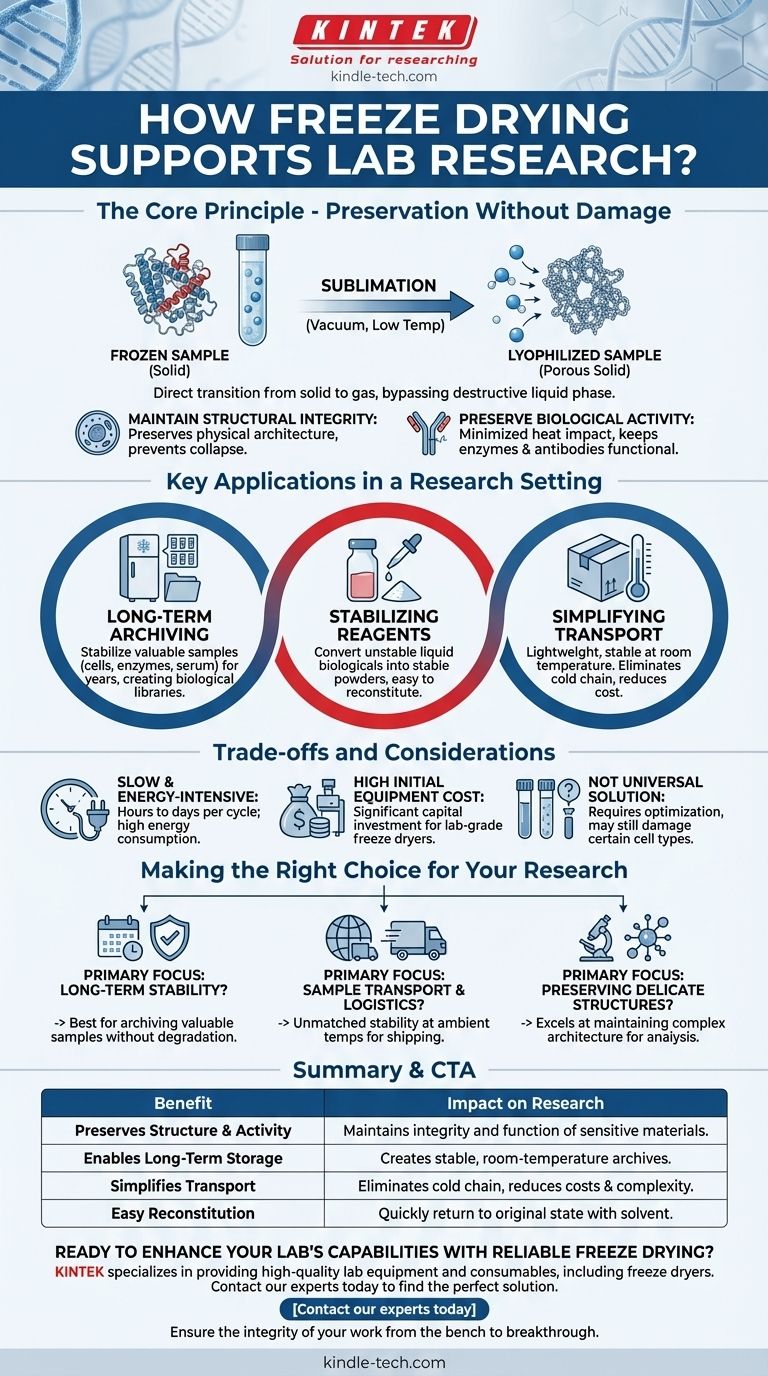
The Core Principle: Preservation Without Damage
To understand why freeze drying is so crucial in research, we must look at how it differs fundamentally from simple heating or evaporation. The entire process is engineered to avoid the damaging effects that water and heat can have on delicate biological molecules.
Sublimation, Not Evaporation
The process hinges on sublimation, the direct transition of a substance from a solid to a gas. A sample is first frozen solid, locking its molecular structure in place. Then, under a deep vacuum, the frozen water turns directly into water vapor, bypassing the destructive liquid phase entirely.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
Because the sample remains frozen solid during drying, its physical architecture is preserved. This is critical for maintaining the shape of complex proteins, the structure of tissues, or the morphology of microorganisms, which would otherwise collapse or denude during conventional drying.
Preserving Biological Activity
Heat is the enemy of many biological molecules, causing proteins to denature and lose their function. Freeze drying is a very low-temperature process, which minimizes impact on product properties and preserves the activity of enzymes, the binding capability of antibodies, and the viability of certain microbes.
Key Applications in a Research Setting
The unique benefits of lyophilization translate into several indispensable applications that remove barriers in scientific work.
Long-Term Sample Archiving
Researchers can stabilize valuable and often irreplaceable samples like cell cultures, serum, and enzymes for years. This allows for the creation of stable biological libraries and ensures that baseline materials are available for future comparative studies.
Stabilizing Reagents and Pharmaceuticals
Many critical reagents, such as antibodies or vaccines, are inherently unstable in liquid form. Freeze drying converts them into a stable powder that can be stored at room temperature and easily reconstituted with water or a solvent just before use, ensuring potency and consistency.
Simplifying Transport and Handling
Lyophilized materials are lightweight, stable, and do not require a cold chain (refrigeration or dry ice) for shipping. This drastically reduces the cost and complexity of sending samples to collaborators or conducting research in the field, all while minimizing the risk of contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While incredibly powerful, freeze drying is a specialized technique with its own set of practical limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging these factors.
The Process is Slow and Energy-Intensive
Lyophilization is not a rapid process. Depending on the sample size and type, a single cycle can take from several hours to multiple days to complete. The equipment required also consumes a significant amount of energy to maintain low temperatures and a deep vacuum.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Laboratory-grade freeze dryers are complex instruments that represent a significant capital investment. For smaller labs or those with infrequent needs, the cost can be a substantial barrier compared to simpler preservation methods like standard freezing.
Not a Universal Solution
While effective for most biologicals, the initial freezing step can still damage certain cell types if not performed with the right protocol and cryoprotectants. Optimizing a freeze-drying cycle for a new type of sample often requires methodical testing and development.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Choosing a preservation method depends entirely on your scientific goal and logistical constraints.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability: Freeze drying is the gold standard for archiving valuable biological samples without degrading their native activity or structure.
- If your primary focus is sample transport and logistics: Lyophilized materials are unmatched for their stability at ambient temperatures, making them ideal for shipping or field use.
- If your primary focus is preserving delicate structures: The process excels at maintaining the complex architecture of proteins, cells, and tissues for subsequent analysis like microscopy or spectroscopy.
Ultimately, freeze drying empowers researchers by effectively pausing biological time, ensuring the integrity of their work from the bench to future breakthroughs.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Impact on Research |
|---|---|
| Preserves Structure & Activity | Maintains the integrity and function of sensitive materials like proteins and cell cultures. |
| Enables Long-Term Storage | Creates stable, room-temperature archives of valuable samples for years. |
| Simplifies Transport | Eliminates the need for a cold chain, reducing costs and complexity for shipping. |
| Easy Reconstitution | Samples can be quickly returned to their original state with water or solvent. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with reliable freeze drying?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including freeze dryers designed to meet the precise demands of laboratory research. Our solutions help you preserve critical samples, stabilize reagents, and streamline your workflow with confidence.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect freeze drying solution for your research needs and ensure the integrity of your work from the bench to breakthrough.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- Why is a laboratory freeze-drying system essential for fermentation biomass? Preserve Sample Integrity for Analysis
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling



















